- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Business Processes
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- Partnership Form
Partnership Form
When the quantum of business is expected to be moderate and the entrepreneur desires that the risk involved in the operation be shared, he or she may prefer a partnership. A partnership comes into existence when two or more persons agree to share the profits of a business, which they run together.
Definition of Partnership
When the quantum of business is expected to be moderate and the entrepreneur desires that the risk involved in the operation be shared, he or she may prefer a partnership. A partnership comes into existence when two or more persons agree to share the profits of a business, which they run together.
This business may be carried on by all or by any of them acting for all. Those who, thus, enter into an agreement are individually called as ‘partners’ and collectively they are called as ‘firm’. Partnership is the outcome of a voluntary agreement between the persons, who after the agreement has been arrived at, would be known as partners.
A partnership is a form of business organization in which two or more persons join together to undertake some form of business activity.
Main Features
- Ease of formation as compared to a company
- Partnership is an association of two or more persons who have joined together to share the profits of business
- Partners contribute to capital and share the responsibility of running the business
- Partnership is based on contractual relationship and created by an agreement between persons called 'partners'
- Principal-agent relationship - The business may be carried on by all or one or more partners acting for all the partners
- Risk of implied authority as each partner acts as an agent of the firm and his acts would bind the firm and all remaining partners
- In respect of business debts, each partner has unlimited liability
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Understand what we mean by GAAP to STAT adjustments. This article discusses the different standards that are used for multiple representations of the financial results for global organizations. Understand the meaning of US GAAP, Local GAAP, STAT, IFRS, and STAT. Finally, understand why accounting differences arise and how they are adjusted for different financial representations.
-
In this article we will help you understand the double-entry accounting system and state the accounting equation and define each element of the equation. Then we will describe and illustrate how business transactions can be recorded in terms of the resulting change in the elements of the accounting equation.
-
An account inquiry is a review of any type of financial account, whether it be a depository account or a credit account. In this tutorial, you learn what we mean by drill through functionality in the context of the general ledger system. We will explain the concept of drill-down and how it enables users to perform account and transaction inquiry at a granular level and the benefits of using this functionality.
-
Legal Structures in Businesses
Businesses not only vary in size and industry but also in their ownership. Most businesses evolve from being owned by just one person to a small group of people and eventually being managed by a large numbers of shareholders. Different ownership structures overlap with different legal forms that a business can take. A business’s legal and ownership structure determines many of its legal responsibilities.
-
Matrix Organizational Structures
In recent times the two types of organization structures which have evolved are the matrix organization and the network organization. Rigid departmentalization is being complemented by the use of teams that cross over traditional departmental lines.
-
Period End Accruals, Receipt Accruals, Paid Time-Off Accruals, AP Accruals, Revenue Based Cost Accruals, Perpetual Accruals, Inventory Accruals, Accruals Write Off, PO Receipt Accrual, Cost Accrual, etc. are some of the most complex and generally misconstrued terms in the context of general ledger accounting. In this article, we will explore what is the concept of accrual and how it impacts general ledger accounting.
-
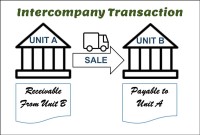
After reading this article the learner should be able to understand the meaning of intercompany and different types of intercompany transactions that can occur. Understand why intercompany transactions are addressed when preparing consolidated financial statements, differentiate between upstream and downstream intercompany transactions, and understand the concept of intercompany reconciliations.
-
Team-Based Organizational Structure
Team-based structure is a relatively new structure that opposes the traditional hierarchical structure and it slowly gaining acceptance in the corporate world. In such a structure, employees come together as team in order to fulfill their tasks that serve a common goal.
-
Defining Organizational Hierarchies
A hierarchy is an ordered series of related objects. You can relate hierarchy with “pyramid” - where each step of the pyramid is subordinate to the one above it. One can use drill up or down to perform multi-dimensional analysis with a hierarchy. Multi-dimensional analysis uses dimension objects organized in a meaningful order and allows users to observe data from various viewpoints.
-
A joint venture (JV) is a business agreement in which the parties agree to develop, for a finite time, a new entity and new assets by contributing equity. They exercise control over the enterprise and consequently share revenues, expenses and assets. A joint venture takes place when two or more parties come together to take on one project.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved