- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Business Processes
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- The Accounting Equation
The Accounting Equation
In this article we will help you understand the double-entry accounting system and state the accounting equation and define each element of the equation. Then we will describe and illustrate how business transactions can be recorded in terms of the resulting change in the elements of the accounting equation.
The Five Account Types:
Double-entry accounting uses five and only five account types to record all the transactions that can possibly be recorded in any accounting system. These five accounts are the basis for any accounting system, whether it is a manual or an automated accounting system. The five account types are the following:
Balance Sheet Accounts:
In accounting, the economic resources of a business are categorized under the terms of assets, liabilities, and owner's equity. These terms also refer to the three types of accounts in which a business records its transactions.
1. Assets:
Things of value that is owned and used by the business. Examples of assets include cash, land, buildings, and equipment.
2. Liabilities:
Debts that are owed by the business. These are the rights of the creditors or third parties over the assets of the business. Examples of liabilities include amounts due to suppliers, loans payable back to banks.
3. Equity:
The owner's claim to business assets. These are the rights of the owners over the assets of the business. Examples include capital invested by the owners, the shares subscribed by the public or the residual profit made by the business last year.
Profit and Loss Accounts:
The operations of the business can either result in profit or loss. It may increase the economic value over a period of time in case of profit or might decrease the economic worth in case of loss. All such activities can be recorded using two types of profit and loss accounts:
4. Revenue:
The amounts earned from the sale of goods and services. Examples include sales, interest received on bank deposits, a commission earned by the business.
5. Expenses:
Costs incurred in the course of business. Examples include purchases made for material, payment of rent, expenses for employee costs.
The balance sheet accounts are permanent accounts that carry a balance from year to year, like checking accounts, accounts receivable, and inventory accounts. The profit and loss accounts are temporary accounts that track revenues and expenses for a yearlong fiscal period and are then closed, with balances transferred to an equity account.
There can be thousands of sub-types; known as natural accounts which help in further classifying the nature of the transaction, but they all belong to one of the above lists, as practically all financial transactions can be recorded using these five types of accounts.
The Economic Impact of Transactions:
Businesses conduct transactions by exchanging goods or services for money. Transactions can take various forms, depending on the company, but whatever kind of transaction has occurred; it impacts the business's resources. The resources of a business refer to its supply of goods, services, information, or expertise that allows the business to operate and grow.
Businesses exchange items of equal value, real or perceived. Imagine that an exchange is like balancing a scale—the left side goes down (a service is given) and the right side reacts (cash is received) to maintain the balance of the scale. The exchange of goods or services, information, or expertise has an impact on the one side of the scale which is compensated by the value that the business gets in exchange that has an impact on the other side of the scale. The perceived value of both these impacts should be equal on the scale.
Accounting uses a technique to show how a transaction changes the business's resources while maintaining a balance, or showing the equal value of the exchange. The accounting equation is a tool that is applied throughout accounting activities to show how transactions affect the asset, liability, and owner's equity accounts.
The Accounting Equation:
The resources owned by a business are its assets. Examples of assets include cash, land, buildings, and equipment. The rights or claims to the assets are divided into two types:
- The Rights of the Creditors
- The Rights of the Owners
The rights of creditors are the debts of the business and are called liabilities. The rights of the owners are called owner’s equity. The following equation shows the relationship among assets, liabilities, and owner’s equity:
- Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity
- This equation is called the accounting equation. Liabilities usually are shown before the owner’s equity in the accounting equation because creditors have first rights to the assets. Given any two amounts, the accounting equation may be solved for the third unknown amount. The equation shown above represents the format seen on a balance sheet.
The profit and loss accounts (representing revenues and expenses account types) also affect equity. Revenues from the sale of goods and services increase equity, while expenses incurred in the course of business decrease equity. Therefore, the accounting equation can be expanded to assets equal liabilities plus equity plus revenues minus expenses.
- Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity + Revenues - Expenses
- Every transaction that has an accounting impact, will affect at least two accounts out of the five accounts explained above. If a transaction causes one side of the equation (assets) to increase, then the other side of the equation (liabilities or owner's equity) must also increase to keep the equation in balance.
You can apply the accounting equation by determining that the total of the asset accounts equals the total of the liability accounts plus the total of the owner's equity accounts. A double-entry accounting system will record the appropriate debits and credits, and track the changes to assets, liabilities, equity, revenue, and expense accounts. Keep this fundamental rule of accounting in mind when you need to determine how a transaction affects your business's resources.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
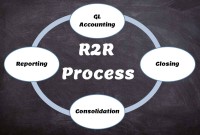
Record to report (R2R) is a finance and accounting management process that involves collecting, processing, analyzing, validating, organizing, and finally reporting accurate financial data. R2R process provides strategic, financial, and operational feedback on the performance of the organization to inform management and external stakeholders. R2R process also covers the steps involved in preparing and reporting on the overall accounts.
-
Internally, an organization can be structured in many different ways, depending on their objectives. The internal structure of an organization will determine the modes in which it operates and performs. Organizational structure allows the expressed allocation of responsibilities for different functions and processes to different entities such as the branch, department, workgroup and individual.
-
Functional Organizational Structures
A functional organizational structure is a structure that consists of activities such as coordination, supervision and task allocation. The organizational structure determines how the organization performs or operates. The term organizational structure refers to how the people in an organization are grouped and to whom they report.
-
What is Accounting & Book Keeping
Accounting is a process designed to capture the economic impact of everyday transactions. Each day, many events and activities occur in an entity, these events and activities are in the normal course of business; however, each of these events may or may not have an economic impact. Events or activities that have an effect on the accounting equation are accounting events.
-
This article explains the process of entering and importing general ledger journals in automated accounting systems. Learn about the basic validations that must happen before the accounting data can be imported from any internal or external sub-system to the general ledger. Finally, understand what we mean by importing in detail or in summary.
-
There are five types of core accounts to capture any accounting transaction. Apart from these fundamental accounts, some other special-purpose accounts are used to ensure the integrity of financial transactions. Some examples of such accounts are clearing accounts, suspense accounts, contra accounts, and intercompany accounts. Understand the importance and usage of these accounts.
-
Global Business Services (GBS) Model
Global business services (GBS) is an integrated, scalable, and mature version of the shared services model. Global Business Services Model is a result of shared services maturing and evolving on a global scale. It is represented by the growth and maturity of the Shared services to better service the global corporations they support.
-
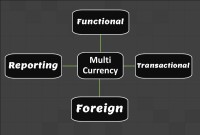
Multi Currency - Functional & Foriegn
Currency is the generally accepted form of money that is issued by a government and circulated within an economy. Accountants use different terms in the context of currency such as functional currency, accounting currency, foreign currency, and transactional currency. Are they the same or different and why we have so many terms? Read this article to learn currency concepts.
-
In some of the ERP tools, there are more than 12 accounting periods in a financial year. This article discusses the concept of accounting calendar and accounting periods. Learn why different companies have different accounting periods. Understand some of the commonly used periods across different organizations and the definition & use of an adjustment period.
-
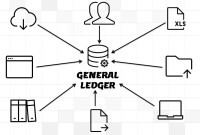
The general ledger is the central repository of all accounting information in an automated accounting world. Summarized data from various sub-ledgers are posted to GL that eventually helps in the creation of financial reports. Read more to understand the role and benefits of an effective general ledger system in automated accounting systems and ERPs.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved