- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Functional
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- Equity and Liability Accounts
Equity and Liability Accounts
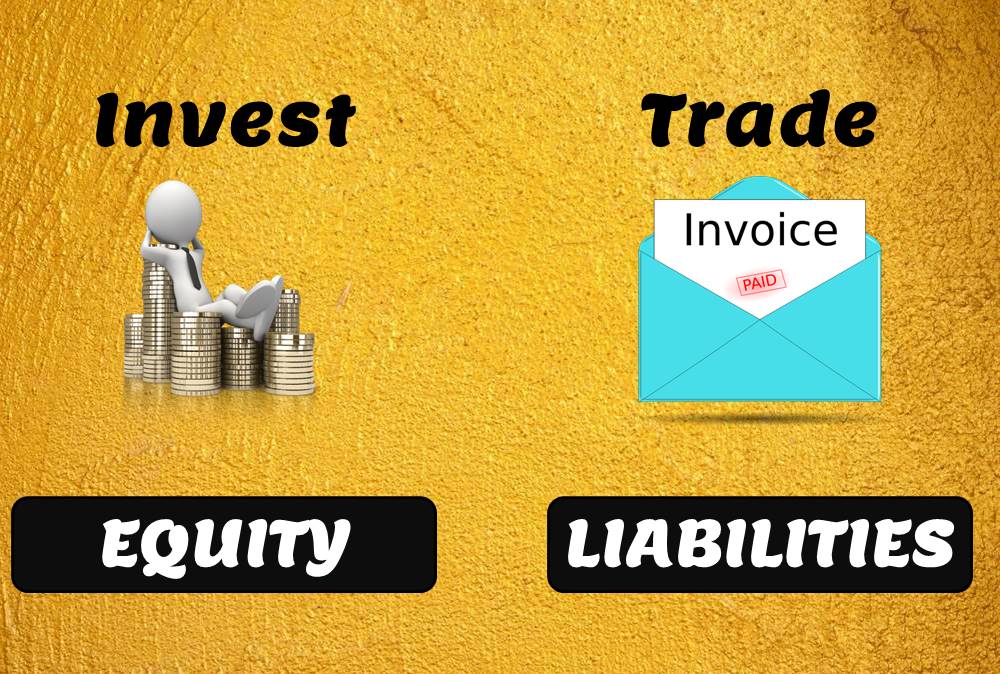
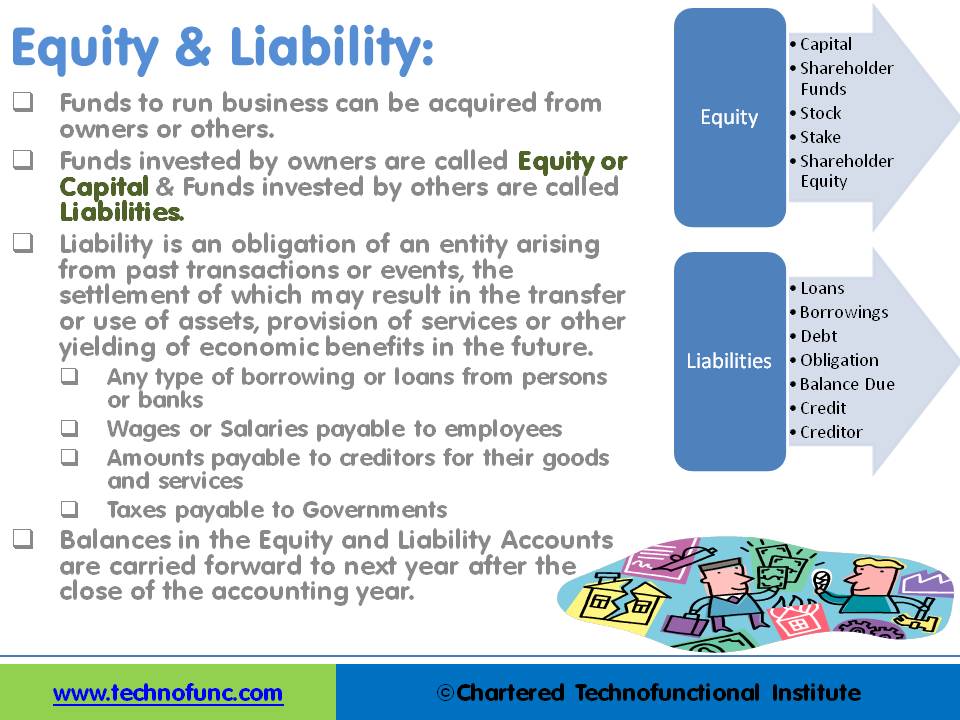
Funds contributed by owners in any business are different from all other types of funds. Equity is the residual value of the business enterprise that belongs to the owners or shareholders. The funds contributed by outsiders other than owners that are payable to them in the future. Liabilities are generally classified as Short Term (Current) and Long Term Liabilities. Current liabilities are debts payable within one year.
Equity Accounts:
The amount of the funds contributed by the owners (the stockholders) added or subtracted by accumulated gains and losses. Equity is the residual value of the business enterprise that belongs to the owners or shareholders.
Funds contributed by owners in any business are different from all other types of funds. Generally, they don’t have any cost of carrying for the business and in the event of winding up of the business, shareholders are entitled to the residual value of the business after discharging all other liabilities. They are expected to remain invested in the business for a long period of time and no immediate payback is anticipated in case of a going concern.
Equity accounts are also referred to as “Capital Account”, “Shareholder’s Funds” or “Accounts”, “Stock, Stake” and “Shareholder Equity”. Normally they have a credit balance and are reflected on the left side of the balance sheet. Profits and losses from each accounting year are added to Equity at the end of each year.
Balances in the Retained Earnings Account are transferred to “Equity” at the end of each accounting year. While running a revaluation of balances, equity is revalued using the historical rates in accordance with the accounting standards. Equity is a separate account type in ERP’s to segregate funds from owners and others.
Liability Accounts:
The number of funds contributed by outsiders other than owners that are payable to them in the future. Liability is an obligation of an entity arising from past transactions or events, the settlement of which may result in the transfer or use of assets, provision of services, or another yielding of economic benefits in the future.
Liabilities are generally classified as Short Term (Current) and Long Term Liabilities. Current liabilities are debts payable within one year, while long-term liabilities are debts payable over a longer period.
Liabilities can be from a lot of sources like Loans, External Borrowings, Debt – Secured and Unsecured, Obligation for services received Balance Due or Credit due to Creditors. Some generally known examples of liabilities are any type of borrowing or loans from persons or banks or wages or salaries paid to employees or amounts payable to creditors for their goods and services and taxes payable to Governments.
Balances in the Equity and Liability Accounts are carried forward to next year after the close of the accounting year. While running a revaluation of balances, liability is revalued using the period end rates in accordance with the accounting standards. Liability is a separate account type in ERP’s to segregate funds from owners and others.
Intercompany transactions also result in receivables and liabilities (payables) between different units of the same entity. Such transactions are settled in cash if they are in the normal course of business. At the time of the final consolidation of accounts, these intercompany liabilities and assets need to be eliminated from the books of the parent entity. We will discuss this concept in detail in the Intercompany chapter.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Driving Business Efficiency through Divisions and Departments
In case of a multi-divisional organizational structure, there is one parent company, or head-office. And that parent owns smaller departments, under the same brand name. Dividing the firm, into several self-contained, autonomous units, provides the optimal level of centralization, in a company.
-
Introduction to Organizational Structures
Organizations are systems of some interacting components. Levitt (1965) sets out a basic framework for understanding organizations. This framework emphasizes four major internal components such as: task, people, technology, and structure. The task of the organization is its mission, purpose or goal for existence. The people are the human resources of the organization.
-
Although technically a general ledger appears to be fairly simple compared to other processes, in large organizations, the general ledger has to provide many functionalities and it becomes considerably large and complex. Modern business organizations are complex, run multiple products and service lines, leveraging a large number of registered legal entities, and have varied reporting needs.
-
Divisional Organizational Structures
The divisional structure or product structure consists of self-contained divisions. A division is a collection of functions which produce a product. It also utilizes a plan to compete and operate as a separate business or profit center. Divisional structure is based on external or internal parameters like product /customer segment/ geographical location etc.
-
Team-Based Organizational Structure
Team-based structure is a relatively new structure that opposes the traditional hierarchical structure and it slowly gaining acceptance in the corporate world. In such a structure, employees come together as team in order to fulfill their tasks that serve a common goal.
-
Explore the concept of journal reversals and understand the business scenarios in which users may need to reverse the accounting entries that have been already entered into the system. Understand the common sources of errors resulting in the reversal of entries and learn how to correct them. Discuss the reversal of adjustment entries and the reversal functionalities in ERPs.
-
GL - Accrued / Unbilled Revenue
Accrued revenues (also called accrued assets) are revenues already earned but not yet paid by the customer or posted to the general ledger. Understand what we mean by the terms accrued revenue, accrued assets, and unbilled revenue. Explore the business conditions that require recognition of accrued revenue in the books of accounts and some industries where this practice is prevalent.
-
What is Accounting & Book Keeping
Accounting is a process designed to capture the economic impact of everyday transactions. Each day, many events and activities occur in an entity, these events and activities are in the normal course of business; however, each of these events may or may not have an economic impact. Events or activities that have an effect on the accounting equation are accounting events.
-
Horizontal or Flat Organizational Structures
Flat organizational structure is an organizational model with relatively few or no levels of middle management between the executives and the frontline employees. Its goal is to have as little hierarchy as possible between management and staff level employees. In a flat organizational structure, employees have increased involvement in the decision-making process.
-
A Company (also called corporation) may be understood as an association of persons in which money is contributed by them, to carry on some business or undertaking. Persons who contribute the money are called the shareholders or the members of the company. A corporation is an artificial being, invisible, intangible and existing only in contemplation of law. Being the mere creature of law, it possesses only those properties which the charter of its creation confers upon it.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved