- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Business Processes
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- GL - Understanding Chart of Accounts
GL - Understanding Chart of Accounts
A chart of accounts (COA) is a list of the accounts used by a business entity to record and categorize financial transactions. COA has transitioned from the legacy accounts, capturing just the natural account, to modern-day multidimensional COA structures capturing all accounting dimensions pertaining to underlying data enabling a granular level of reporting. Learn more about the role of COA in modern accounting systems.
What is a Chart of Accounts?
A chart of accounts (COA) is a list of the accounts used by a business entity to record and categorize financial transactions. COA is used to organize the finances of the entity and to segregate expenditures, revenue, assets, and liabilities in order to give interested parties a better understanding of the financial health of the entity.
The chart of accounts is a list of all the accounts and their numbers contained in the general ledger. The accounts are listed in the order of assets, liabilities, owner's equity, revenue, and expenses. Transactions can be posted to each defined account in COA and it can capture balances in the general ledger chart of accounts is a way to outline the accounting system of a business, the chart of accounts establishes how the business will operate, what information will be captured, and what information will subsequently be readily retrievable by the system for reporting and other needs.
Is Chart of Accounts worth discussing? Does it really matter?
Have you ever wondered after hearing such phrases from accountants like "It's not in the chart of accounts. We don't know how to enter your transaction" or "We can't process your invoice without an account number." In the case of new general ledger implementations, nothing moves forward unless the chart of account has been finalized.
While to many non-financial managers and also to new IT implementers increased focus on the chart of accounts seems unwarranted and it appears that the client is unnecessarily slowing down the project by discussing chart of accounts too much. That's not really their purpose—and everyone who has worked in an IT project involving general ledger knows that this structure needs to be finalized first before other discussions can start and that too because it has a serious impact on the entire general ledger design.
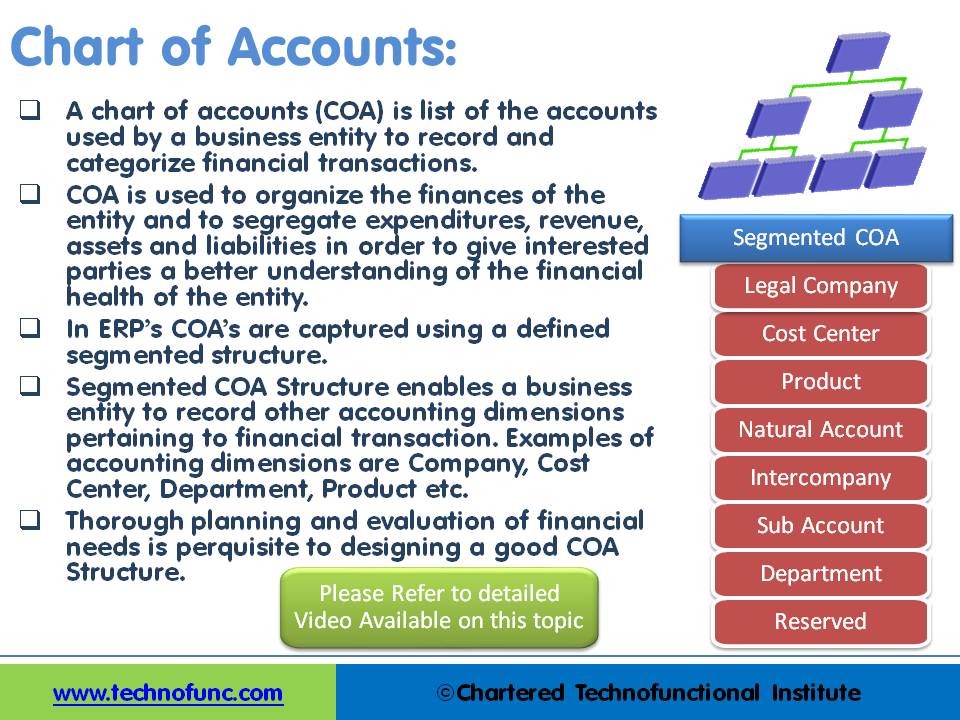
Why we need a Chart of Accounts?
The entire recording process of any accounting system requires a basic organization of data so that the accounting data can be clubbed into meaningful accounts and represented in a way useful for the users and stakeholders. For example – purchases on credit from vendors through invoices can be later summarized and reported with some clarity as to what was purchased, why it was purchased, what organization(s) benefited from those expenditures, and what is the unpaid liability on account of all those purchases. That basic organization is called a chart of accounts.
You might think of the organizing system for your company's accounting data as a collection of buckets, or accounts, each with a particular kind of data inside. There might be a bucket for each ledger account names and associated numbers used by a company, arranged in the order in which they normally appear in financial statements—Assets, Liabilities, Owners' Equity or Stockholders' Equity, Revenue, and Expenses.
For management analysis, there will also be a bucket for each product or service the company sells and one for each type of department or cost center where those expenses might incur as it sells its products or services. The chart of accounts is an organized, comprehensive list of all those buckets. The buckets, in turn, are labeled with their appropriate account number and arranged by the kind of data they hold, so that accountants can quickly find the right bucket in which to store the latest piece of data about a particular accounting transaction. These buckets are then arranged and rearranged during the accounting process and their contents are counted and checked to produce reports that summarize the data they contain.
Purpose of Chart of Accounts:
General Ledger is used to recording and store each individual account and their transactions. The Chart of Accounts is the basis of any accounting system. The purpose of the Chart of Accounts is to classify each financial transaction and record it with reference to appropriate business dimensions enabling the users to select or extract the financial data through account inquiry screens or reports. Finally enabling reporting on (or enquire about) the sum total of financial transactions at various levels on the chart.
Adding more dimensions to the Chart of Accounts:
In ERP’s COA’s are captured using a defined segmented structure. Segmented COA Structure enables a business entity to record other accounting dimensions pertaining to financial transactions.
Modern organizations are complex generally consisting of many different lines of business; operating in different geographies, dealing in multiple products and services, running different projects, and moving resources and employees across these functions. The "chart of accounts” must reflect these complexities to enable effective management and external reporting. An effective chart of accounts structure can track revenue and expenses appropriately for different business dimensions like departments, geographies, product lines, etc. and can provide accurate analysis for decision making, and for reporting to government agencies, sponsors, and stakeholders.
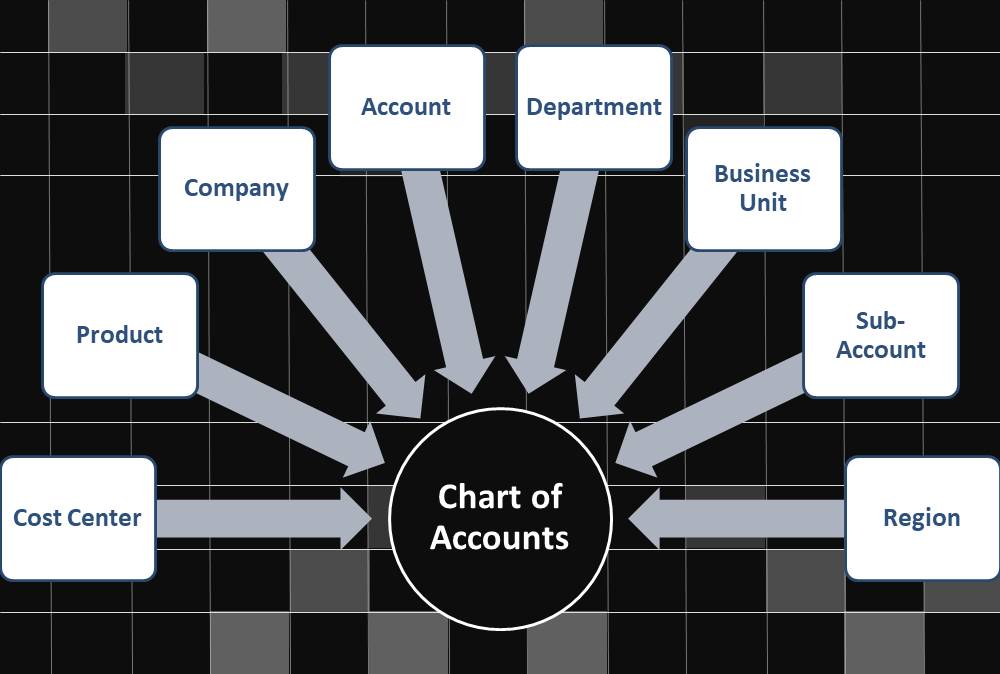
What is Chart of Accounts Segment?
In automated accounting systems and ERPs, the chart of accounts is made up of and represented as a string of numeric and alphanumeric fields that act as identifiers. The companies define different segments to capture relevant business dimensions along with the natural account associated with the transaction. Companies may define anywhere from one to dozen segments to make up their Chart of Accounts and capture granular level business information associated with the transaction.
Examples of accounting dimensions are Company, Cost Center, Department, Product, etc. The figure below shows an example of the Segmented Chart of Accounts Structure using some of the commonly used business dimensions.
Thorough planning and evaluation of financial needs is a prerequisite to designing a good COA Structure. We have created a separate tutorial on GL Accounts that helps you understand the concept of Natural Accounts and some key GL Accounts. There is a full tutorial on the understanding of COA in detail and best practices to define an effective COA Structure.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
The purpose of the general ledger is to sort transaction information into meaningful categories and charts of accounts. The general ledger sorts information from the general journal and converts them into account balances and this process converts data into information, necessary to prepare financial statements. This article explains what a general ledger is and some of its major functionalities.
-
When the quantum of business is expected to be moderate and the entrepreneur desires that the risk involved in the operation be shared, he or she may prefer a partnership. A partnership comes into existence when two or more persons agree to share the profits of a business, which they run together.
-
The sole trader organization (also called proprietorship) is the oldest form of organization and the most common form of organization for small businesses even today. In a proprietorship the enterprise is owned and controlled only by one person. This form is one of the most popular forms because of the advantages it offers. It is the simplest and easiest to form.
-
Hierarchical Organization Structures
Hierarchical structure is typical for larger businesses and organizations. It relies on having different levels of authority with a chain of command connecting multiple management levels within the organization. The decision-making process is typically formal and flows from the top down.
-
In this article, we will explain the general Ledger journal processing flow from entering journals to running the final financial reports. Understand the generic general ledger process flow as it happens in automated ERP systems. The accounting cycle explains the flow of converting raw accounting data to financial information whereas general ledger process flow explains how journals flow in the system.
-
A Company (also called corporation) may be understood as an association of persons in which money is contributed by them, to carry on some business or undertaking. Persons who contribute the money are called the shareholders or the members of the company. A corporation is an artificial being, invisible, intangible and existing only in contemplation of law. Being the mere creature of law, it possesses only those properties which the charter of its creation confers upon it.
-
Multi Currency - Functional & Foriegn
Currency is the generally accepted form of money that is issued by a government and circulated within an economy. Accountants use different terms in the context of currency such as functional currency, accounting currency, foreign currency, and transactional currency. Are they the same or different and why we have so many terms? Read this article to learn currency concepts.
-
Introduction to Legal Entities Concept
Modern business organizations operate globally and leverage a large number of registered legal entities, and operate through complex matrix relationships. To stay competitive in the current global business environment, they must often develop highly diverse and complex organizational structures that cross international borders. Learn more about Legal Entities and their importance for businesses.
-
Network Organizational Structures
The newest, and most divergent, team structure is commonly known as a Network Structure (also called "lean" structure) has central, core functions that operate the strategic business. It outsources or subcontracts non-core functions. When an organization needs to control other organizations or agencies whose participation is essential to the success, a network structure is organized.
-
Trial Balance in General Ledger
One of the greatest benefits of using a double-entry accounting system is the capability to generate a trial balance. What do we mean by trial balance? As the name suggests a trial balance is a report that must have its debits equals to credits. Understand the importance of trial balance and why it is balanced. Learn how it is prepared and in which format.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved