- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Business Processes
- Cash Management
- Automated Clearing
Automated Clearing
In automated clearing, Bank statement details are automatically matched and reconciled with system transactions. Learn how this process works and what are the perquisites to enable the same.
Automated Clearing
In automated clearing, Bank statement details are automatically matched and reconciled with system transactions.
This method is ideally suited for bank accounts that have a high volume of transactions.
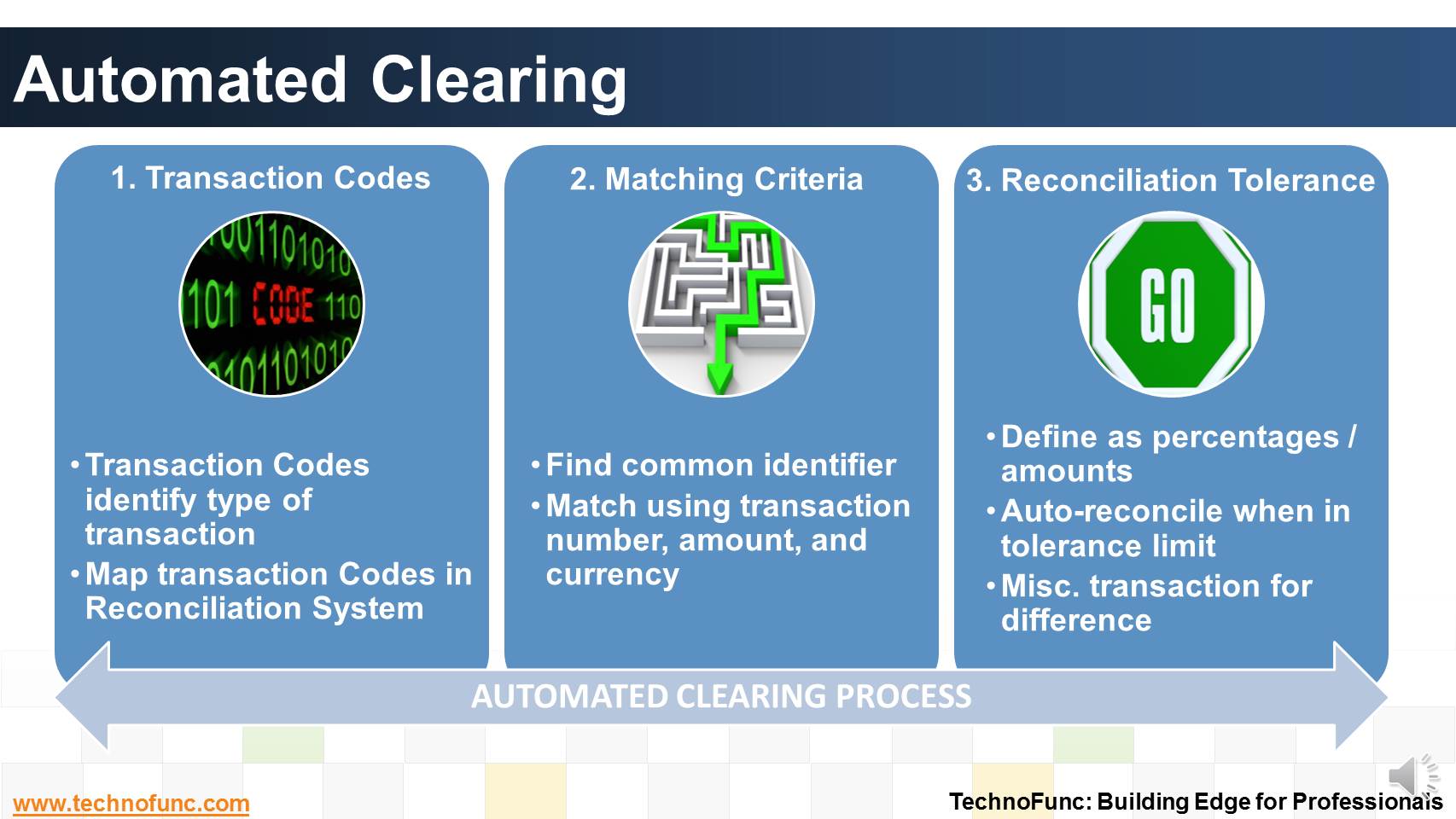
The following three are the basic steps are involved in Automated Clearing Process:
1 Map Transaction Codes
Bank statement lines are coded to identify the type of transaction the line represents. Since each bank might use a different set of transaction codes, the first step towards automatic clearing is to map each code that is used by a particular bank for which the transactions need to be reconciled.
2 Matching Criteria
Automated matching can only be done if you can find a common identifier between the transaction details as recorded in your sub ledgers and the bank statement.
Automated systems generally match a bank statement line against a payables payment transaction, receivables receipt transaction, payroll disbursals and miscellaneous transactions using a transaction number (such as the payment or deposit number), bank account, amount, and currency.
3 Reconciliation Tolerance:
Reconciliation tolerances are defined in the system as percentages and/or amounts.
If tolerance is defined then the difference between the statement line and sub-ledger transaction line will be auto-reconciled when it is within the tolerance limit. The system also creates a miscellaneous transaction for the difference between the remittance batch amount and the bank statement line.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
The Cash Management component ensures that the enterprise has sufficient liquidity for payments that are due and to monitor payment flows. Learn how treasury plays an important role in cash management for the enterprise.
-
Disbursement Float is the time taken from payment creation to settlement. Collection float is the sum total of time taken by Payment Float; Mail Float; Processing Float and Availability Float. Learn more!
-
Technology has enabled the treasury function by providing various solutions to manage it's complicated tasks. This article explains various types of treasury management systems available in the market.
-
What is Invoice to Cash Process
In this article, we will explore the business process area known as; Invoice to Cash; Also known as I2C. Learning objectives for this lesson are: Meaning of Invoice to Cash Process; Sub Processes under Invoice to Cash; Process Flow for Invoice to Cash; Key Transactions Fields; Key Setups/Master Data Requirements.
-
The objective of Financial risk management is to protect assets and cash flows from any risk. Treasury function works to accurately assess financial risks by identifying financial exposures including foreign exchange, interest rate, credit, commodity and other enterprise risks. Learn about the various risks that are managed by treasury.
-
What are the various sources of cash in an organization. Which sources increase the cash available with the enterprise and which sources results in outflow of the cash? Let us explore!
-
In automated clearing, Bank statement details are automatically matched and reconciled with system transactions. Learn how this process works and what are the perquisites to enable the same.
-
Although there is no straight forward answer to the question, how to best organize a treasury function, this article provides an generic view of the way large MNCs creates departments or sub-functions within the treasury function.
-
Cash Management - Integrations
Cash Management integrates cash transactions from various sources like Receivables, Payables, Treasury and creates reconciliation accounting entries after matching transactions with Bank Statements.
-
Suspense and clearing accounts resemble each other in many respects but there exists important fundamental difference between the two. Read more to explore these differences.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved










