- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Emerging Technologies
- Additive manufacturing
Additive manufacturing
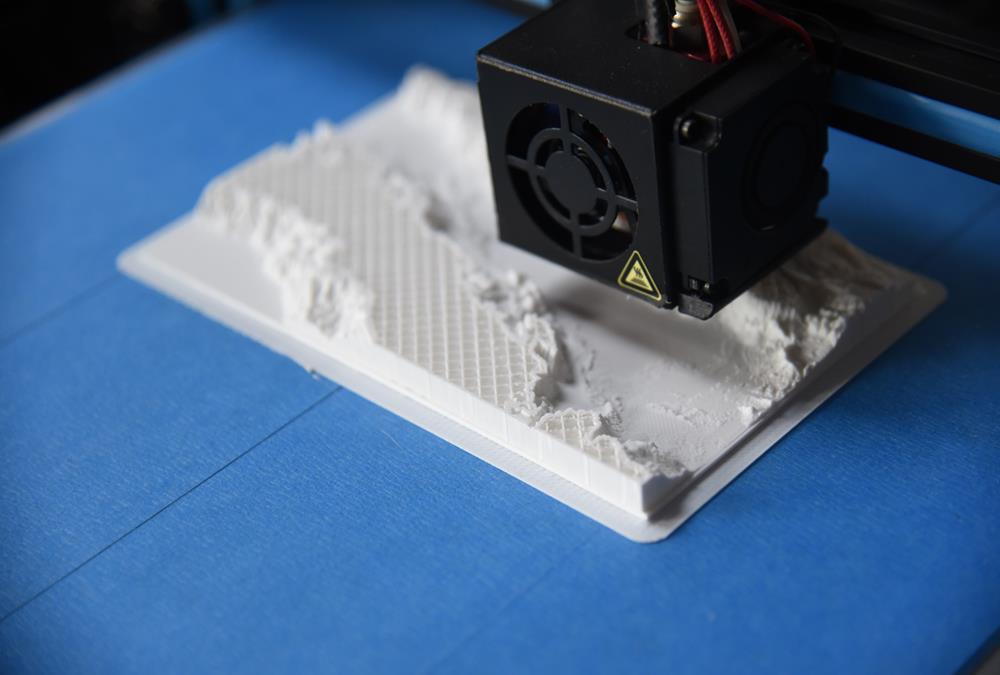
Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, is a transformative approach to industrial production, by adding layer-upon-layer of material, a computer-controlled process that creates three-dimensional objects shaped into the desired product by parts of it being removed in a variety of ways.
Introduction
Additive Manufacturing (AM) also known as 3D printing builds up a part (or features onto parts) layer by layer from geometry described in a 3D design model whereas in the traditional subtractive manufacturing methods one starts with a solid block of material and then cut away the excess to create a finished part. There are several different additive manufacturing technologies, 3D printing being the most well-known.
Application of Technology
Using Computer-Aided Design, 3D computer models of the required target object are created. Objects can be of almost any shape or geometry and typically are produced using digital model data from a 3D model or another electronic data source. These are uploaded into the metal printer. Using the models as building instructions, the printer, adds a metal powder layer by layer, each time fusing the layer into the solid metal with a high-power laser. In this way, complete 3D objects get constructed by 3D printing or AM by building a three-dimensional object from a computer-aided design (CAD) model by successively adding material layer by layer. 3D printed objects are generally very rough and require additional machining and finishing before they can leave the factory as final products.
- Some benefits of 3D metal printing an exciting new technology are given below:
- Highly efficient, producing minimal waste when compared to traditional subtractive manufacturing
- Reduces lead times and total cost of complex components
- Ability to create new geometries and designs with complex features and finer details
- The products designed could be lighter compared to traditionally designed products
- Can be easily tailored for very specific situations like medical implants
- Technology is ideal for rapid prototype development
Business Case Example
Early additive manufacturing equipment and materials were developed in the 1980s. Additive Manufacturing is establishing itself as a proven technology that can transform supply chains, empower customization and can disrupt traditional industries. AM is now beginning to make significant inroads, and with the advantages of design for additive manufacturing, it is clear to engineers that much more is to come. With the right application and the right design approach, serial production with 3D Printing is the reality in future. Plastics and metals can be used to create the following product examples:
- Industrial machines and equipment
- Automotive vehicles and aircraft
- Personalized consumer products
- Customized production tools and tooling
- Medical devices and models
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
An autonomous vehicle (AV), also known as driverless car, robo-car, or robotic car, is a vehicle that is capable of sensing its environment and moving safely with little or no human input. It utilizes a fully automated driving system & how this technology is deployed will change how we get around forever.
-
Robotics is one of the most advanced and emerging technologies that deals with physical robots. Robots are programmable machines that are usually able to carry out a series of functions that can help and assist humans in their day-to-day lives and keep everyone safe.
-
Robotic Process Automation is the technology that allows anyone today to create your own software robots to automate any business process. RPA emulate and integrate the actions of a human interacting within digital systems to execute a business process.
-
Cloud storage delivers a cost-effective, scalable alternative to storing files on on-premise hard drives or storage networks. Cloud storage is a service that enables saving the data on an offside storage system. Cloud storage is the storage of data online in the cloud
-
The science of building smart machines capable of performing tasks that makes it possible for machines to learn from experience, adjust to new inputs, and perform human-like tasks. Learn about implications for our future its applications
-
Machine learning (ML) is the process of teaching a computer system on how to make accurate predictions when fed data through the study of computer algorithms that improve automatically through experience. It is a method of data analysis that automates analytical model building
-
Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, is a transformative approach to industrial production, by adding layer-upon-layer of material, a computer-controlled process that creates three-dimensional objects shaped into the desired product by parts of it being removed in a variety of ways.
-
Internet of Things & Industrial Internet
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) refers to interconnected sensors, instruments, and other devices networked together with computers' industrial applications, including manufacturing and energy management. It brings together brilliant machines, advanced analytics, and people at work.
-
Block Chain & Distributed Ledgers
Blockchain is a distributed, decentralized, public ledger. A distributed ledger is merely a type of database spread across multiple sites, regions, or participants. It is a consensus of replicated, shared, and synchronized digital data. Learn more about how the blockchain system is going to change the way you transact business
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved