- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Business Processes
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- Introduction to Legal Entities Concept
Introduction to Legal Entities Concept
Modern business organizations operate globally and leverage a large number of registered legal entities, and operate through complex matrix relationships. To stay competitive in the current global business environment, they must often develop highly diverse and complex organizational structures that cross international borders. Learn more about Legal Entities and their importance for businesses.
Legal Forms and Structures
In a rapidly changing national and global business environment, it has become necessary that corporate entities are organized in tune with the emerging economic trends, enable good corporate governance, and enable protection of the interests of the investors and other stakeholders. Further, due to the continuous increase in the complexities of business operation, the forms of corporate organizations are constantly changing.
This section provides an overview of some of the most commonly used legal forms and structures by corporate organizations across the globe along with a brief discussion of related laws, rules, procedures, and regulations that need compliance. How a company structures its long-term operations in a foreign country, effectively defines how it will be taxed hence the choice could have a significant potential effect on the profitability.
Regulations prevalent in most of the countries generally allow foreign entities to choose classification as a corporation (subsidiary), partnership, unincorporated branches; Limited Liability Companies (LLCs), distributor and manufacturer representatives, and joint ventures. Each choice has its own implications and complications. Generally, corporates operate as a separate legal entity with limited liability. Typical business models of foreign corporations conducting business activities in other countries involve wholly-owned Subsidiaries, Joint Ventures, Representative Offices, or Foreign Branches.
What is a Legal Entity?
A legal entity is an artificial person having separate legal standing in the eyes of law. Some of the attributes associated with a legal entity are:
- A legal entity has the legal capacity to enter into agreements or contracts, assume obligations, incur and pay debts, sue and be sued in its own right, and to be held responsible for its actions.
- Legal Entities file the accounts and take care of accounting. Legal Entity is the organizational unit for Financial Accounting for which a completely self-contained set of accounts needs to be drawn up for purposes of external reporting.
- Legal Entity possesses separate existence for tax purposes. Legal Entities pay the taxes and therefore need tax registrations.
- Trade between Legal Entities needs intercompany supported by adequate legal documentation.
- Legal Entities own the money and bank accounts
- Legal Entities comply with whatever needs compliance – The “Legal” in the word “Legal Entity”. This includes recording of all relevant transactions and generating all supporting documents required for financial statements.
- Foreign Branches of such corporations can also assume obligations and have legal obligations to submit financial information to foreign governments.
- Legal entities such as parent companies own or control subsidiaries. A large corporation can own many legal entities as its subsidiaries.
Subsidiaries as Legal Entities:
Subsidiaries are a common feature of business life, and all multinational corporations organize their operations in this way. Examples include holding companies such as Berkshire Hathaway, Time Warner, or Citigroup; as well as more focused companies such as IBM or Xerox. These, and other MNCs, organize their businesses into national and functional subsidiaries, often with multiple levels of subsidiaries.
A subsidiary is a company that is completely or partly owned by another corporation that owns more than half of the subsidiary's stock, and which normally acts as a holding corporation which at least partly or wholly controls the activities and policies of the daughter corporation. The controlling entity is called its parent company, parent, or holding company.
A subsidiary may itself have subsidiaries, and these, in turn, may have subsidiaries of their own. A parent and all its subsidiaries together are called a "group", although this term can also apply to cooperate companies and their subsidiaries with varying degrees of shared ownership.
Subsidiaries are separate, distinct legal entities for the purposes of taxation, regulation, and liability. For this reason, they differ from divisions, which are businesses fully integrated within the main company, and not legally or otherwise distinct from it.
For the purposes of liability, taxation, and regulation, subsidiaries are distinct legal entities. A subsidiary can sue and be sued separately from its parent and its obligations will not normally be the obligations of its parent. If a parent company owns a foreign subsidiary, the company under which the subsidiary is incorporated must follow the laws of the country where the subsidiary operates, and the parent company still carries the foreign subsidiary's financials on its books (consolidated financial statements).
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Period End Accruals, Receipt Accruals, Paid Time-Off Accruals, AP Accruals, Revenue Based Cost Accruals, Perpetual Accruals, Inventory Accruals, Accruals Write Off, PO Receipt Accrual, Cost Accrual, etc. are some of the most complex and generally misconstrued terms in the context of general ledger accounting. In this article, we will explore what is the concept of accrual and how it impacts general ledger accounting.
-
Shared Services is the centralization of service offering at one part of an organization or group sharing funding and resourcing. The providing department effectively becomes an internal service provider. The key is the idea of 'sharing' within an organization or group.
-
A Company (also called corporation) may be understood as an association of persons in which money is contributed by them, to carry on some business or undertaking. Persons who contribute the money are called the shareholders or the members of the company. A corporation is an artificial being, invisible, intangible and existing only in contemplation of law. Being the mere creature of law, it possesses only those properties which the charter of its creation confers upon it.
-
General Ledger - Advanced Features
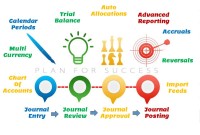
Modern automated general ledger systems provide detailed and powerful support for financial reporting and budgeting and can report against multiple legal entities from the single system. These systems offer many advanced functionalities right from journal capture to advanced reporting. This article will provide an overview of some advanced features available in today's General Ledgers.
-
In this article we will focus on and understand the accounting process which enables the accounting system to provide the necessary information to business stakeholders. We will deep dive into each of the steps of accounting and will understand how to identify accounting transactions and the process for recording accounting information and transactions.
-
Global Business Services (GBS) Model
Global business services (GBS) is an integrated, scalable, and mature version of the shared services model. Global Business Services Model is a result of shared services maturing and evolving on a global scale. It is represented by the growth and maturity of the Shared services to better service the global corporations they support.
-
In most of the automated financial systems, you can define more than 12 accounting periods in a financial year. This article will explain the concept of the adjustment period and the benefits of having adjustment periods. Adjustment periods have their inherent challenges for the users of financial statements and there is a workaround for those who don’t want to use adjustment periods.
-
Legal Structures in Businesses
Businesses not only vary in size and industry but also in their ownership. Most businesses evolve from being owned by just one person to a small group of people and eventually being managed by a large numbers of shareholders. Different ownership structures overlap with different legal forms that a business can take. A business’s legal and ownership structure determines many of its legal responsibilities.
-
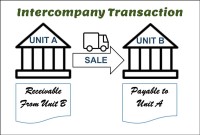
After reading this article the learner should be able to understand the meaning of intercompany and different types of intercompany transactions that can occur. Understand why intercompany transactions are addressed when preparing consolidated financial statements, differentiate between upstream and downstream intercompany transactions, and understand the concept of intercompany reconciliations.
-
In this article, we will describe how to determine if an account needs adjustment entries due to the application of the matching concept. Learners will get a thorough understanding of the adjustment process and the nature of the adjustment entries. We will discuss the four types of adjustments resulting from unearned revenue, prepaid expenses, accrued expenses, and accrued revenue.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved