- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Leadership Skills
- Team Leadership
- Level Five Leadership
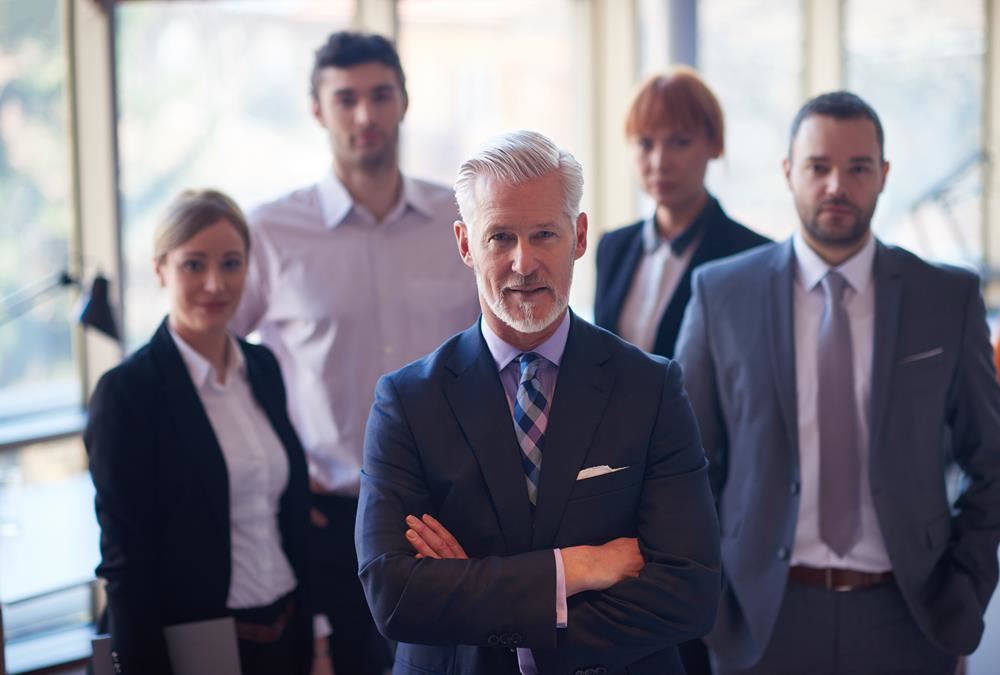
Level Five Leadership
“Level 5 Leadership”, this term was coined by Jim Collins in his book “Good to Great” and it is all about achieving "Greatness" as a leader. This article will explain what we mean by Level 5 Leadership and what the characteristics of a Level 5 leader are. What it takes to achieve greatness as a leader, and what are the steps and strategies that one can use to move up to this top level of leadership.
What is Level 5 Leadership?
Level 5 Leadership is a term that was coined by Jim Collins in his book “Good to Great: Why Some Company’s Make the Leap and Other Don’t”. As Collins says in his book, "We were surprised, shocked really, to discover the types of leadership required for turning a good company into a great one." What he seems to have found is what The Economist calls, "The Cult of the Faceless Boss." Truly great leaders have a specific blend of skills along-with certain characteristics that are harder to define. In his own words "The good-to-great executives were all cut from the same cloth. It didn't matter whether the company was a consumer or industrial, in crisis or steady-state, offered services or products. It didn't matter when the transition took place or how big the company. All the good-to-great companies had Level 5 leadership at the time of the transition. Furthermore, the absence of Level 5 leadership showed up as a consistent pattern in the comparison companies..."
Collins observed a set of "personality attributes" which identifies who they are rather than what they know and all exhibited extreme personal humility with an intense professional will.
The personality attributes that he found were:
1. Level 5 leaders are all very bright people who know their business. They are self-confident enough to set up their successors for success.
2. They are intelligent with business and domain knowledge to effectively manage their companies.
3. Level 5 leaders have humility. They are humble and modest.
4. Level 5 leaders seek success so that their team and organization can thrive.
5. Level 5 leaders share credit for success with the entire team or organization and happily accept blame for mistakes. They give credit to others for their success and take full responsibility for poor results. They "attribute much of their success to 'good luck' rather than personal greatness."
6. Level 5 leaders ask for help when they need it.
7. Level 5 Leaders are incredibly disciplined in their work. They have "unwavering resolve."
8. Level 5 Leaders succeed with their teams and spend quality time to find the right set of people. They develop their people to help them reach their full potential (get the right people on the bus).
9. Level 5 Leaders are passionate about their job, about what they do. They display "workmanlike diligence - more plow horse than show horse."
Collin’s Five Levels of Leadership:
Level 5 is the highest level in a hierarchy of leadership capabilities. Leaders at the other four levels in the hierarchy can produce high levels of success but not enough to elevate organizations from mediocrity to sustained excellence. “Good-to-Great” transformations are not possible without Level 5 leadership. Let's look at each of the five levels in more detail:
Level 1: Highly Capable Individual
The leader at this level makes productive contributions through talent, knowledge, skills, and good work habits. At this level, the leader possesses useful levels of knowledge; and has the talent and skills needed to do a good job.
Level 2: Contributing Team Member
At Level 2, the leader contributes to the achievement of group objectives; works effectively with others in a group setting. The leader uses his knowledge and skills to help the team succeed. The leader has the ability to work effectively, productively, and successfully with other people in the group.
Level 3: Competent Manager
At Level3, the leader organizes people and resources toward the effective and efficient pursuit of predetermined objectives. The leader has the ability to organize a group effectively to achieve specific goals and objectives.
Level 4: Effective Leader
At Level 4, the leader catalyzes commitment to and vigorous pursuit of a clear and compelling vision; stimulates the group to high-performance standards. This is the category where most successful leaders fall into. Here, the leader has the ability to stimulate a department or organization to meet performance objectives and achieve a vision. Level 4 leaders have their own visions of what the business needs to do to succeed. They decide on a direction and then get people to implement their vision.
Level 5: Great Leader
This level sits on top of a hierarchy of capabilities and the four other layers lie beneath it. Each one is appropriate in its own right, but none with the power of Level 5. We do not need to move sequentially through each level of the hierarchy to reach the top but to be a fully-fledged Level 5; we need the capabilities of all the lower levels, plus the special characteristics of level 5. At Level 5, the leader has all of the abilities needed for the other four levels, plus they have the unique blend of humility and will that's required for true greatness. Leader at this level builds enduring greatness through a paradoxical combination of personal humility plus professional will.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Charles Darwin had once commented that “It is not the strongest or the most intelligent who will survive but those who can best manage change.” Agility means the capability of rapidly and efficiently adapting to changes and recently, agility has been applied in the context of software development, agile enterprise, and agile leadership. Agile leaders play an important, even essential, role in scaling agility in an organization. Understand how being an agile leader helps in effectively catalyzing organizational change.
-
Crisis leadership is a very important part of leading in today's world. The skills a leader needs in order to guide people during a crisis are different from the skills needed to help a group grow. Are you a good crisis leader? What is your leadership style in case of a business crisis situation? A business crisis can test the strongest of leaders, read this article to explore how to ensure you’re ready to take action and weather the storm when one strikes you.
-
Narrative leadership is interpreted as the leader who aspires to construct leadership by telling stories. Leadership is a task of persuasion, of winning people’s minds and hearts. Storytelling is thus inherently suited for the task of leadership. Learn about the narrative leadership style and how to use this style to inspire and motivate followers or to manage change.
-
We define Lean as the systematic elimination of waste through a continual effort to decrease inefficiency; the lean leader strives to create a more efficient organization. Lean leadership is a philosophy. It is a consistent way of thinking and being in your role as a leader. The focus of this approach is on raising new leaders and help their team embrace a culture of continuous improvement. Learn what we mean by lean leadership style and its principles.
-
Power is the ability to exercise influence or control over others. Leadership involves authority and it is very important for leaders to understand what type of power they're using. The 5 Types of Power in Leadership are Coercive power, expert power, legitimate power, referent power, and reward power. Authority is the right to command and extract obedience from others. It comes from the organization and it allows the leader to use power.
-
Charisma is a certain quality of an individual personality, by virtue of which he is set apart from ordinary men. Charismatic Leader gathers followers, through dint of personality and charm. Understand the meaning and concept of Charismatic Leadership and the qualities of a charismatic leader. Gain an understanding of the advantages and disadvantages of using charismatic leadership. Finally, explore the difference between charismatic and transformational leadership.
-
Narcissistic leadership is a leadership style in which the leader is only interested in him. Narcissists are good for companies that need people with vision and the courage to take them in new directions. Such leaders sometime might be highly successful, but is it a style to be followed. Learn the various types of narcissistic leadership and the characteristics of such leaders.
-
Understanding of how individuals of different cultures interact with each other is very important. Not all individuals can adapt to the leadership styles expected in a different culture whether that culture is organizational or national. In a fast-paced business environment, developing a richer understanding and sensitivity to other cultures is a skill that leaders must possess. Learn to be effective in a cross-cultural setting.
-
Leadership has been defined in different ways by different sets of scholars. In very simple terms leadership can be defined as the skill of a person to influence an individual or a group for achievement of a goal in a given situation. One can use different dimensions and perspectives to define leadership. Through the evolution of leadership thought, leadership has been defined in various ways discussed here.
-
Appreciative leaders encourage contributions from those around them and facilitate the discussion to mutually solve problems. Understand the concept of Appreciative Leadership and learn about tools to create and ask powerful questions - that lead to new discoveries and possibilities. Instead of focusing on what’s wrong in the workplace, learn about, and build upon what works. Learn in this article the art to apply appreciative inquiry to specific situations and challenges at your workplace.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved