- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Leadership
- Leadership & Management
- Principles of Management
Principles of Management
Principles of management are fundamental concepts and advisory guidelines for managerial decision making. By using management principles, managers can more easily achieve the objectives and avoid making mistakes in their activities. Management principles can be applied to any kind of organization and to managers at all organizational levels.
A principle can be defined as a fundamental statement of truth providing a guide to thought or action. Principles help to understand what results can be expected when a particular management principle is applied. These management principles emerge based on certain qualities/characteristics that have relevance to management theory and practice.
Principles of management are to the manager as a guidebook of strengths and weaknesses which provides fundamental truths, expressed as quantitative data based on years of experience and testing. The manager can use these principles to take timely guidance for various management issues as these management principles have been developed from years of experience and testing, in public and private, in big and small organizations. By using management principles, managers can effectively achieve business objectives and avoid making fundamental mistakes in their actions and decisions. They are basic guides and a framework for reference but not absolute as managers need to take actions based on the context in which they operate. They are like working hypotheses that are reasonably well established, accepted, and used in many successful organizations, and managers must adapt them to their specific situation.
As more research is conducted, we gain more understanding of the way management principles operate; new principles will emerge, some existing management principles will get modified, and some others will be discarded not being truly representative of management practice in today’s context.
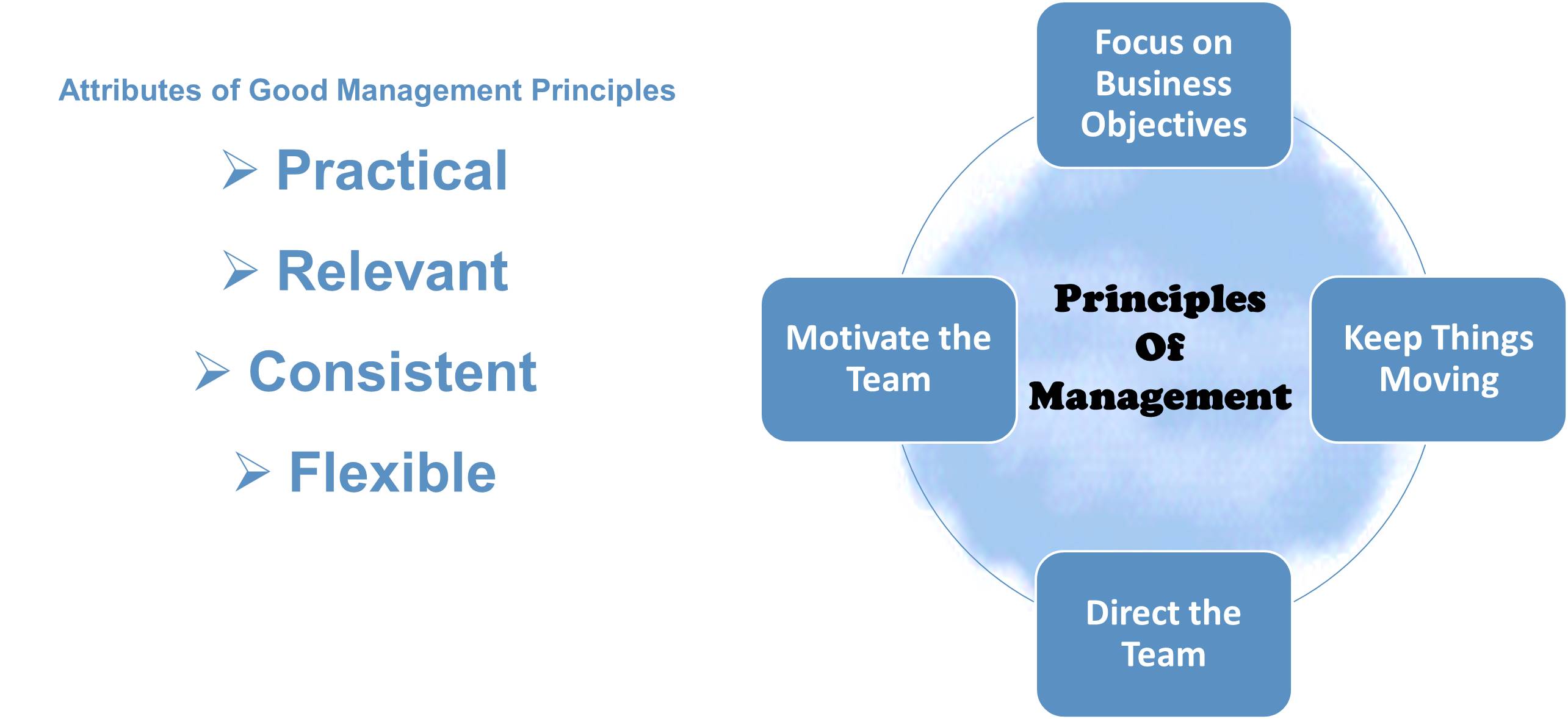
Henri Fayol (1849-1925), a French industrialist and a prominent European management theorist, developed a general theory of management. Fayol outlined the fourteen principles of management. Given below are some of the other attributes of good management principles:
- Practical: Management principles should have a practical application, which means they can be applied in the organizational context and remain appropriate
- Relevant: Management principles should not be restricted to one business scenario but they should be invariably applicable to the various broad forms of organizational structures and different businesses operating in different business domains.
- Consistent: The management principles should be consistent in their applicability and application meaning thereby that under a similar set of circumstances, similar business results can be expected.
- Flexible: Business operates in different environments and has multiple types of products and services. They build different operational and organizational structures. Management principles should take into accounts the particular differences or changes in the conditions that affect the organization. The use of management principles is intended to simplify, guide, and facilitate management work.
Therefore, management principles are a guiding key to actions that should be taken in a particular business context. They provide the guidelines from which the manager can understand the situation and recommended action and apply that in his particular context. They represent the major considerations in current management thought.
Given below are some of the important principles of management that will help you to build a better understanding of the management process:
Focus on Business Objectives
Management is always purposeful focused on the achievement of specific business objectives and goals. Managerial success is measured by the extent to which these objectives have been met. Management should keep a continued focus on the work needed to be accomplished.
Keep Things Moving
Management is responsible for making things happen and meet business goals. Managers should focus their efforts on bringing about successful action as per the vision and mission of the organization. They must provide direction to set goals, keep things moving, follow through to ensure members of the group accomplish the task they have been assigned.
Directing the Team
Management is accomplished by managing the team. The manager needs to relinquish the natural tendency to perform all things oneself and should focus on getting the tasks accomplished through the efforts of the group members. Management is thus associated with the efforts of the group. A group is necessary to accomplish business goals as an enterprise comes into existence to attain these goals, and these goals can be achieved only through group effort rather than by one person alone.
Motivating the Team
Management is an outstanding means for exerting a real impact on human, social, and political life. A manager can do much to improve the work-environment he operates in and the resources he deals in. A manager must stimulate and motivate people to do things better, and in the process should assist favorable organizational actions to take place. A manager can achieve progress, bring hope, and help group members acquire the better things in life.
These principles of management will definitely help you in discharging your roles and responsibilities as a manager. Understanding these principles will also broaden your understanding of the theories of management that every manager should be aware of.
Suggested Reading and Resources
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
The development of teams is an ongoing process because the composition of the team may keep on changing. The new members may join and the old members may leave the team. The team members pass through several stages for the development of the team and there has been a lot of research to identify these stages. In this article, we discuss the common theories of team development.
-
The best career choices are ones that match your values. Each person has several values that are important to him. These values are highly personal and knowing them provides a clearer sense of what's most important to you in your life and career. Career values are the beliefs you consider important from a work standpoint. Values help you understand what you want from a job? Explore a few examples of work values that can influence career path and job satisfaction.
-
Management theories are the recommended management strategies that enable us to better understand and approach management. Many management frameworks and guidelines were developed during the last four decades.
-
All the teams are dynamic in nature and they take time to come together, they form, develop, and grow in stages, over a period of time. Teams go through five progressive stages: Forming, Storming, Norming, Performing and Adjourning. In this article, we want to introduce you to these stages of team development and certain strategies that you can use to help the team grow and develop in each of these stages.
-
What are the functions which a leader does to establish as a leader? What are the activities undertaken by them to become great leaders, rather revolutionary leaders? The most important tasks done by a leader in all situations are defining the vision, mission, and goals, leading the team, administrative functions, motivating followers, decision making and conflict resolution, and continuous development.
-
Many different types of teams have been identified by social scientists. Managers may encounter the diverse types of challenges while managing different kinds of teams. Challenges associated with Cross-Functional Teams might be different from that of a Geographically Dispersed Team or a Virtual Team. This article explores some common categories and subtypes of teams.
-
Team Foundation in Forming Stage
This is the first stage of team development. This is the stage when the foundation of the team is laid. During the Forming stage, team members have a high dependence on their leader for guidance. Learn the practical strategies you can use during this stage to help your team develop into a highly effective performing team.
-
Teams are part of the modern organizational culture. Whether you are a team leader or a team member, having a better understanding of how teams work, and being able to identify where the team is in the process, is a critical part of ensuring the team is ultimately successful. Start with the basics and understand what a team is and what role they play in an organization.
-
Theory Z also called the "Japanese Management" style is a leadership theory of human motivation focused on organizational behavior, communication, and development. It assumes that employees want to enter into long term partnerships with their employers and peers. Offering stable jobs with an associated focus on the well-being of employees results in increased employee loyalty to the company.
-
There are four major factors in leadership called Leader, Follower, Communication, and Situation. The success of the leader is dependent on how the leader is effectively able to communicate and motivate followers to perform desired tasks using the appropriate leadership style best suited for the given situation. Interdependencies and dynamics of these four factors of leadership must be considered by a leader to be effective.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved