- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Leadership Skills
- Leadership Theories
- Attribution Theory of Leadership
Attribution Theory of Leadership
The attribution theory of leadership deals with the formation of individual opinions about the reasons for particular events or observations. People will always try to understand why people do what they do. The leader will make a judgment about his employees based on his attribution of the causes of the employees' performance. Individuals will also make inferences about the leader and react to poor performance by the leader.
Attribution theory is attributed to the work done by Heider (1958), Jones and Davis (1965), and Kelley (1967, 1972, 1973). Attribution became an active area of organizational behavior research in the 1980s. It is a model of leadership evaluation that assumes that individuals make inferences about leadership ability by observing and interpreting certain environmental and behavioral cues. Attribution theory is best understood through an example. If you relate well with someone, you’re more likely to evaluate that person’s performance favorably; however on the other side, if someone else constantly irritates you the wrong way, you may be more inclined to evaluate that person’s performance punitively.
Attribution Theory:
People try to identify the reasons for observed events by collecting information that can help explain them. People constantly try to form chains of cause and effect explanations for observed incidents and experiences. These attributions by humans help them to assign an order to the world around them and increase their ability to understand the behavior of self and others.
Attribution Theory deals with the:
- Formation of individual opinions about the reasons for particular events or observations.
- Formation of opinions about the behavior of other people
- Formation of opinions about oneself
- How individuals explain their own successes and failures
- How individuals explain the behaviors and outcomes of others
- Whether the cause of the behavior is a characteristic of the follower (an internal attribute)
- Whether the cause of the behavior is a characteristic of the situation (an external attribute)
- Whether a follower's behavior is likely to remain constant (stable)
- Whether a follower's behavior is likely to change over time (unstable)
Attribution theory describes how individuals develop causal explanations for behaviors and outcomes, and how their causal explanations influence subsequent reactions. People see behavior as being caused either by the individual (i.e. dispositional) or by the environment (situational). It makes a distinction between internal and external causes.
Attribution Theory of Leadership:
It is a model of leadership evaluation that assumes that individuals make inferences about leadership ability by observing and interpreting certain environmental and behavioral cues. A two-step attributional model of leadership was proposed by Green and Mitchell (1979) suggesting that leaders make attributions (try to understand) about the cause of the performance before deciding on the appropriate action to take. A leader attributes various factor(s) for a follower's performance (internal, external, stable, unstable). These ascribed attributions influence leader's expectations for future performance as well as his behavior toward the follower.
The attribution model suggests that leaders observe their followers’ behavior, make inferences about the causes of that behavior (i.e., whether it is the result of internal, personal factors or of external, circumstantial ones), and then respond on the basis of those inferences. Attribution is the name given to this subjective process, in that we attribute causes, results, problems, and so on, to others, often with less than adequate information on which to base our judgment.
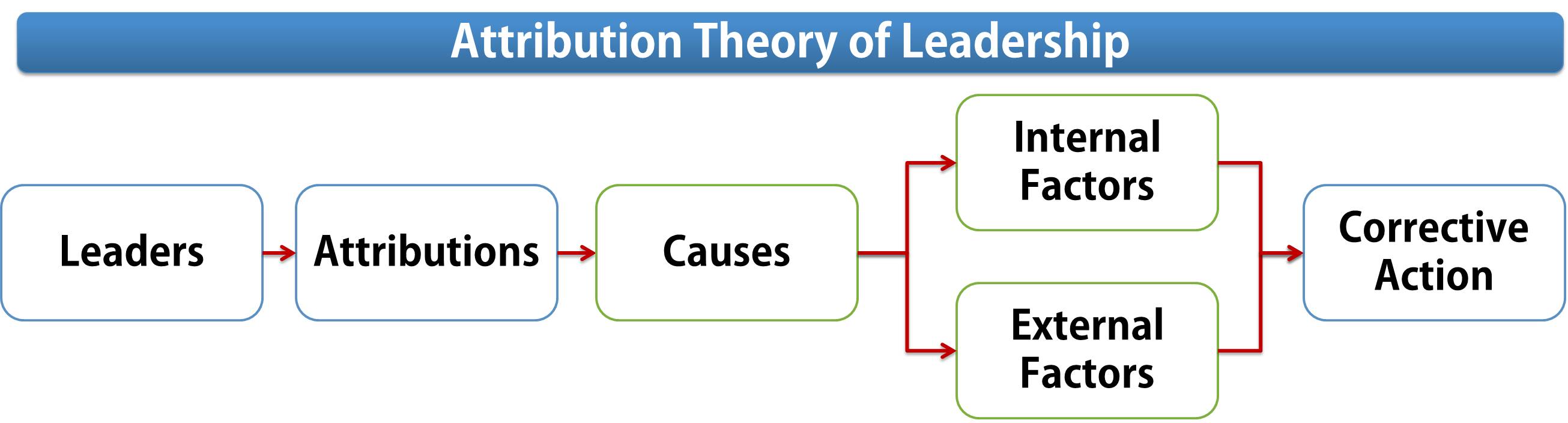
Internal Factors Influencing Behavior
Internal attributions include follower’s lack of interest, inexperienced followers, absenteeism by followers, or any other cause due to follower’s side.
If a leader attributes a follower's poor performance to internal factors such as low effort or a lack of ability, he or she may reprimand, dismiss, or provide training for the employee concerned. If a manager attributes an employee's poor performance to a lack of effort, then it will impact employees' performance appraisal poorly.
External Factors Influencing Behavior
External causes include, poor performance mainly due to machines break down, tool break down, material inventory problem, material quality problem, or any other cause by external factors, which are beyond the control of followers
If, however, poor performance is attributed to external factors such as a lack of material, or to work overload, the leader would need to concentrate on these factors and improve the situation instead of giving negative feedback to the employee. If a manager perceives that an employee's poor performance is due to a lack of skill, the manager may most likely assign the employee to required training or provide some assistance in terms of instructions or coaching.
Corrective Action by Leader
The leader will take corrective action:
- Towards the situation, if he attributes performance problems to external causal factors
- Towards follower when he attributes the performance problem to internal factors
For example, a manager who makes an internal attribution by concluding that an employee’s poor performance on a recent project was due to personal characteristics that led to lack of motivation, he is likely to decide on a harsher disciplinary action. Corrective action is more likely to be punitive in nature when attributed to lack of effort
However if he made an external attribution by assigning the reason of poor performance to the situation like a lockout situation say due to corona pandemic, the person was not able to visit clients and hence the decline in sales volume, the corrective action by the manager will be targeted towards remedying the situation.
Applicability to Organizations/Leadership
Attributions are critical to management because managers' and employees' judgments and actions are often based on perceived causes of behavior. Given below are some implications for organizations:
- Influence perception about employees based on observed performance and derived attributions to causes
- Managers will make a performance-related judgment based on observed behavior and attributions
- Inaccurate judgment about the causes of poor performance can have negative repercussions for the organization
- Attributions may influence employee motivation both positively and negatively
- Understanding attributions can improve managerial effectiveness
What is the attribution theory of leadership?
Attribution theory of leadership assumes that individuals make inferences about leadership ability by observing and interpreting certain environmental and behavioral cues. Leaders make attributions (try to understand) about the cause of the performance before deciding on the appropriate action to take. A leader attributes various factor(s) for a follower's performance (internal, external, stable, unstable). These ascribed attributions influence leader's expectations for future performance as well as his behavior toward the follower.
What is an example of attribution theory?
An example of attribution theory could be a manager who makes an internal attribution by concluding that an employee’s poor performance on a recent project was due to personal characteristics that led to a lack of motivation. Once he makes such a judgment, he is likely to decide on a harsher disciplinary action. In this case, the corrective action is more likely to be punitive in nature as it has been attributed by the manager to lack of effort.
What is an example of an external attribution?
An example of a manager making an external attribution is when he assumes that the poor performance of the employee is due to external situations. For example, due to lockdown situation created by corona pandemic, the employee was not able to visit clients to make sales calls, and hence there was an observed decline in sales volume. In this case, the manager has assigned the cause to external attribution and the corrective action by the manager will be targeted towards remedying the situation either by lowering his targets or looking for virtual sales opportunities.
What does the attribution theory mean?
Attributions theory means a lot for management because it establishes that managers' and employees' judgments and actions are often based on perceived causes of behavior. Managers make perceptions about employees based on observed performance and derived attributions to causes. Managers will eventually make a performance-related judgment based on observed behavior and attributions. These decisions based on attributions may influence employee motivation both positively and negatively and hence understanding attributions can improve managerial effectiveness.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
The skills approach to leadership suggests that certain skills are important for effective leadership. Skills are what leaders can learn and develop, whereas traits are innate characteristics. The main skills needed for leadership, according to one such theory, are technical, human, and conceptual.
-
There are four major factors in leadership called Leader, Follower, Communication, and Situation. The success of the leader is dependent on how the leader is effectively able to communicate and motivate followers to perform desired tasks using the appropriate leadership style best suited for the given situation. Interdependencies and dynamics of these four factors of leadership must be considered by a leader to be effective.
-
Investment Theory of Creativity
Sternberg in the year 2006, proposed the investment and confluence theory focused on understanding creativity. According to the investment theory, creativity requires a confluence of six distinct but interrelated resources known as intellectual abilities, knowledge, styles of thinking, personality, motivation, and environment. It emphasizes that creativity is not about one thing, but about a system of things.
-
Self-leadership is a normative model of self-influence by the use of several behavioral strategies to gain a comprehensive self-influence perspective about oneself. Self-leadership is developing an understanding of your capabilities and abilities to influence your own communication, emotions, and behaviors to lead and influence others. Self-leadership is about personal growth and developing foresight.
-
Substitutes for leadership theory is based on understanding the context within which leadership occurs. Different situational factors can enhance, neutralize, or substitute for leader behaviors like under certain circumstances, situational factors may substitute for leadership. These substitutes are of two types - substitutes and neutralizers. Substitutes take away from the leader's power and help group members increase their performance. Neutralizers only remove influence from the leader.
-
Reciprocal influence theory also known as reciprocal determinism is authored by Albert Bandura and states that an individual's behavior influences and is influenced by both the social world and personal characteristics. Three factors that influence behavior are the environment, the individual, and the behavior itself. Certain leader behaviors can cause subordinate behaviors and reciprocal influence on the leader by the group.
-
All the teams are dynamic in nature and they take time to come together, they form, develop, and grow in stages, over a period of time. Teams go through five progressive stages: Forming, Storming, Norming, Performing and Adjourning. In this article, we want to introduce you to these stages of team development and certain strategies that you can use to help the team grow and develop in each of these stages.
-
Situational Theories of Leadership
The situational theories of leadership assume that the most effective style of leadership depends from situation to situation. Situational leadership is a leadership style in which the leader must adjust to match the development needs of the followers. They must adapt varying behaviors to strike the right balance between task & relationship based on different levels of maturity of followers and also as followers develop and cultivate their skills.
-
The Vroom-Yetton model is designed to optimize for the current situation the leadership style for best decision-making. Its a decision model formulated with contribution from Arthur Jago on how to make group decisions. The leader must gather information from the team prior to making the decision and involves more people in the decision process.
-
Communication has as its central objective the transmission of meaning. The process of communication is successful only when the receiver understands an idea as the sender intended it. How does a message or an idea travel from one person to another? To transmit our message, we engage in a sensitive and complex process of communication, with different elements like sender, message, channels, receiver, noise, and feedback.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved










