- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Leadership
- Change Management
- Administrative Theory by Fayol
Administrative Theory by Fayol
The administrative theory of management is focused on principles that could be used by managers to coordinate the internal activities of organizations. The most prominent of the administrative theorists was Henri Fayol. Fayol observed a work stoppage and judged it to be a management failure. He believed that organizational managerial practices are important for driving predictability and efficiency in organizations.
Fayol’s Administrative Management Theory
The administrative theory of management is focused on principles that could be used by managers to coordinate the internal activities of organizations. The most prominent of the administrative theorists was Henri Fayol. Fayol observed a work stoppage and judged it to be a management failure. He believed that organizational managerial practices are important for driving predictability and efficiency in organizations.
While the proponents of scientific management developed principles that could help the individual workers perform their tasks more efficiently, the administrative theory focused on principles that could be used by managers to coordinate the internal activities of organizations. The most prominent of the administrative theorists was Henri Fayol.
Henri Fayol (1849-1925), was a French industrialist and a prominent European management theorist. Henri Fayol is known as the Father of Management and he developed a general theory of management and also, laid down the 14 principles of Management. Fayol was unknown to American managers and scholars until his most important work, "General and industrial management", was translated into English in 1949. These 14 principles of management are used to manage an organization and are beneficial for prediction, planning, decision-making, organization and process management, control, and coordination.

Administrative Management
Many of the managerial concepts that make the foundation of modern management thought were first articulated by Fayol. Fayol believed that with scientific forecasting and proper methods of management, satisfactory predictable results were sure to follow. The theory falls under the Administrative Management school of thought (as opposed to the Scientific Management School led by Fredrick Taylor).
According to Fayol, the business operations of an organization could be divided into six broad activities.
- Technical: Producing and manufacturing products
- Commercial: Buying, selling and exchange
- Financial: Search for optimal use of capital
- Security: Protecting employees and property
- Accounting: Recording and taking stock of costs, profits, liabilities, maintaining balance sheets and compiling statistics
- Managerial: Planning, organizing, commanding, coordinating and controlling
Fayol’s Five Elements of Management
Fayol studies primarily focused on the last activity which is “Managerial Activity”. He identified five major elements of management that depict the expected behaviors that managers should engage in to achieve the business objectives of the organization effectively. The five elements of management are:
- Planning
- Organizing
- Commanding
- Coordinating
- Controlling
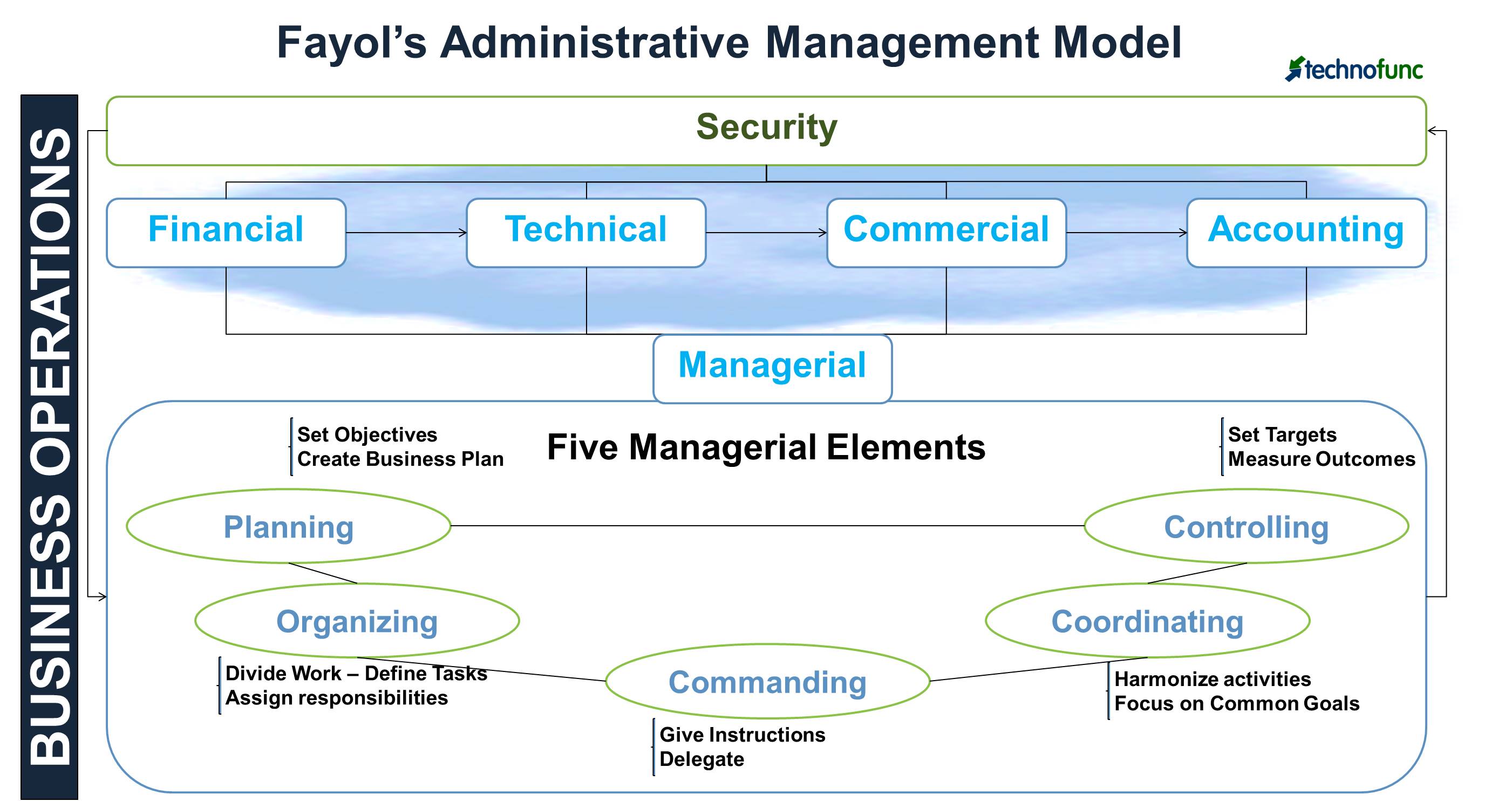
Let us briefly discuss these five elements of management as described by Fayol and relevant for modern enterprises and managers even today.
1. Planning:
Planning is the most important managerial function. It is a future-oriented exercise to creating a business plan, determining the different stages to execute and track the plan and define the technology and resources necessary to implement the plan. Planning is all about identifying in advance what needs to be done, how it will be done, and what are the timelines and responsibilities for execution. It lays down the roadmap of the current organizational state to where the organization wants to be. The outcome of the planning function is logical goals and their timelines. Managers should engage in both short-range and long-range planning.
2. Organizing:
Once a plan of action is designed, managers have the visibility of what is expected and by when. To achieve these milestones, they need to solve for resources and assign them appropriate tasks. They need to focus on providing everything necessary to carry out the plan; including raw materials, machinery and tools, capital, funds, and human resources. They must identify and establish responsibilities for each of the departments or divisions, and specifying organizational relationships.
3. Command:
Managers need to implement the plan by efficiently utilizing the allocated resources. They must understand the strengths/weaknesses of their workforce and the limitations of the resources at hand. Managers must lead and motivate employees to achieve the goals of the organization. Employees may require the proper allocation of resources and an effective support system and supervision. Directing requires exceptional interpersonal skills and the ability to motivate and inspire people while balancing the staff and production needs.
4. Coordination:
Organizations are interdependent systems and need coordination among different departments to stay in sync and targeted on the plan. Manager’s biggest responsibility is to "harmonize" all required activities across different functions to facilitate and ensure organizational success as per the agreed plan. Managers need good Communication Skills to ensure that the coordinating mechanism is working effectively. Managers are needed to synchronize the elements of the organization and must take into account the delegation of authority and responsibility and span of control within units.
5. Control:
The final element of management as described by Fayol involves the comparison of the activities of the personnel to the plan of action. It is the control and evaluation component of management. Control function ensures that tasks have been completed with required quality in all areas and helps to detect deviations if any from the organization's plan. This ensures quality performance with regard to business objectives and satisfactory results while maintaining an orderly and problem-free environment. Controlling includes information management, measurement of performance, and the institution of corrective actions.
Relevance in the modern workplace
Fayol believed that managerial practices were the key component to predictability and efficiency in organizations. Fayol’s five management functions are clearly similar to modern management functions - planning, organizing, staffing, and controlling. Fayol's concept of management forms the cornerstone of contemporary management theory. Many of Fayol's practices are still alive in today's workplace. These elements can be found in modern organizations in several ways: as for accepted practices in some industries, as revamped versions of the original principles or elements, or as remnants of the organization's history to which alternative practices and philosophies are being offered. The new manager in the digital age must acquire the latest leadership skills and management skills to succeed in today’s competitive world.
Suggested Reading and Resources
Related Links
Creation Date Sunday, 23 August 2020
Hits 107492
You May Also Like
-
Functional leadership theory addresses specific leader behaviors that are expected to contribute most to the organizational effectiveness by focusing on how the leadership process occurs. The leader should ensure that all needs of the group get addressed.
-
Process & Stages of Creativity
Creative ideas do not come just like that. There is a process to it. There are a number of techniques of creativity to support the generation of ideas but the widely practiced ones are brainstorming and lateral thinking. Most innovations are not so much the product of sudden insights as they are the result of a conscious process that often goes through multiple stages. The creative process can be divided into four stages of preparation, incubation, evaluation, and implementation.
-
In this study of power, Raven identified five bases of power as coercive, reward, legitimate, referent, and expert. The 5 Types of Power can help you decide when it is appropriate to use a particular type of power in important situations. Leadership involves authority and it is very important for leaders to understand what type of power they're using.
-
Early studies on leadership were done at Ohio State University using the Leader Behavior Description Questionnaire to identify the leader's observable behaviors. Ohio State study on leadership found two behavioral characteristics of leadership - people-oriented (consideration) and task-oriented (initiating structure) leadership style.
-
The Path-Goal theory defines the characteristics of followers and organizational context and the corresponding leadership style best suited to these factors. A leader should adapt to a behavior that is most relevant for a given employee and work environment mix to achieve a goal. The application of theory drives increased employees' motivation, empowerment, and satisfaction resulting in increased productivity.
-
The two-factor theory also known as Herzberg's motivation-hygiene theory and dual-factor theory. This motivator-hygiene theory states that certain factors cause job satisfaction whereas certain separate factors cause dissatisfaction in the workplace. An organization can adjust these factors to influence motivation. These factors are respectively termed as motivators and hygiene factors.
-
Maslow's hierarchy of needs is a motivational theory that explains that people are motivated by five basic categories of human needs. These needs are physiological, safety, love and belonging, esteem, and self-actualization. There is a little scientific basis for this concept of a hierarchy of needs.
-
The great man theory of leadership is a 19th-century idea that states a person is either a natural-born leader or not. Some people are born with the necessary leadership attributes that help them create a great impact on society, politics, or the military. The theory focuses on identifying the innate qualities and characteristics possessed by great men.
-
Normative leadership theories are built on moral principles and tell leaders how they ought to act. Victor Vroom formulated the normative model of leadership that specifically address leader behavior explicitly built on moral principles or norms. Normative leadership theories tell leaders how they should act to raise the moral performance inside the working group and manage their different responsibilities.
-
In emergent leadership, the leader is not appointed or elected to the leadership role but emerges as the leader as he is perceived by others over time as a result of the group's interaction. A person steps up as the leader over time by taking on tasks voluntarily, helping others complete their tasks better, and building consensus among groups.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved











"Everyone needs some concepts of management; in the home, in affairs of state, the need for managerial ability is in keeping with the importance of the undertaking, and for individual people, the need is everywhere in greater accordance with the position occupied".