- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Leadership
- Leadership Theories
- Situational Leadership - Application
Situational Leadership - Application
Situational Leadership Theories are well known and frequently used for training leaders within organizations. Practical application is how to choose the right leadership approach for the situation. The theory emphasizes leader flexibility and advises leaders to flex their style based on the followers' needs. Leaders must adapt their leadership style to fit the prescribed task, understanding given situation/maturity of followers.
How does this Approach Works?
The situational approach is constructed around the idea that different employees are at different level of development or maturity stages which represents the relative competence and commitment of subordinates for a given task. For leaders to be effective in such situations, it is essential that they determine where subordinates are on the maturity levels and adapt their leadership styles so that their style matches with the style of the development level and the followers can be benefited by the time and energy spent by the leader on it. In a way this approach is mutually beneficial to both follower and the leader as leader can also save his time and energy by understanding the maturity levels of the follower.
It is designed to increase the frequency and quality of conversations about performance and development between managers and the people they work with so that competence is developed, commitment is gained, and talented individuals are retained. Highlighted below are the key learning objectives from this theory:
- Develop an understanding of Interaction Styles and how this model can assist in gaining a greater understanding of yourself and others
- Understand how your preferences can influence you and others
- Understand the importance of adapting own interaction style to increase effectiveness
- Be able to diagnose others’ development levels and choose the appropriate leadership style
- Know why there is no best leadership or coaching style
- Learn to use a common language for coaching and developing others
- Understand the negative impact of over supervision and under supervision on others’ performance and morale
Steps to Apply Situational Leadership Model:
1. Determine the nature of the situation.
2. Understand the nature and complexity of the task at hand
3. Evaluate the skills and the desire of the subordinates to do the task being asked to perform.
4. Identify correctly the specific developmental level at which their subordinates are functioning.
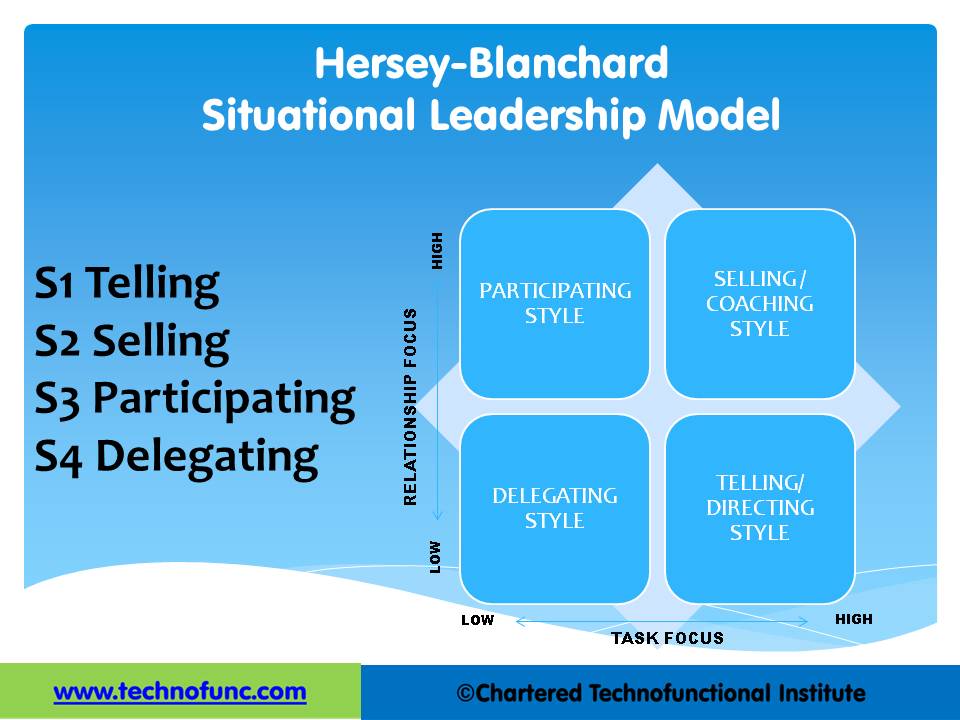
5. Adapt his or her style to the prescribed leadership style represented in the table given in the previous article.
Practical Applications of the Situational Approach:
- This theory is well known and frequently used for training leaders within organizations.
- Perceived by organizations as an effective model for training people to become effective leaders and use the skills in workplace to solve common workplace conflicts.
- Highly practical, easy to understand, sensible theory that can be applied in a variety of settings and situations.
- Provide leaders with a valuable set of guidelines that can facilitate and enhance leadership.
- Emphasizes leader flexibility and recognizes that employees act differently with different tasks and leaders need to flex their style based on the situational or followers need.
- It is an encompassing model with a wide range of applications.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Authentic leadership is a new approach to leadership in which leaders are genuine, self-aware, transparent, build honest relationships, and work on an ethical foundation. Authenticity is one of the core values of leadership. Authentic leaders have truthful self-concepts and they inspire by promoting openness by acting in a real, genuine, and sincere way. Authenticity requires self-awareness and the ability to act in accordance with one's true self.
-
Early studies on leadership were done at Ohio State University using the Leader Behavior Description Questionnaire to identify the leader's observable behaviors. Ohio State study on leadership found two behavioral characteristics of leadership - people-oriented (consideration) and task-oriented (initiating structure) leadership style.
-
Contingency Theories of Leadership
Contingency theories of leadership focus on both the leader's persona as well as the situation/environment in which that leader operates. These theories consider the context of leadership which means whether or not the leadership style suits a particular situation and states that a leader can be effective in one circumstance and a failure in another one. A leader will be most effective when he applies the right leadership style to a given situation and environment around him. Contingent leaders are flexible and adaptable.
-
The skills approach to leadership suggests that certain skills are important for effective leadership. Skills are what leaders can learn and develop, whereas traits are innate characteristics. The main skills needed for leadership, according to one such theory, are technical, human, and conceptual.
-
The Vroom-Yetton model is designed to optimize for the current situation the leadership style for best decision-making. Its a decision model formulated with contribution from Arthur Jago on how to make group decisions. The leader must gather information from the team prior to making the decision and involves more people in the decision process.
-
The open systems model of leadership acknowledges the influence of the environment on organizations. An open system regularly exchanges feedback with its external environment. The environment also provides key resources that are necessary to sustain and lead to change and survival. Leadership in an open system should focus on influence, open communication, and patterns to control expanding the number of variables created by external dynamics.
-
Role theory is a concept in sociology and the role theory of leadership borrows these concepts to explain how people adapt to specific organizational and leadership roles. How the leaders and followers in an organizational context define their own roles, define the roles of others, how people act in their roles and how people expect people to act in their roles within the organization.
-
The four theory of leadership was formulated after studying hundreds of leaders and the model includes four basic dimensions of effective leadership - support; interaction; facilitation; goal emphasis, and work facilitation. This model was tested as a predictor of an organization's effectiveness.
-
Symbolic Interaction and Social Change
George Herbert Mead, an American philosopher, affiliated with the University of Chicago founded the theory of symbolic interactionism. A major aspect of this is that people interact by symbols both verbal and non-verbal signals and every interaction makes a contribution to the mental make-up of the mind thus every interaction with someone, changes you and you go away a different person signifying that humans and change go together.
-
The style approach emphasizes that one style of leadership behaviour cannot be effective in all situations. Earlier theories treated leadership exclusively as a personality trait and behavior approach has widened the scope by including the behaviors of leaders and what they do in various situations. Explore how you can benefit from the concepts to understand your own behaviors and what are some of the leadership tools based on the style approach to leadership.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved










