- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Business Processes
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- Network Organizational Structures
Network Organizational Structures
The newest, and most divergent, team structure is commonly known as a Network Structure (also called "lean" structure) has central, core functions that operate the strategic business. It outsources or subcontracts non-core functions. When an organization needs to control other organizations or agencies whose participation is essential to the success, a network structure is organized.
The newest, and most divergent, team structure is commonly known as a Network Structure (also called "lean" structure) has central, core functions that operate the strategic business. It outsources or subcontracts non-core functions. When an organization needs to control other organizations or agencies whose participation is essential to the success, a network structure is organized. In this, the main organization creates a network of relevant agencies and it influences in different ways.
A network structure has little bureaucracy and features decentralized decision making. This structure is very flexible, and it can adapt to new market challenges almost immediately. Flexibility is one of the main reasons why firms pursue network organizational structure in the first place. This allows them to change its production techniques, quantity, products’ designs or stop the production completely without facing any major problems.
Such an organization works like an advanced computer network where many autonomous organizational units interact with each other and the external world to deliver outcomes. Goals and strategy is set by central management but there involvement is limited to building on the capabilities of network units and monitoring progress. Network structure is widely used in non-business organizations which have sociopolitical objectives.
For instance, the National Industrial Development Corporation assigned with the task of rapid industrial development in the country may resort to a network structure in their objective to build an industrial estate. They will act as the lead agency and involve the various other agencies like Electricity Boards, Municipal Authorities, Land Development Authorities, Authorities for Water & Sewage Control, Department for communication facilities etc. They will also need to establish a network with people who would ultimately be using the industrial estate. It would also use the services of an advertising agency to promote the industrial estate and attract maximum number of entrepreneurs. For the construction of sheds and factories they may have to utilize the services of private construction agencies. Thus, a network structure envisages the utilization of a number of different services offered by different agencies. There is need to coordinate the different inputs and synchronize them towards the ultimate objective.
A network structure is meant to promote communication and the free flow of information between different parts of the organization as needed. Managers coordinate and control relations both internal and external to the firm. A social structure of interactions is fostered to build and manage formal and informal relationships. The goal of this structure is to achieve rapid organizational evolution and adaptation to constantly changing external and internal environments. But there's an almost inevitable loss of control due to its dependence on third parties, and all the potential problems that come from managing outsourced or subcontracted teams.
An organization that has been using network structure is H&M (Hennes & Mauritz), a very popular brand that has followers world over. H&M has outsourced the production and processing of their goods to different countries majorly Asian and South East Asian countries. H&M is the core company in its case. As it can be seen, the core company distributes its functions to different companies which, in this case, are present in different countries: product development company in Australia, Call center company in New Zealand, the Accounting company in Australia, Distribution company in Singapore and Manufacturing company in Malaysia.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
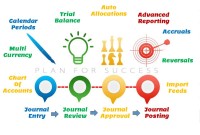
General Ledger - Advanced Features
Modern automated general ledger systems provide detailed and powerful support for financial reporting and budgeting and can report against multiple legal entities from the single system. These systems offer many advanced functionalities right from journal capture to advanced reporting. This article will provide an overview of some advanced features available in today's General Ledgers.
-
Global Business Services (GBS) Model
Global business services (GBS) is an integrated, scalable, and mature version of the shared services model. Global Business Services Model is a result of shared services maturing and evolving on a global scale. It is represented by the growth and maturity of the Shared services to better service the global corporations they support.
-
GL - Accrued / Unbilled Revenue
Accrued revenues (also called accrued assets) are revenues already earned but not yet paid by the customer or posted to the general ledger. Understand what we mean by the terms accrued revenue, accrued assets, and unbilled revenue. Explore the business conditions that require recognition of accrued revenue in the books of accounts and some industries where this practice is prevalent.
-
There are two commonly used methods of accounting - Cash Basis and the Accruals Basis. Understand the difference between accruals and reversals. Recap the earlier discussion we had on accruals and reversals and see the comparison between these two different but related accounting concepts. Understand how the action of accruing results in reversals subsequently in the accounting cycle.
-
Internally, an organization can be structured in many different ways, depending on their objectives. The internal structure of an organization will determine the modes in which it operates and performs. Organizational structure allows the expressed allocation of responsibilities for different functions and processes to different entities such as the branch, department, workgroup and individual.
-
A Company (also called corporation) may be understood as an association of persons in which money is contributed by them, to carry on some business or undertaking. Persons who contribute the money are called the shareholders or the members of the company. A corporation is an artificial being, invisible, intangible and existing only in contemplation of law. Being the mere creature of law, it possesses only those properties which the charter of its creation confers upon it.
-
A joint venture (JV) is a business agreement in which the parties agree to develop, for a finite time, a new entity and new assets by contributing equity. They exercise control over the enterprise and consequently share revenues, expenses and assets. A joint venture takes place when two or more parties come together to take on one project.
-
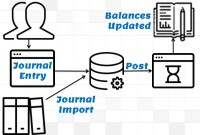
GL - Journal Posting and Balances
In this tutorial, we will explain what we mean by the posting process and what are the major differences between the posting process in the manual accounting system compared to the automated accounting systems and ERPs. This article also explains how posting also happens in subsidiary ledgers and subsequently that information is again posted to the general ledger.
-
Business Metrics for Management Reporting
Business metric is a quantifiable measure of an organization's behavior, activities, and performance used to access the status of the targeted business process. Traditionally many metrics were finance based, inwardly focusing on the performance of the organization. Businesses can use various metrics available to monitor, evaluate, and improve their performance across any of the focus areas like sales, sourcing, IT or operations.
-
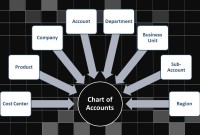
GL - Understanding Chart of Accounts
A chart of accounts (COA) is a list of the accounts used by a business entity to record and categorize financial transactions. COA has transitioned from the legacy accounts, capturing just the natural account, to modern-day multidimensional COA structures capturing all accounting dimensions pertaining to underlying data enabling a granular level of reporting. Learn more about the role of COA in modern accounting systems.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved