- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Leadership
- Creativity Tools
- Collaborative Leadership
Collaborative Leadership
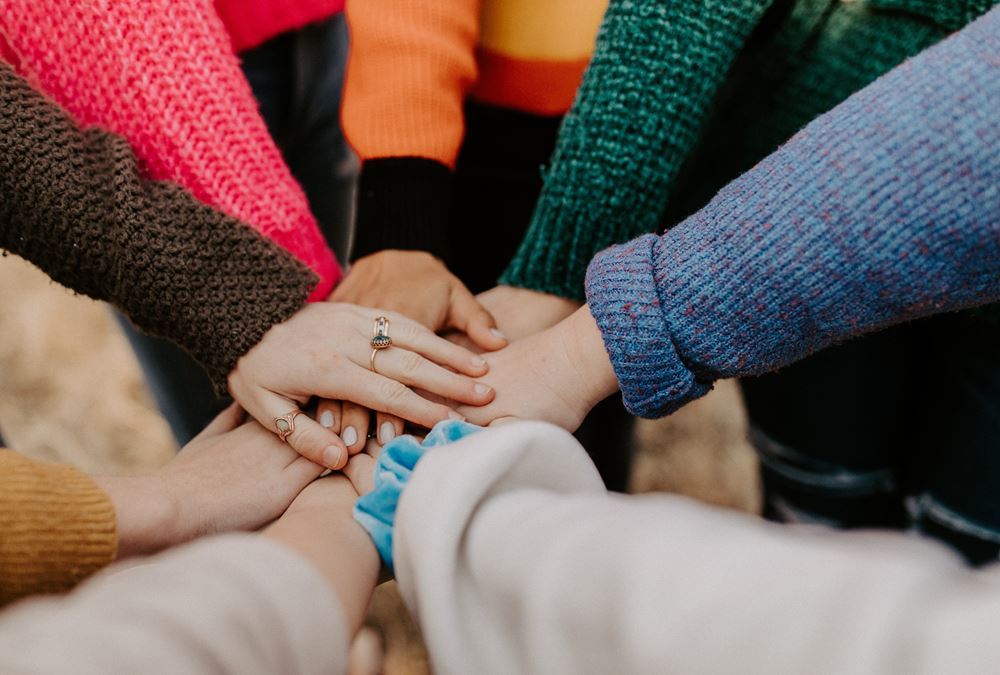
Collaborative leadership is all about collaborative problem-solving and decision-making or can also be defined as the leadership of a collaborative effort. . The term started to appear in the mid-1990s in response to the formation of long term public-private partnerships to rebuild public infrastructure. Learn how you can use principles of collaborative leadership to enhance your leadership skills for being an effective leader.
What is Collaborative Leadership?
There could be two ways to define collaborative leadership, first, it could be the leadership of a collaborative effort and second, it could be leadership as a collaborative effort. The term Collaborative Leadership describes an emerging body of theory and management practice which is focused on the leadership skills and attributes needed to deliver results across organizational boundaries. Collaboration is a purposeful relationship in which all parties strategically choose to cooperate in order to accomplish a shared outcome. A collaborative leader is the one who has the ability to take responsibility for a heterogeneous team to accomplish a shared need/purpose. Collaboration requires managers to achieve success through people and resources outside their control.
Some common themes that appear from these definitions are listed below:
1. There exists a common purpose or shared need
2. Successful outcome of the shared need depends on contributions from the heterogeneous team, more or less in the nature of voluntary contributions
3. Everyone is on an equal footing and enjoys the same rights and responsibilities
4. All need to work together to solve a problem, create something new, or run an organization or initiative; different talents or abilities are called for success
5. The leader is not the formal leader, does not have absolute control of the group, but has assumed the responsibility for guiding and coordinating the process by which the group decides upon and carries out actions to accomplish its goals
6. Leadership is permanently shared by all or several, members of the group. Group guides itself
Characteristics of Collaborative Leaders:
1. Willingness to take risks, finds the personal motive for collaborating
2. Eager listeners and likes building relationships
3. Passion for the cause; have long term vision
4. Optimistic about the future
5. Able to share knowledge, power, and credit
6. Effective Communicators; ability to simplify complex situations for the group
7. Ability to handle group conflict
8. Ability to motivate, inject energy, passion, and drive into the team
Situations where Effective:
1. Public-Private Partnerships
2. Global Supply Chains
3. Civic collaboration to solve complex community problems
4. On-line collaboration – Linux, Wikipedia, etc.
5. Political collaboration to tackle global issues such as the credit crunch, climate change, and terrorism
6. Situations where problems are serious and complex
7. Situations when there are a number of diverse stakeholders
8. Situations when stakeholders have varied interests
9. Situations when an issue affects a whole organization or a whole community
Leadership Tasks for Collaborative Leader:
1. Inspiring commitment and action
2. Proving guidance and helps people develop the vision and passion
3. Facilitator and a great problem solver
4. Inclusiveness/building broad-based involvement
5. Motivation and participation
6. Fostering close relationships among staff members
7. Restating arguments, ideas, or issues so that everyone's clear on them
8. Ensuring all voices are heard
9. Keeping the focus on what's best for the group
10. Helping the group to identify and obtain the necessary resources to do the work
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Leadership has been defined in different ways by different sets of scholars. In very simple terms leadership can be defined as the skill of a person to influence an individual or a group for achievement of a goal in a given situation. One can use different dimensions and perspectives to define leadership. Through the evolution of leadership thought, leadership has been defined in various ways discussed here.
-
Narrative leadership is interpreted as the leader who aspires to construct leadership by telling stories. Leadership is a task of persuasion, of winning people’s minds and hearts. Storytelling is thus inherently suited for the task of leadership. Learn about the narrative leadership style and how to use this style to inspire and motivate followers or to manage change.
-
Frederick Winslow Taylor started the “Scientific Management Movement”, and attempted to study the work process scientifically. Scientific management, also called Taylorism, was a theory of management that analyzed and synthesized workflows. It is a system for increasing the efficiency of manpower to its maximum potential and streamlining production to improve efficiency. This article explores this theory in more detail.
-
A good leadership style is something that every effective leader must have in order to succeed, but identifying what that entails or does not entails might be difficult to understand. Most of the research on leadership focuses on the exemplary, best practices, and positive attributes of effective and successful leaders. This article talks about a new approach to learn leadership using lessons from bad leadership. That is the lessons to be learned by examining leaders who have not effectively exercised their power, authority, or influence.
-
We define Lean as the systematic elimination of waste through a continual effort to decrease inefficiency; the lean leader strives to create a more efficient organization. Lean leadership is a philosophy. It is a consistent way of thinking and being in your role as a leader. The focus of this approach is on raising new leaders and help their team embrace a culture of continuous improvement. Learn what we mean by lean leadership style and its principles.
-
Laissez-faire is a style of leadership that affords the group members a great deal of independence. Tasks are delegated to the group members and they are responsible to see the project through to fruition. Research has shown that this style of leadership leads to the lowest levels of productivity. This article explains this style and covers the implications of having a hands-off approach and the situations where this style could be effective.
-
Have you ever resonated that there seem to be as many different ways to lead people as there have been great leaders? When we recall the success of Mahatma Gandhi, Nelson Mandela, Abraham Lincoln, Napoleon Bonaparte to Steve Jobs and Jack Welch, we also notice that they all used different approaches that were suitable to their specific situations and circumstances. Over the last century, researchers and psychologists have developed simple ways to describe the “Styles of leadership” and in this section, we will explore these commonly known leadership styles.
-
Emergent leadership occurs when a group member is not appointed or elected as leader, but rather that person steps up as the leader over time within-group interactions. Have you ever faced challenges in getting accepted into your new role of position as a leader? Groups don't automatically accept a new "boss" as a leader. Emergent leadership is what you must do when taking over a new group. Learn more about emergent leadership.
-
Power is the ability to exercise influence or control over others. Leadership involves authority and it is very important for leaders to understand what type of power they're using. The 5 Types of Power in Leadership are Coercive power, expert power, legitimate power, referent power, and reward power. Authority is the right to command and extract obedience from others. It comes from the organization and it allows the leader to use power.
-
There are four major factors in leadership called Leader, Follower, Communication, and Situation. The success of the leader is dependent on how the leader is effectively able to communicate and motivate followers to perform desired tasks using the appropriate leadership style best suited for the given situation. Interdependencies and dynamics of these four factors of leadership must be considered by a leader to be effective.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved