- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Domain Knowledge
- Hospitality Domain
- Components of Tourism Industry
Components of Tourism Industry
The tourism sector is a range of businesses and organizations involved in delivering the tourism product. All the elements of tourism are related and interact; in essence, the tourism industry is a system of customers and suppliers who demand and supply tourism products and services. In relation to tourism, very often you will come across terms like tourism products and services. These components of travel and tourism can be broadly divided into six key areas highlighted below.
The tourism sector is a range of businesses and organizations involved in delivering the tourism product. Travel agents and tour operators are mostly found in the traveler-generating region, attractions, and the hospitality industry are found in the destination region, and the transport industry is largely represented in the transit route region. Demand for tourism in the generating region is inherently volatile, seasonal, and irrational. Yet this demand is satisfied by a destination region where supply is fragmented, inflexible, and dominated by fixed investment costs. All the elements of tourism are related and interact; in essence, the tourism industry is a system of customers and suppliers who demand and supply tourism products and services.
Travel & Tourism – Products & Services
The tourist products are both, a physical as well as a psychological construction. They all transform a tourist’s dreams into reality. Risks are higher in tourism services because these services are considered luxuries and often not given the same attention as essential services. Local people often express hostility to tourism because they see it as an expression of Five Star culture, extending the gap between their lifestyle and that of the tourist. For the producer of the service, there are also risks. Travel services are consumed while going to and at the destination. They cannot be tested, seen, sampled, or compared in advance.
In tourism, demand is often irrational and trends also change rapidly. But the building up of services often requires lead time. Once capacity is offered, the hotel and transport service, for example, it often lasts longer than the demand for it. This requires great ingenuity on the part of the producer to ensure that the service remains profitable.
The components of travel and tourism can be broadly divided into six key areas. We will discuss each of these areas in this slide and this will help you understand the players in this industry.
1. Travel Agent & Their Services:
The intermediaries constitute the travel agency, tour operator, and guide services. The constituent which co-relates all the components of tourism is the travel agent/tour operator who has accumulated knowledge, expertise, and contacts with providers of services. He is a useful and invaluable intermediary between the traveler and the suppliers of tourist services i.e. airlines, transport companies, hotels, and auto rental companies. The functions of the travel agency depend upon the scope of activities it is involved in and also the size and the location. The agency has specialized departments each having .to perform different functions such as:
- Providing travel information
- Preparing itineraries
- Liaising with providers of services
- Planning and costing tours
- Ticketing
- Providing foreign currency
- Insurance, etc.
A travel agent provides information to the people on various travel destinations advises them of available holiday packages to suit their tastes and budget and chart their travel plan. He would generally sell the travel associated products like currency exchange, car rentals, insurance, etc.
2. Tours & Tour Operator’s Services:
Some of the travel agents are also tour operators who manufacture tourism products. They plan, organize, and sell tours. They make all the necessary arrangements e.g. transport, accommodation, sightseeing, insurance, entertainment, and other allied services, and sell this 'package' for an all-inclusive price. A package tour may be a special interest tour, mountain tour, adventure tour, or a pilgrimage tour. These tours are escorted and include transportation, meals, sightseeing, accommodation, and guide services. The escort or the group leader is responsible for maintaining the schedule of the tour and for looking after all the arrangements.
Tours and their characteristics are closely linked to the motivation of the tourist. The motivation or purpose of a visit is usually a holiday or vacation, including a visit with friends and relations, meetings, and conferences, including other business activities, health, and sports, religion and Culture, or special interests, including study tours, etc. The purpose of the visit determines the nature of the tour in the following ways:
- Are you free to choose your destination?
- Is price/time a constraint?
- Is quality a determining factor? What facilities and services do you require?
Tours can be within national boundaries or in any place in the world. Such a decision will have an impact on the economy of both, the country of origin and the tourist’s destination site. Tours also focus on unique natural or geographical features like the coastline, islands, mountains, health resorts, countryside, etc. At such locations, the provision of tourist services and the pressure of tourists are bound to have impacts on the environment, economy, and local social practices and on the people.
In the case of an independent or tailor-made tour, the visitor buys services individually. This he does either by making reservations in advance, directly or through a travel agent, or on an ad hoc basis during the tour. The latter is called a walk-in arrangement which depends on availability. A package or inclusive tour is an arrangement in which packages are assembled by tour operators who buy the individual elements in advance from the producers and the wholesalers. Because these services are bought in advance in large numbers, the tour operator buys at a special discount price (20% to 30% lower than the market price). He then sells individual and group tours either directly or through travel agents who are performing the retail function. For this travel agents earn a commission (2% to 10%).
Tour operators offer holiday packages which comprise of
- Travel like by rail, road, or air.
- Accommodation like hotels, resorts, apartments, guesthouses
- Travel services like airport pick and drop, sightseeing, excursions, etc.
These tour operators may be the wholesale operators who operate tours only through retail travel agencies or they may be direct sell operators who market their product directly to the public. The purchase of a tour is a speculative investment by the tourist, who anticipates the pleasure the consumption of such a product will result in. Tourist consumption and anticipation are related to services that after the basic necessities and comforts are provided, leisure activities are also organized. However, it has often been said that selling tours are similar to selling dreams. For example, a tour is more than buying a mere collection of services like an aircraft seat, a hotel bed, meals, and the opportunity to see the Taj Mahal. The tourist is buying, temporarily, a strange environment including unique climatic and geographical features and intangible benefits like a bargain, luxury service, hospitality, atmosphere, culture, and heritage.
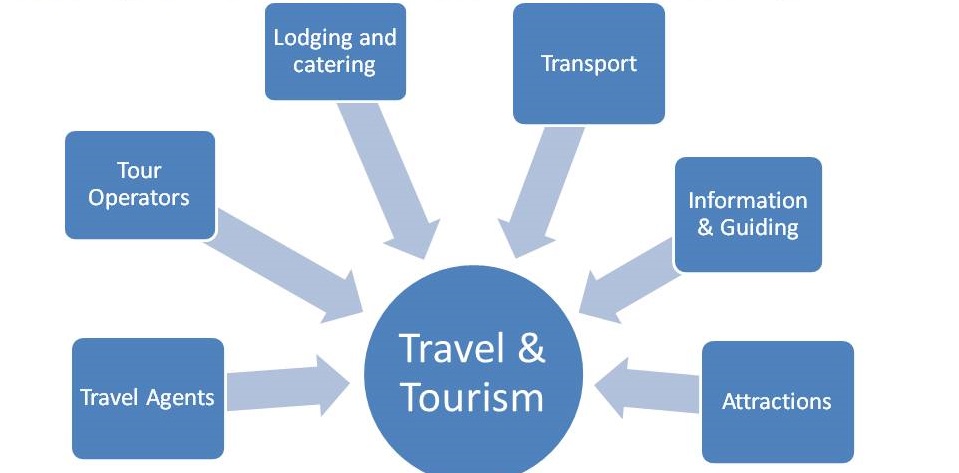
3. Lodging and Catering Services:
A tourist not only travels but also stays somewhere. And here comes in accommodation. It could be of different types i.e. from cottages or tourist lodges to a houseboat or a five-star hotel. A tourist has to eat also and here comes the role of catering and food. Restaurants, fast-food joints all play a role in this regard with a different cuisine to offer. Different forms of entertainment are provided as attractions at the destinations.
Accommodation can be in the formal (hotel) sector or the subsidiary sector (guesthouse, campsite, apartment on rent, etc.). Catering can be on a meal plan which includes a variety of options. For example, an American plan including 3 meals, a Modified American plan including breakfast and lunch or dinner, and a European plan including breakfast only.
This component consists of those who provide accommodation to the people in the form of hotels, resorts, apartments, camps, guest houses, etc. The accommodation may be marketed individually or through tour operators in the form of a package. Direct marketing may require huge costs on the advertisement and sell through a tour operator guarantees the occupancy rate throughout a holiday season. These service providers also take care of the catering needs of the people b providing them huge cafeterias, various fast food outlets in house or in the form of a Galleria.
4. Various Kinds of Transport:
You need a mode of transport to travel or to suggest one to your client if you are a travel agent or a tour operator. Further, travel depends on the availability of seats, etc. Today, the travel industry is a highly developed industry with its various branches in the areas of road, rail, air, and water. Transport providers are those operating any major form of transport. They could be airlines, cruise lines, car rentals, and rail companies. A tourist’s choice of transport would depend on the travel budget, destination, time, purpose of the tour, and convenience to the point of destination.
Transport and accommodation are purchased at an inclusive price. This means that the prices of the individual components of the services required by the tourist cannot be determined by the buyer. Transport services can be scheduled (run according to a time-table) or chartered (according to demand). Local transfers and sight-seeing can be organized by coach, taxi, etc. For those who like to do things on their own, the rent-a-car option is also available.
5. Information & Guide Services:
The guide services play a vital role in tourism as a tourist feels comfortable when the essence of the culture is explained-especially when it is done in his own language. The tourist information and guidance providers include a number of service providers such as those offering insurance, recreational, communication, and banking services; government agencies; tour guides; industry associations; packaging agents; ticketing agents; and holiday sellers.
6. Tourist Attractions:
This part focuses upon the tourism destination as a fundamental unit of analysis for tourism not only do destinations, their images, and their digital traces attract tourists, motivate the visit and therefore energize the tourism system, but they are also at the sharp end of tourism, at the same time suffering and benefiting from visitation. The richness and variety of destinations is a key driver of the success of tourism and they demonstrate a complex pattern across the world where tourism is attracted to the unique, the exotic, and the vulnerable at the same time, tourism destinations are forever expanding as the pleasure periphery reaches ever more distant and remote locations, including the Polar Regions. They are also increasingly represented through tourists leaving digital traces of their visits and memories via online posts and Facebook becomes the new ‘postcard’.
Destinations have many common features, but a key distinction is between the ‘attractions’, which draw the visit, and the ‘support facilities’, which are essential for tourism but support rather than draw the visit. The principle of attraction is to establish the need for the attraction in a particular location to invite more footfalls. It may be a huge theme park, a museum, a gallery, a heritage building, an educational center, etc. Many countries see the need to have one or more visitor attractions in the area to widen their appeal and attract huge potential tourists.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
How does Tourism Industry impact a country? The impact of the tourism industry can be classified into the social & cultural impact, economic impact, and environmental impact. Social & cultural impact signifies the impact which it creates in terms of social changes. The economic impact can be quantified in terms of monetary benefits and overall economic development of the society. Environmental impact refers to the impact on nature and the surrounding areas.
-
Economic Impact of Tourism Industry
The tourism industry has contributed to the economic growth of a country through factors like industrialization, education, advanced technology, a higher number of qualified professionals, opening up of foreign markets, liberal trade policies, and better advertising and strategic marketing. The income generated helps the national balance of payments, earning revenue through direct taxation, as well as from indirect taxes on goods and services purchased by the tourists.
-
Wealthy people have always traveled to distant parts of the world, to see great buildings, works of art, learn new languages, and experience new cultures, and to taste different cuisines. There has been an up-trend in tourism over the last few decades and now national or international travel for short breaks is very common. Tourists have a wide range of budgets and tastes, and a wide variety of resorts and hotels have been developed to cater for them.
-
Challenges in the Tourism Industry
Top challenges confronting tourism are taxation, travel marketing, infrastructure issues, and security and cross border regulations. Too many tourism destinations are not prepared for visitors. Tourists or travelers can at times deem travel marketing to be exaggerated. Another major challenge that the tourism industry faces is the fluctuating rates and cost inflation. New challenges seem to arise quickly impacting the industry as a whole.
-
Components of Tourism Industry
The tourism sector is a range of businesses and organizations involved in delivering the tourism product. All the elements of tourism are related and interact; in essence, the tourism industry is a system of customers and suppliers who demand and supply tourism products and services. In relation to tourism, very often you will come across terms like tourism products and services. These components of travel and tourism can be broadly divided into six key areas highlighted below.
-
Environmental Impact of Tourism Industry
The environment is the surrounding atmosphere or condition for existence. The impact of tourism on the environment is both positive and negative. This article considers the major issue of the consequences of tourism for the environment. This is a complex area as, whilst tourism is dependent upon environmental quality to attract and support visitors, it also can have a detrimental effect upon those very environments – and their climate.
-
Overview of Hospitality Industry
Hospitality is the act of kindness in welcoming and looking after the basic needs of customers. The hospitality industry is a broad group of businesses that provide services to customers. The industry can be broken down into three basic areas: accommodations, food and beverage, and travel and tourism. Hospitality is actually one facet of the service industry. It primarily involves addressing customer satisfaction and catering to the needs of guests.
-
Social & Cultural Impact of Tourism
Tourism may have different effects on the social and cultural aspects of life in a particular region depending on the strengths of the region. The effect can be positive or negative. Tours also focus on unique natural or geographical features like the coastline, islands, mountains, health resorts, countryside, etc. At such locations, the provision of tourist services and the pressure of tourists are bound to have impacts on the environment, economy, and local social practices and on the people.
-
We all travel and have been a tourist, perhaps many times in our life. Tourism and tourist are so common words that they find mention in newspapers and magazines almost on a daily basis. In spite of its popularity, have you ever deliberated what the definition of travel and tourism is? What components constitute the tourism industry? Who qualifies to be called a tourist? Well, this article attempts to explore the words "travel”, “tourism” and "tourist'- both technically as well as conceptually.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved









