- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Industry Knowledge
- Banking Domain
- Banking Operations: Understanding Modern Banking Products
Banking Operations: Understanding Modern Banking Products
Banking has changed radically in the last 20 years, and it is now one of the most competitive businesses in the world. Like any business, a bank must attract customers in order to make money. There is an ever-wider array of services that are offered by the banking industry today. Technology has impacted the banking industry and changed the way it used to operate. With changing times, banks are also offering new innovative products to meet the dynamic evolving needs of its customers. Learn about various banking products and services.
Several types of products and services are offered by banks today and modern banks are continuously tailoring their offerings to match consumer needs. Banks have started offering financial services such as credit cards, innovative lending options, and technology-related services. In this article, we will discuss the various banking products and services that exist today.
Savings Accounts:
 The Savings Bank Accounts are meant for individuals keeping deposits with banks, operating singly or jointly with other individuals, associations, clubs, etc. The Savings Bank accounts can be operated either with a checkbook facility or without a checkbook facility. Where cheque book facility is not provided or not opted for, remittances in cash and withdrawals through withdrawal slip are allowed. There is usually a limit on the number of transactions allowed in Savings Bank account and these accounts are not meant for business or trading activities etc. A bare minimum Interest at the rate as prescribed may be paid on the monthly minimum balance maintained in the account. Where cheque book facility is extended, the party can draw cheques on the account which can be collected by 3rd parties through the clearing office. A deposit in cash and cash withdrawals by way of cheque or through ATM is allowed. Cheques / DDs etc., favoring the account holder are collected into the account. Almost all banking institutions offer a traditional savings account and other savings options. Today they offer a variety of ways to compound interest that maximizes the earnings for customers. They also offer special savings accounts (for example flexi savings account or money-market accounts) that may offer higher interest rates.
The Savings Bank Accounts are meant for individuals keeping deposits with banks, operating singly or jointly with other individuals, associations, clubs, etc. The Savings Bank accounts can be operated either with a checkbook facility or without a checkbook facility. Where cheque book facility is not provided or not opted for, remittances in cash and withdrawals through withdrawal slip are allowed. There is usually a limit on the number of transactions allowed in Savings Bank account and these accounts are not meant for business or trading activities etc. A bare minimum Interest at the rate as prescribed may be paid on the monthly minimum balance maintained in the account. Where cheque book facility is extended, the party can draw cheques on the account which can be collected by 3rd parties through the clearing office. A deposit in cash and cash withdrawals by way of cheque or through ATM is allowed. Cheques / DDs etc., favoring the account holder are collected into the account. Almost all banking institutions offer a traditional savings account and other savings options. Today they offer a variety of ways to compound interest that maximizes the earnings for customers. They also offer special savings accounts (for example flexi savings account or money-market accounts) that may offer higher interest rates.
Loans & Lending:
 Lending makes up most of a bank's business. Many bank deals are more complex than automobile or home loans. In fact, banks lend money to businesses and governments in a wide variety of ways, with loan duration ranging from short terms to very long terms. Bank lending is the main reason that people are able to own homes and cars without waiting forever to buy them. Home loans still constitute an important part of the banking business. Loan decisions need to be made in a healthy, rational way to borrowers who are qualified for the loans they obtain. The automobile and housing industries have grown hand in hand with solid banking industry. A variety of loan products provides many choices for banks to transfer money into the economy. In the far-ranging and fast-shifting world of banking, strong management skills, and a thorough understanding of finance and market dynamics are required by banks to manage these modern financial banking products.
Lending makes up most of a bank's business. Many bank deals are more complex than automobile or home loans. In fact, banks lend money to businesses and governments in a wide variety of ways, with loan duration ranging from short terms to very long terms. Bank lending is the main reason that people are able to own homes and cars without waiting forever to buy them. Home loans still constitute an important part of the banking business. Loan decisions need to be made in a healthy, rational way to borrowers who are qualified for the loans they obtain. The automobile and housing industries have grown hand in hand with solid banking industry. A variety of loan products provides many choices for banks to transfer money into the economy. In the far-ranging and fast-shifting world of banking, strong management skills, and a thorough understanding of finance and market dynamics are required by banks to manage these modern financial banking products.
Current Accounts:
 Current accounts are opened by individuals, sole proprietary concerns, partnership firms, companies, clubs, associations, trusts, govt./local bodies, cooperative societies, etc. This Account is meant for Individuals / Institutions having a large number/volume of transactions, mainly for meeting their day-to-day business and operational requirements for parking their operational fund balances. No interest is generally provided on the balances in Current Account as the Bank renders a considerable service in operation and maintenance of the Account. These Accounts are operated only through the cheques provided by the Bank drawn either in individual or representative capacity, either singly or jointly. The Cheques, Bills, DDS, etc. of parties are collected through the Current Accounts and cash/clearing payments are made in respect of cheques issued by the Account holders. Over Drafts, secured or otherwise, are provided as per the separate loan rules in this regard. Accounts of individuals' facility of withdrawal from ATM is also provided.
Current accounts are opened by individuals, sole proprietary concerns, partnership firms, companies, clubs, associations, trusts, govt./local bodies, cooperative societies, etc. This Account is meant for Individuals / Institutions having a large number/volume of transactions, mainly for meeting their day-to-day business and operational requirements for parking their operational fund balances. No interest is generally provided on the balances in Current Account as the Bank renders a considerable service in operation and maintenance of the Account. These Accounts are operated only through the cheques provided by the Bank drawn either in individual or representative capacity, either singly or jointly. The Cheques, Bills, DDS, etc. of parties are collected through the Current Accounts and cash/clearing payments are made in respect of cheques issued by the Account holders. Over Drafts, secured or otherwise, are provided as per the separate loan rules in this regard. Accounts of individuals' facility of withdrawal from ATM is also provided.

Fixed Deposits:
 These are deposits of a specified sum of money permitted to be made in multiples of the specified amount for a specified period. For example, a Fixed Deposit of Rs. 5000/- for 12 months period. Fixed Deposits may be accepted for Days, Months, Years, or their combination, as per the request of customer. If the deposit is for a minimum period of 12 months, then interest may be paid monthly, quarterly, half-yearly, or yearly. These deposits are repayable to the customer on the expiry of the period for which the deposit is made. However, the account holders are permitted to make premature encashment of such deposits in case of exigency/need – in such an event the principal amount is paid along with interest as applicable for the period for which the deposit was actually with the banks, less penalty of certain percentage points on the applicable rate of interest. The interest is normally paid at quarterly rests for credit of the customer’s Savings / Current account as per standing instructions or allowed to be withdrawn in cash by the customer or paid to him by way of Bankers Cheque / Pay Order and by way of D.D. for out-location customers. Loans against the Fixed Deposit may be issued to the customers on surrender of duly discharged Fixed Deposit receipt with a letter of lien through a separate Depositor Loan A/c.
These are deposits of a specified sum of money permitted to be made in multiples of the specified amount for a specified period. For example, a Fixed Deposit of Rs. 5000/- for 12 months period. Fixed Deposits may be accepted for Days, Months, Years, or their combination, as per the request of customer. If the deposit is for a minimum period of 12 months, then interest may be paid monthly, quarterly, half-yearly, or yearly. These deposits are repayable to the customer on the expiry of the period for which the deposit is made. However, the account holders are permitted to make premature encashment of such deposits in case of exigency/need – in such an event the principal amount is paid along with interest as applicable for the period for which the deposit was actually with the banks, less penalty of certain percentage points on the applicable rate of interest. The interest is normally paid at quarterly rests for credit of the customer’s Savings / Current account as per standing instructions or allowed to be withdrawn in cash by the customer or paid to him by way of Bankers Cheque / Pay Order and by way of D.D. for out-location customers. Loans against the Fixed Deposit may be issued to the customers on surrender of duly discharged Fixed Deposit receipt with a letter of lien through a separate Depositor Loan A/c.
Recurring Deposit:
 Deposits under this category are in the nature of fixed amounts being paid in by the depositor every month subject to a minimum amount and in multiples thereafter for a specified period of years involving monthly payments ranging from 12 to 120 months. Under this deposit scheme, interest is cumulated at quarterly rests based on month-end balances in the account, and the pre-determined amount is fixed as payable at the end of the period of deposit. The rules relating to foreclosure and grant of loan against this deposit are similar to that under Fixed Deposit except that in the event of foreclosure of a Recurring Deposit, interest is paid based on monthly balances without accumulation for the incomplete quarter. In a computerized environment, the basic procedures of interest calculation, etc., are inbuilt in the Core Banking Solution (CBS), and as such the users are fully guided by the system.
Deposits under this category are in the nature of fixed amounts being paid in by the depositor every month subject to a minimum amount and in multiples thereafter for a specified period of years involving monthly payments ranging from 12 to 120 months. Under this deposit scheme, interest is cumulated at quarterly rests based on month-end balances in the account, and the pre-determined amount is fixed as payable at the end of the period of deposit. The rules relating to foreclosure and grant of loan against this deposit are similar to that under Fixed Deposit except that in the event of foreclosure of a Recurring Deposit, interest is paid based on monthly balances without accumulation for the incomplete quarter. In a computerized environment, the basic procedures of interest calculation, etc., are inbuilt in the Core Banking Solution (CBS), and as such the users are fully guided by the system.
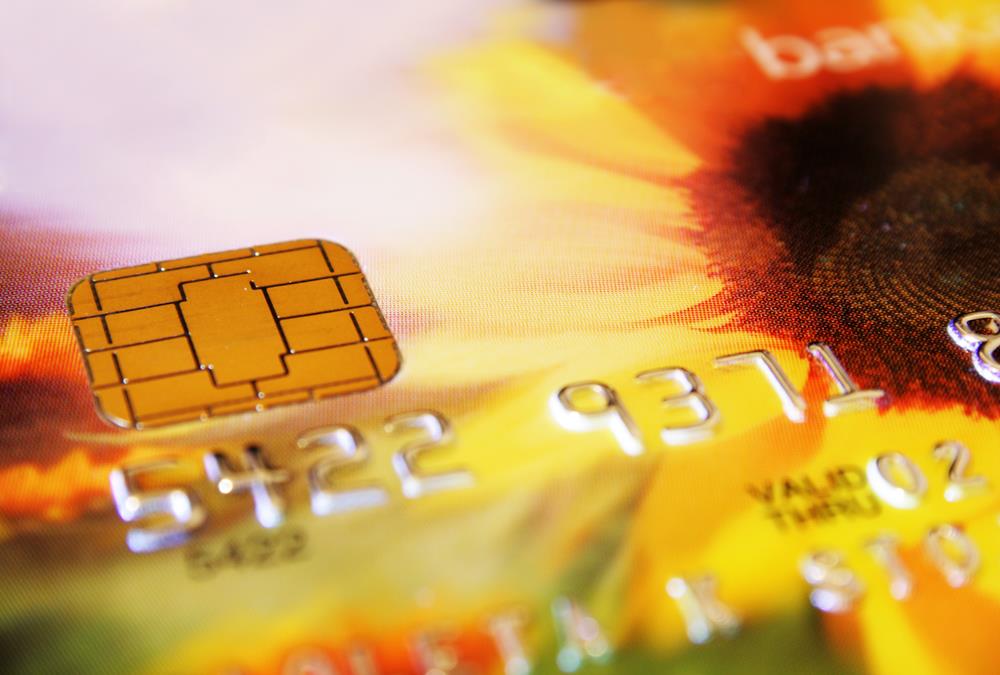
Credit Cards:
 Credit cards issued by banks are another form of lending, and they are not only good business for the bank, but they also help the economy. Offering Credit Card is a profitable form of lending for banks that has greatly expanded in the last few years. Banks compete fiercely for this business and offer varying forms and types of credit-card accounts. Many banks change or negotiate rates with consumers, and special low-rate promotions and various types of discounts are being offered as an incentive to use the card and do purchasing. People buy things with credit, and keep merchandise moving and manufacturing producing at a more rapid rate than if transactions had to take place in cash. Although there is a risk in the unwise use of credit cards by consumers, the judicious use of credit stimulates the economy.
Credit cards issued by banks are another form of lending, and they are not only good business for the bank, but they also help the economy. Offering Credit Card is a profitable form of lending for banks that has greatly expanded in the last few years. Banks compete fiercely for this business and offer varying forms and types of credit-card accounts. Many banks change or negotiate rates with consumers, and special low-rate promotions and various types of discounts are being offered as an incentive to use the card and do purchasing. People buy things with credit, and keep merchandise moving and manufacturing producing at a more rapid rate than if transactions had to take place in cash. Although there is a risk in the unwise use of credit cards by consumers, the judicious use of credit stimulates the economy.
Second Mortgage Loans:
 New types of lending are being made available to consumers. Second-mortgage loans also called home-equity loans are secured by the difference between the value of a home and the amount the homeowner still owes on it. The loans may take the form of a special credit card, a line of credit, or a single disbursement. They have become a popular form of credit because the interest in them is tax-deductible for the consumer.
New types of lending are being made available to consumers. Second-mortgage loans also called home-equity loans are secured by the difference between the value of a home and the amount the homeowner still owes on it. The loans may take the form of a special credit card, a line of credit, or a single disbursement. They have become a popular form of credit because the interest in them is tax-deductible for the consumer.
Automated Teller Machines (ATMs):
 Modern ATMs have made "banker's hours" irrelevant. Customers can now perform almost any banking function from an ATM, and have access to their accounts day or night. Networked ATMs have made it possible to do business with one's bank at any time from almost anywhere in the world. ATMs reduce transaction costs, encourage the use of the banking channels, and help banks earn income from fees. ATMs are available in a variety of venues, including shopping centers, amusement parks, universities, airports, sports arenas, and workplaces.
Modern ATMs have made "banker's hours" irrelevant. Customers can now perform almost any banking function from an ATM, and have access to their accounts day or night. Networked ATMs have made it possible to do business with one's bank at any time from almost anywhere in the world. ATMs reduce transaction costs, encourage the use of the banking channels, and help banks earn income from fees. ATMs are available in a variety of venues, including shopping centers, amusement parks, universities, airports, sports arenas, and workplaces.
Smart Cards & Payroll Cards:
 Smart Cards are credit, debit, or other types of cards that have embedded microchips. Smart cards are useful for a wide variety of "electronic purse" applications, which allow the card to store a value. When the card is used, the stored value decreases. You may have used these already in grocery or video-rental stores. Payroll cards are a specific type of smart card used by banks to facilitate salary payments between employers and employees. By using a bank as an intermediary, payroll cards enable an employer to load salary payments onto an employee's smart card. Employees can then access their pay even if they do not have a bank account.
Smart Cards are credit, debit, or other types of cards that have embedded microchips. Smart cards are useful for a wide variety of "electronic purse" applications, which allow the card to store a value. When the card is used, the stored value decreases. You may have used these already in grocery or video-rental stores. Payroll cards are a specific type of smart card used by banks to facilitate salary payments between employers and employees. By using a bank as an intermediary, payroll cards enable an employer to load salary payments onto an employee's smart card. Employees can then access their pay even if they do not have a bank account.
Online Banking:
 Online banking takes advantage of growing Internet use. Whether called Internet banking, electronic banking, home banking, or PC banking, online banking allows customers to perform banking transactions from their home computers. Everything from balance inquiries to bill paying to apply for a loan may be available online at any time. There are various benefits of e-banking provided to customers like it provides 24 hours, 365 days a year services to the customers of the bank. Customers can make some of the permitted transactions from office or house or while traveling or via mobile telephone. Greater customer satisfaction by offering unlimited access to the bank, not limited by the walls of the branch, and less risk and greater security to the customer as they can avoid traveling with cash. The banks also stand to gain by e-banking as it provides a competitive advantage and unlimited network and is not limited to the number of branches. Load on branches can be considerably reduced by establishing the centralized database and by taking over some of the accounting functions.
Online banking takes advantage of growing Internet use. Whether called Internet banking, electronic banking, home banking, or PC banking, online banking allows customers to perform banking transactions from their home computers. Everything from balance inquiries to bill paying to apply for a loan may be available online at any time. There are various benefits of e-banking provided to customers like it provides 24 hours, 365 days a year services to the customers of the bank. Customers can make some of the permitted transactions from office or house or while traveling or via mobile telephone. Greater customer satisfaction by offering unlimited access to the bank, not limited by the walls of the branch, and less risk and greater security to the customer as they can avoid traveling with cash. The banks also stand to gain by e-banking as it provides a competitive advantage and unlimited network and is not limited to the number of branches. Load on branches can be considerably reduced by establishing the centralized database and by taking over some of the accounting functions.
Mobile Banking:
 Mobile banking has grown in popularity as reliance on sophisticated cell phones and related technology has grown. Consumers can execute a variety of banking transactions with mobile phones. Customers can check their account balances, make requests for payments, and even receive updates regarding their accounts on their mobile phones.
Mobile banking has grown in popularity as reliance on sophisticated cell phones and related technology has grown. Consumers can execute a variety of banking transactions with mobile phones. Customers can check their account balances, make requests for payments, and even receive updates regarding their accounts on their mobile phones.
Banking Domain Knowledge - Resources
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Definition of Bank: Meaning of the term Bank and the Business of Banking
What do we mean by the word bank? How did the word bank originate? What is the most simple and concise definition of a bank that explains the fundamentals of the banking process? Does the definition of banking vary from country to country? What are the key differentiators between any other business and a Bank? Get answers to all these questions and explore the basics of bank and banking as an industry.
-
History of Banking: Evolution of Banking as an Industry
Banking is one of the oldest industries and banking in the form that we know of began at about 2000BC of the ancient world. It started with merchants making grain loans to farmers and traders while carrying goods between cities. Since then, the banking industry has evolved from a simplistic barter system and gift economies of earlier times to modern complex, globalized, technology-driven, and internet-based e-banking model. In this article, we will take you through the major events and developments in the history of the banking industry.
-
History of Banking: Famous Banks from the Past
Seven hundred years ago a bank was established in Venice, which made transactions resembling modern banking. In 1407, another bank was founded in Italy under the name of Banco di San Giorgio which was one of the oldest chartered banks in Europe. Sveriges Riksbank (Riksbanken), is the central bank of Sweden and the world's oldest central bank. The Bank of England is the second oldest central bank in the world, and most modern central banks have been based on that model. Let us explore some interesting events as we learn more about these early banking institutions.
-
History of Banking: The Gold Standard & Fractional Reserve Banking
Gold has always been considered as a safe economic investment and treated like a currency. All of the economically advanced countries of the world were on the gold standard for a relatively brief time. Under a gold standard, the value of a unit of currency, such as a dollar, is defined in terms of a fixed weight of gold and banknotes or other paper money are convertible into gold accordingly. Explore the fascinating history of the gold standard through the lens of history and also learn why banks hold back a certain fraction of deposits as reserves.
-
Overview of Banking Industry: The Industry Basics
Banks play a key role in the entire financial system by mobilizing deposits from households spread across the nation and making these funds available for investment, either by lending or buying securities. Today the banking industry has become an integral part of any nation’s economic progress and is critical for the financial wellbeing of individuals, businesses, nations, and the entire globe. In this article, we will provide an overview of key industry concepts, main sectors, and key aspects of the banking industry’s business model and trends.
-
Banking Sector, Segments & It's Classifications
The banking industry players deal in a variety of products from savings accounts to loans and mortgages, offer various services from check cashing to underwriting, caters to different types of customers from individuals to large corporates, serve diverse geographies from rural villages to cross-border operations. Thus the banking industry is made up of several types of banks, with their own objectives, roles, and functions. In this article, we will explore the various sectors, segments, and classifications of banking based on parameters like products, customers, types, etc.
-
Type of Banks: Different Types of Banks in India & their Functions
This article explains the banking structure in India and how different banks are classified as per RBI Norms. The Indian banking industry has been divided into two parts, organized and unorganized sectors. The organized sector consists of Reserve Bank of India, Commercial Banks and Co-operative Banks, and Specialized Financial Institutions (IDBI, ICICI, IFC, etc.). The unorganized sector, which is not homogeneous, is largely made up of money lenders and indigenous bankers. Learn what we mean by nationalized banks, scheduled banks, public sector banks, private banks, and foreign banks.
-
Types of Banks: Different Banks & their Classifications (Global)
The banking industry caters to various sections of society thus the focus of banking becomes varied, catering to the diverse needs of clients through different products, services, and methods. To meet this, we need distinctive kinds of banks addressing complex business & social needs. In this article, we will explain various types of banking institutions ranging from retail banks, commercial banks, co-operative banks, investment banks, central banks to various other types of specialized banks.
-
Banking Operations: Understanding Various Transactions & Activities
Banks perform a variety of operations ranging from basic or primary functions like day to day transactions at a branch to others that maybe the agency or general utility services in nature. The transactions that are incidental to revenue/sales or sustaining the business are an important element of the banking industry value chain. In this article, we will look at the key operations performed in the course of banking.
-
Banking Industry Business Model - Understanding How the Banking System Works
Banks are commercial profitable institutions and need to increase their business, grow their revenue, and provide returns to their owners. Unlike other stores and shops, banks are providing services rather than selling their products. Learn how banks get their funds and how they make money on services. Read more to learn how the banks earn their profit!
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved