- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Business Processes
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- Global Business Services (GBS) Model
Global Business Services (GBS) Model
Global business services (GBS) is an integrated, scalable, and mature version of the shared services model. Global Business Services Model is a result of shared services maturing and evolving on a global scale. It is represented by the growth and maturity of the Shared services to better service the global corporations they support.
Global business services (GBS) is an integrated, scalable, and mature version of the shared services model. Global Business Services Model is a result of shared services maturing and evolving on a global scale. It is represented by the growth and maturity of the Shared services to better service the global corporations they support. Global Business Services framework adds value to the shared services model by taking the model beyond labor arbitrage. This model adds consistent approaches to global services strategy formation, transition, and governance resulting in improved collaboration across the entire enterprise ecosystem. GBS provides services beyond transactional functions and provides value to the organization by enabling standardization, scalability, technology, well defined and optimized processes and business analytics. Under this model the entire organization collectively start leveraging global business services to accelerate attainment of corporate strategies.
General Electric, Bank of America, American Express are some examples who have already established Global Business Services model for their entire finance functions where a Global Operations Finance Team provides record to report and statutory and tax compliance services to all the businesses under its umbrella.
Main Features of GBS model:
- Integrated compilation of service offerings for multiple support functions within a company
- Global in nature with respect to both delivery centers and customers
- Service provides can be both internal and/or external
- Service providers are managed centrally by GBS organization
- Service offerings by GBS are standardized and follow process model with defined roles and responsibilities and handshakes at each interaction
- Global process ownership
- Integrated application suite(s)/Information Systems across the enterprise with well-defined processes and best practices
- Virtual centers of expertise to build and disseminate subject-matter expertise
- Defined and well tracked operational metrics to measure speed, quality and costs
- Standardization of processes and practices that result in the GBS organization being run like an independent entity
- Ability to take competitive advantage of cost arbitrage and third party expertise
- Mix of service delivery models - Captive offshore; In-house shared services centers; outsourced delivery models; “hybrids”
Value drivers of GBS Model
- Cost savings through economies of scale and labor arbitrage
- Simplification and standardization of processes
- Advanced analytics and visibility across different structures (legal/operational) of the enterprise
- Ability to hire and retain global talent
- Skill arbitrage: value derived from access to higher-skilled labor across globe
- Ability to work in shifts leveraging the time zone differences across globe
- Ability to deploy advanced tools and technology
- Ability to deliver scalability to processes and functions
Functions that can be shared across business units
- Sourcing and Procurement
- Buy to Pay – Accounts Payable
- Invoice to Cash – Accounts Receivable
- Payroll Management
- Record to Report – General Ledger
- Fixed Assets Management
- Statutory Reporting and Tax Reporting
- Human Resources
- Information Technology
- Vendor Management
- Customer Management
- Master Data Maintenance
All the models described above represent matrix structures. However, Matrix Structures can become overly complex, effectively having to uphold two hierarchies, with potential tensions between the two.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Global Business Services (GBS) Model
Global business services (GBS) is an integrated, scalable, and mature version of the shared services model. Global Business Services Model is a result of shared services maturing and evolving on a global scale. It is represented by the growth and maturity of the Shared services to better service the global corporations they support.
-
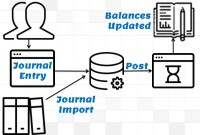
This article explains the process of entering and importing general ledger journals in automated accounting systems. Learn about the basic validations that must happen before the accounting data can be imported from any internal or external sub-system to the general ledger. Finally, understand what we mean by importing in detail or in summary.
-
GL - Journal Posting and Balances
In this tutorial, we will explain what we mean by the posting process and what are the major differences between the posting process in the manual accounting system compared to the automated accounting systems and ERPs. This article also explains how posting also happens in subsidiary ledgers and subsequently that information is again posted to the general ledger.
-
GL - Different Accounting Methods
The accounting method refers to the rules a company follows in reporting revenues and expenses. Understand the two common systems of bookkeeping, single, and double-entry accounting systems. Learners will also understand the two most common accounting methods; cash and accrual methods of accounting and the advantages and disadvantages of using them.
-
The purpose of the general ledger is to sort transaction information into meaningful categories and charts of accounts. The general ledger sorts information from the general journal and converts them into account balances and this process converts data into information, necessary to prepare financial statements. This article explains what a general ledger is and some of its major functionalities.
-
Trial Balance in General Ledger
One of the greatest benefits of using a double-entry accounting system is the capability to generate a trial balance. What do we mean by trial balance? As the name suggests a trial balance is a report that must have its debits equals to credits. Understand the importance of trial balance and why it is balanced. Learn how it is prepared and in which format.
-
An account inquiry is a review of any type of financial account, whether it be a depository account or a credit account. In this tutorial, you learn what we mean by drill through functionality in the context of the general ledger system. We will explain the concept of drill-down and how it enables users to perform account and transaction inquiry at a granular level and the benefits of using this functionality.
-
Although technically a general ledger appears to be fairly simple compared to other processes, in large organizations, the general ledger has to provide many functionalities and it becomes considerably large and complex. Modern business organizations are complex, run multiple products and service lines, leveraging a large number of registered legal entities, and have varied reporting needs.
-
An allocation is a process of shifting overhead costs to cost objects, using a rational basis of allotment. Understand what is the meaning of allocation in the accounting context and how defining mass allocations simplifies the process of allocating overheads to various accounting segments. Explore types of allocations and see some practical examples of mass allocations in real business situations.
-
Introduction to Organizational Structures
Organizations are systems of some interacting components. Levitt (1965) sets out a basic framework for understanding organizations. This framework emphasizes four major internal components such as: task, people, technology, and structure. The task of the organization is its mission, purpose or goal for existence. The people are the human resources of the organization.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved