- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Business Processes
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- Matrix Organizational Structures
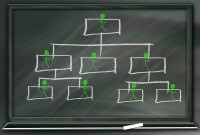
Matrix Organizational Structures
In recent times the two types of organization structures which have evolved are the matrix organization and the network organization. Rigid departmentalization is being complemented by the use of teams that cross over traditional departmental lines.
In recent times the two types of organization structures which have evolved are the matrix organization and the network organization. Rigid departmentalization is being complemented by the use of teams that cross over traditional departmental lines.
Matrix structure is the combination of two or more structures explained above. This is the structure that is adopted by most of the multinational companies. In a matrix context, the business support functions also ensure coordination across the business functions within each sub-function (such as procurement, production, marketing, distributing, etc.). They are also responsible for specialization related coordination, training, development and learning, problem solving, development of norms, standards and guidelines for functioning as appropriate to the area of specialization.
For example, we can have a functional structure and then assign a manager for each product. Some employees will have two managers: functional manager and product manager.
Main Features of Matrix Structure
Shared Services is the centralization of service offering at one part of an organization or group sharing funding and resourcing. The providing department effectively becomes an internal service provider. The key is the idea of 'sharing' within an organization or group. To accelerate business benefits such as lower cost of operations and improved business processes, the vast majorities of organizations centralize some functions into shared services and outsource various others to third-party service providers because some support functions tend to be similar across industries.
The matrix structure is a combination of the product and functional organization and is usually created for executing a project which requires the skilled services of a functional man as well as the specialized knowledge of a product man. Large turnkey projects in specialized fields require a matrix structure.
The distinguishing characteristic of a matrix structure is that it operates under a dual authority. A person is accountable to two bosses at the same time, one his usual boss and the other his boss for the duration of the project. Obviously the problems emanating from this type of structure relate to conflicting roles and authority arising out of an ambiguous demarcation of authority and responsibility. In a Matrix Structure, people typically have two or more lines of report. This type of organization may combine both functional and divisional lines of responsibility, allowing it to focus on divisional performance while also sharing specialized skills and resources.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Prepayments and Prepaid Expenses
Prepayments are the payment of a bill, operating expense, or non-operating expense that settle an account before it becomes due. Learn the concept of prepaid expenses. Understand the accounting treatment for prepaid expenses. Understand the concept by looking at some practical examples and finally learn the adjusting entry for these expenses.
-
Internally, an organization can be structured in many different ways, depending on their objectives. The internal structure of an organization will determine the modes in which it operates and performs. Organizational structure allows the expressed allocation of responsibilities for different functions and processes to different entities such as the branch, department, workgroup and individual.
-
GL - Accrued / Unbilled Revenue
Accrued revenues (also called accrued assets) are revenues already earned but not yet paid by the customer or posted to the general ledger. Understand what we mean by the terms accrued revenue, accrued assets, and unbilled revenue. Explore the business conditions that require recognition of accrued revenue in the books of accounts and some industries where this practice is prevalent.
-
Operational Structures in Business
Large organizations grow through subsidiaries, joint ventures, multiple divisions and departments along with mergers and acquisitions. Leaders of these organizations typically want to analyze the business based on operational structures such as industries, functions, consumers, or product lines.
-
Matrix Organizational Structures
In recent times the two types of organization structures which have evolved are the matrix organization and the network organization. Rigid departmentalization is being complemented by the use of teams that cross over traditional departmental lines.
-
The general ledger is the central repository of all accounting information in an automated accounting world. Summarized data from various sub-ledgers are posted to GL that eventually helps in the creation of financial reports. Read more to understand the role and benefits of an effective general ledger system in automated accounting systems and ERPs.
-
When the quantum of business is expected to be moderate and the entrepreneur desires that the risk involved in the operation be shared, he or she may prefer a partnership. A partnership comes into existence when two or more persons agree to share the profits of a business, which they run together.
-
Driving Business Efficiency through Divisions and Departments
In case of a multi-divisional organizational structure, there is one parent company, or head-office. And that parent owns smaller departments, under the same brand name. Dividing the firm, into several self-contained, autonomous units, provides the optimal level of centralization, in a company.
-
Multitude of these legal and operational structures clubbed with accounting and reporting needs give rise to many reporting dimensions at which the organization may want to track or report its operational metrics and financial results. This is where business dimensions play a vital role.
-
In this article we will focus on and understand the accounting process which enables the accounting system to provide the necessary information to business stakeholders. We will deep dive into each of the steps of accounting and will understand how to identify accounting transactions and the process for recording accounting information and transactions.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved