- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Functional
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- GL - Account Allocations
GL - Account Allocations
An allocation is a process of shifting overhead costs to cost objects, using a rational basis of allotment. Understand what is the meaning of allocation in the accounting context and how defining mass allocations simplifies the process of allocating overheads to various accounting segments. Explore types of allocations and see some practical examples of mass allocations in real business situations.
What is Account Allocation?
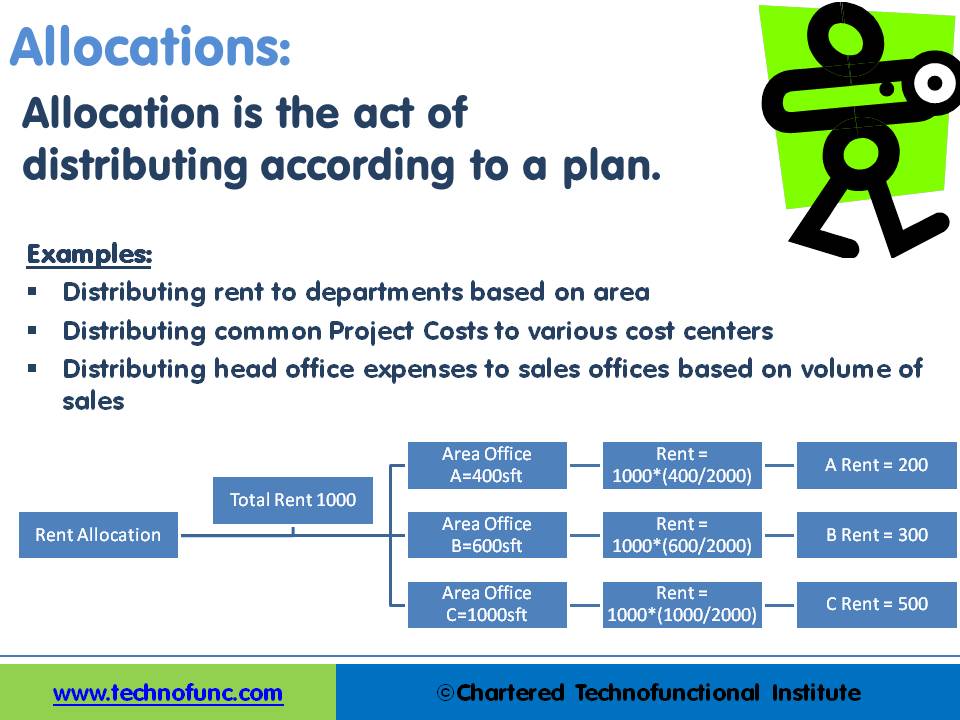
Allocation is the act of distributing according to a plan. As per the dictionary allocate means to set apart for a special purpose; designate; distribute according to a plan. From an accounting context, it means a system of dividing overhead expenses between the various departments of a business. Figuratively, earmarked is often used in regard to monetary allocations although it is heard in other contexts as well.
The allocation also refers to a piece of the pie, a share in the profits, a portion of whatever is being divided up and parceled out usually money, but in an accounting context is applicable to account balances. This expression probably has its origin in the graphic representation of budget allotments in circular, pie-shaped form, with various sized wedges or pieces indicating the relative size of allocations to different agencies, departments, etc.
Concept of Mass Allocations:
Mass allocations is a functionality offered by many automated systems and ERPs to distribute the account balances from one account to several others based on a formula or mathematic logic. Users can define a Mass Allocation formula to create journals that allocate revenues and expenses across a group of cost centers, departments, divisions, locations, and so on using any accounting dimension available. Users can include parent values in allocation formulas that can enable allocating to the child values referenced by the parent without having to enumerate each child separately.
Different Type of Allocations:
The commonly used allocations can be grouped as follows:
- Net Allocations: allocated amounts that reflect changes to the cost pool.
- Step–Down Allocations: distributing amounts from one allocation pool to a subsidiary allocation pool.
- Rate-Based Allocations: using current, historical, or estimated rates to allocate costs.
- Usage-Based Allocations: using statistics such as headcount, units sold, square footage, number of deliveries, or computer time consumed to calculate allocation amounts.
- Standard Costing Allocations: using statistics such as sales units, production units, number of deliveries or customers served to perform standard costing.
Examples of Allocation:
Allocations can be used in various practical business situations. For example, consolidated rent paid can be allocated to another division based on the area of usage, or, a pool of marketing costs can be allocated to several departments based on the ratio of department revenues to total revenues. Some of the commonly used examples are:
- Distributing rent to departments based on area
- Distributing common project costs to various cost centers
- Distributing head office expenses to sales offices based on the volume of sales
- Distributing marketing costs to product lines based on revenue
- Distributing common employee expenses to employee cost for assessments
In the example shown in the figure, we have a company which has taken a 1000 square feet office space on rent. The expenses for rent are borne by the head-office and payment to the landlord is also made by the head office. To know the true profitability of each of the departments (Department A, B & C) the rent needs to be allocated to each one of them.
Each department occupies different areas and the company has taken the measurement of the areas occupied by each of the departments. In the example shown here, the rent is being allocated to different departments based on their usage factor. This is an example of the concept of allocation and automated accounting systems help handle complex allocations programmatically.
Difference between Allocations & Recurring Journals:
Recurring Journals are for transactions that repeat every accounting period and allocation Journals are for single journal entry using an accounting or mathematical formula to allocate revenues and expenses across a group of accounting dimensions like cost centers, departments, divisions, locations, or product lines depending upon usage factors.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
GL - Different Accounting Methods
The accounting method refers to the rules a company follows in reporting revenues and expenses. Understand the two common systems of bookkeeping, single, and double-entry accounting systems. Learners will also understand the two most common accounting methods; cash and accrual methods of accounting and the advantages and disadvantages of using them.
-
An organizational design is the process by which a company defines and manages elements of structure so that an organization can control the activities necessary to achieve its goals. Good organizational structure and design helps improve communication, increase productivity, and inspire innovation. Organizational structure is the formal system of task and activity relationships to clearly define how people coordinate their actions and use resources to achieve organizational goals.
-
Introduction to Organizational Structures
Organizations are systems of some interacting components. Levitt (1965) sets out a basic framework for understanding organizations. This framework emphasizes four major internal components such as: task, people, technology, and structure. The task of the organization is its mission, purpose or goal for existence. The people are the human resources of the organization.
-
After reading this article the learner should be able to understand the meaning of intercompany and different types of intercompany transactions that can occur. Understand why intercompany transactions are addressed when preparing consolidated financial statements, differentiate between upstream and downstream intercompany transactions, and understand the concept of intercompany reconciliations.
-
In this article we will help you understand the double-entry accounting system and state the accounting equation and define each element of the equation. Then we will describe and illustrate how business transactions can be recorded in terms of the resulting change in the elements of the accounting equation.
-
Operational Structures in Business
Large organizations grow through subsidiaries, joint ventures, multiple divisions and departments along with mergers and acquisitions. Leaders of these organizations typically want to analyze the business based on operational structures such as industries, functions, consumers, or product lines.
-
Internally, an organization can be structured in many different ways, depending on their objectives. The internal structure of an organization will determine the modes in which it operates and performs. Organizational structure allows the expressed allocation of responsibilities for different functions and processes to different entities such as the branch, department, workgroup and individual.
-
Although technically a general ledger appears to be fairly simple compared to other processes, in large organizations, the general ledger has to provide many functionalities and it becomes considerably large and complex. Modern business organizations are complex, run multiple products and service lines, leveraging a large number of registered legal entities, and have varied reporting needs.
-
Explore the concept of journal reversals and understand the business scenarios in which users may need to reverse the accounting entries that have been already entered into the system. Understand the common sources of errors resulting in the reversal of entries and learn how to correct them. Discuss the reversal of adjustment entries and the reversal functionalities in ERPs.
-
In this article, we will describe how to determine if an account needs adjustment entries due to the application of the matching concept. Learners will get a thorough understanding of the adjustment process and the nature of the adjustment entries. We will discuss the four types of adjustments resulting from unearned revenue, prepaid expenses, accrued expenses, and accrued revenue.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved