- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Leadership
- Leadership Theories
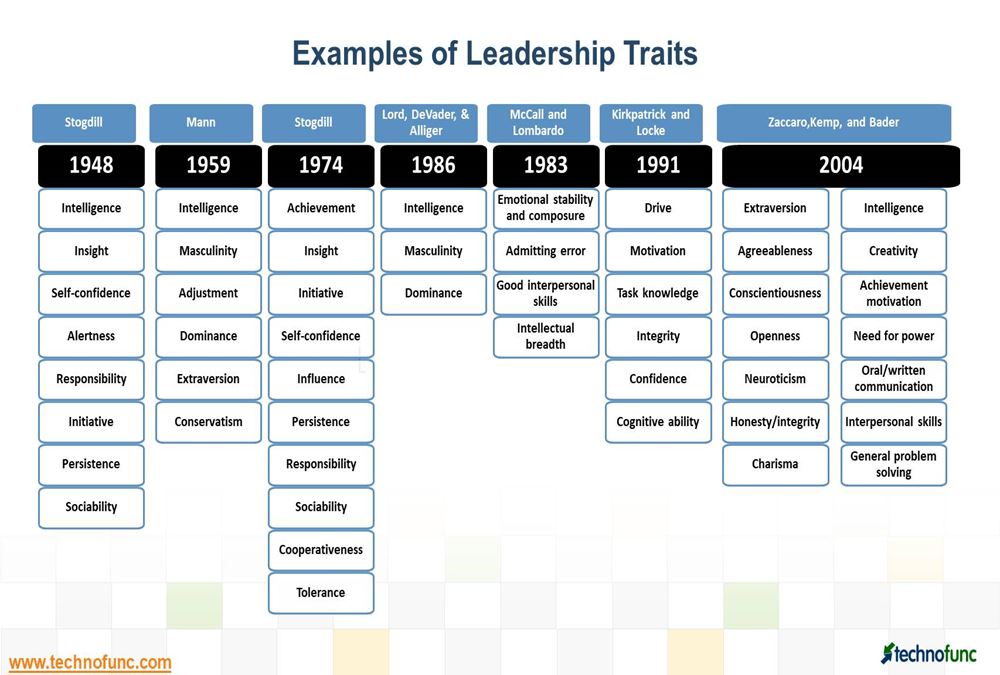
- Leadership Traits – A great List
Leadership Traits – A great List
What are the qualities and characteristics of a good leader? Great leaders possess core leadership traits and skills. The list includes the most important leadership qualities and skills to look for in a great leader. These are must-have traits of a powerful and successful leader, the qualities a leader possess to be great.
A broad classification to six categories of traits is also done below:
Physical Characteristics of the Leader:
- Age
- Height
- Weight
- Alertness
- Energetic
- Masculinity
- High energy level
- Physical stamina
- Tolerance for stress
- Not concerned about being overworked
- Vitality
Background Characteristics of the Leader:
- Education
- Social Status
- Mobility
- Experience
- Experience in a variety of different types of situations
- Broader perspective
- Expertise in dealing with different types of problems
- Competent and skilled
Intelligence Characteristics of the Leader:
- Ability
- Judgment
- Knowledge
- Clever (intelligent)
- Conceptually skilled
- Creative
- Knowledgeable about group task
- Intellectual breadth
- Insight
- Learns from experience
- Adapts to change
- Good judgment
- Foresight
- Intuition
- Creativity
- Self-knowledge
- Coordinator
- Objective
- Decisive
- Asks for more responsibility
- Knows how to delegate
Personality/Emotional Characteristics of the Leader:
- Aggressiveness
- Alertness
- Dominance
- Decisiveness
- Enthusiasm
- Extroversion
- Independence
- Self-confidence
- Authoritarianism
- Assertive
- Tolerant of stress
- Conservatism
- Desire to improve
- Understands own strengths and weaknesses
- Self-objectivity
- Emotional intelligence
- Self-awareness
- Empathy
- Self-regulation
- Ambitious
- Courageous
- Knows self
- Risk taker
- Not intimidated by superiors
- Personal competence
- Optimistic
- Exhibits concern for others
- Encourages and engages opposing viewpoints
- Constant and reliable
- Self-disciplined
- Determination
- Need to achieve
- Caring
- Empathizing
- Constancy
Task-Oriented Characteristics of the Leader:
- Achievement Needs
- Responsibility
- Initiative
- Persistence
- Ambitiousness
- Achievement-orientated
- Decisive
- Persistent
- Willingness to assume responsibility
- Organized (administrative ability)
Social Characteristics of the Leader:
- Sociability
- Supervisory Ability
- Cooperativeness
- Popularity
- Prestige
- Tact
- Diplomacy
- Adaptability
- Adjustment
- Cooperative
- Dependable
- Tactful
- Persuasive
- Socially skilled
- Emotional stability and composure
- Good interpersonal skills
- Well-adjusted
- Oriented toward improving self
- Detached
- Honest
- Ethical
- Trustworthy
- Behavioral flexibility
- Understanding
- Empathy
- Social Insight
- Charm
- Tact
- Diplomacy
- Persuasiveness
- Listener
- Collaborative
- Strong motivator
- Cooperative
- Influencer
Communication:
- Ability to communicate
- Ability to articulate a vision
- Ability to persuade others
- Communicate purpose
- Communicate direction
- Communicates passion to others
- Good communication skills
- Use metaphors
- Experts at one-to-one communication
- Superior speakers
- Excellent writing skills
- Creates and maintains a communications network
- Has people keep them informed on problem situations
- Networks with people inside the organization
- Maintains contacts outside the organization
- Doesn’t depend on only one source for information
- Able to communicate with key individuals
- Eager to explore new approaches to their work
- Are not fuzzy about results, interested in ways to track their progress
- Communicates persuasively
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
The Leader-Member Exchange Theory (LMX), also called the Vertical Dyad Linkage Theory is a relationship-based approach that focuses on the two-way (dyadic) relationship to get the best from all team members. How leaders maintain their position in groups and develop an exchange with each of their subordinates. How leaders and members develop relationships that can contribute to growth or hinder development.
-
Continuum of leadership is a leadership theory based on the relationship between the level of freedom given to the team and the level of authority used by the manager. The chosen leadership style will depend on multiple factors, including the leader's personality.
-
The cognitive resource theory states the influence of the leader's resources on his or her reaction to stress. The cognitive resources of a leader are experience, intelligence, competence, and task-relevant knowledge. Stress is common in resource managing situations, and this cognitive theory emphasizes how intelligence and experience are each best under different stress situations. This theory is the reconceptualization of the Fiedler model.
-
Idiosyncrasy Credit Model of Leadership builds upon the awareness that when the emergent leader meets the team's expectations, idiosyncrasy credits are awarded. These credits depend on how the leader fulfilled follower's expectations and what is the impact of the leader's decisions on the follower. When the balance of credits shifts, another leader will emerge.
-
Leadership traits refer to personal qualities that define effective leaders. Here are the major leadership qualities that can make someone a good leader. Five key traits that are common in leaders can be learned and sharpened with time.
-
Life cycle theory of Leadership
Situational Leadership Theory was first introduced in 1969 as the life cycle theory of leadership. This theory suggests that type of leadership style appropriate in a given situation depends on the maturity of the follower. As per life cycle theory, leader need to match the leadership style according to the situation and leader behavior varies as the group matures.
-
Role theory is a concept in sociology and the role theory of leadership borrows these concepts to explain how people adapt to specific organizational and leadership roles. How the leaders and followers in an organizational context define their own roles, define the roles of others, how people act in their roles and how people expect people to act in their roles within the organization.
-
In the field of communication studies, there are numerous models. No one model is suitable for all purposes and all levels of analysis. Some common models are known as Lasswell Model, George Gerbner Model, David Berlo Model, Shanon and Weaver Model, Osgoods Model, and Schramm Model. All these describe the four components of the communication process, namely, the source (communicator), the message, the channel, the receiver (audience).
-
Certain generally accepted truths or principles of communication are important to consider when communicating with others. These principles hold true for all people in every culture. By understanding these principles, you will experience greater communication effectiveness. An effective communication system is one that achieved its objectives. Communication is effective where there are no barriers to communication.
-
Situational Leadership - Application
Situational Leadership Theories are well known and frequently used for training leaders within organizations. Practical application is how to choose the right leadership approach for the situation. The theory emphasizes leader flexibility and advises leaders to flex their style based on the followers' needs. Leaders must adapt their leadership style to fit the prescribed task, understanding given situation/maturity of followers.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved