- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Leadership Skills
- Leadership Theories
- Five-Factor Personality Model
Five-Factor Personality Model
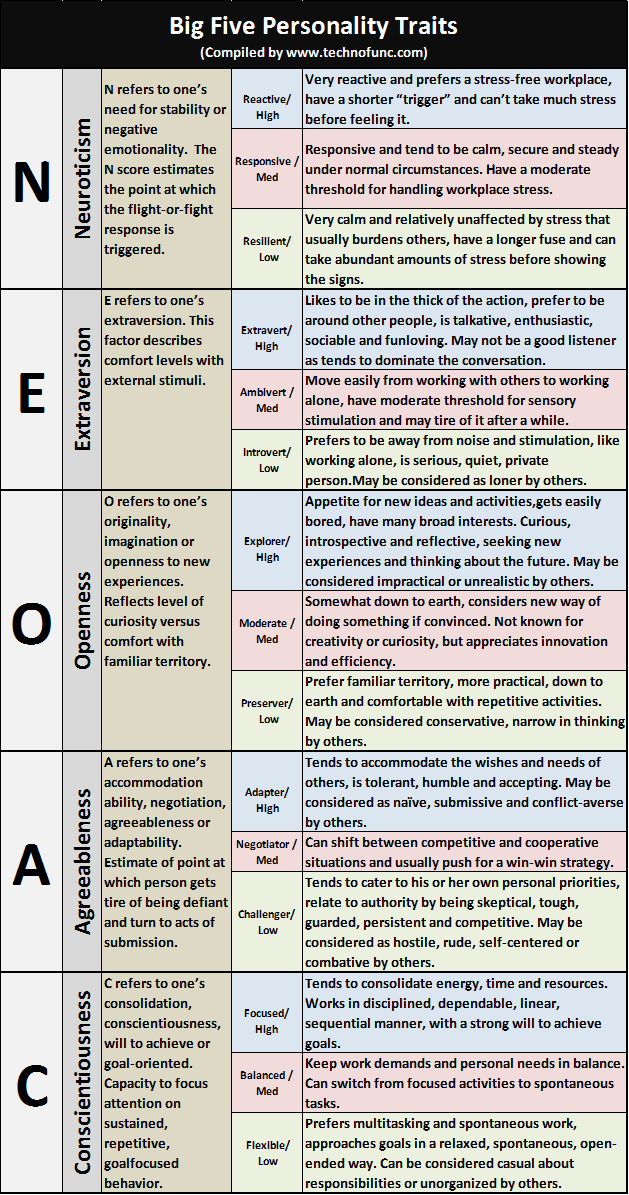
Five Factors Model (FFM) also known as Five-Factor Personality Model is based on five broad personality traits which are extraversion, neuroticism, openness to experience, agreeableness, and conscientiousness represented by acronym OCEAN, these traits are often referred to as the “Big Five”.
What are Big Five Personality Traits:
Over the past 25 years, a consensus has emerged among researchers regarding the basic factors that make up what we call personality. Psychologists now believe that of all the various methods for classifying personality dimensions, only one stands out as the most statistically robust: the Big Five. These factors, commonly called the Big Five, are neuroticism, extraversion, openness, agreeableness and conscientiousness.
N = Neuroticism = Need for stability, negative emotionality
E = Extraversion = Positive emotionality, sociability
O = Openness = Originality, imagination
A = Agreeableness = Accommodation, adaptability
C = Conscientiousness = Consolidation, will to achieve, goal-oriented
Table below provides the description, attributes and explanations for each of the factors listed above. These five personality factors are the most reliable for differentiating personality traits. The Big Five synonym clusters appear to account for most differences among individual personalities, describing five universal dimensions. We score a high, low or mid-range rating in each dimension and interpretations of the scores is given below:
|
Big Five Personality Traits |
||||
|
N |
Neuroticism |
N refers to one’s need for stability or negative emotionality. The N score estimates the point at which the flight-or-fight response is triggered. |
|
Very reactive and prefers a stress-free workplace, have a shorter “trigger” and can’t take much stress before feeling it. |
|
Responsive / |
Responsive and tend to be calm, secure and steady under normal circumstances. Have a moderate threshold for handling workplace stress. |
|||
|
Resilient/ |
Very calm and relatively unaffected by stress that usually burdens others, have a longer fuse and can take abundant amounts of stress before showing the signs. |
|||
|
E |
Extraversion |
E refers to one’s extraversion. This factor describes comfort levels with external stimuli. |
|
Likes to be in the thick of the action, prefer to be around other people, is talkative, enthusiastic, sociable and funloving. May not be a good listener as tends to dominate the conversation. |
|
Ambivert / |
Move easily from working with others to working alone, have moderate threshold for sensory stimulation and may tire of it after a while. |
|||
|
Introvert/ |
Prefers to be away from noise and stimulation, like working alone, is serious, quiet, private person.May be considered as loner by others. |
|||
|
O |
Openness |
O refers to one’s originality, imagination or openness to new experiences. Reflects level of curiosity versus comfort with familiar territory. |
|
Appetite for new ideas and activities,gets easily bored, have many broad interests. Curious, introspective and reflective, seeking new experiences and thinking about the future. May be considered impractical or unrealistic by others. |
|
Moderate / |
Somewhat down to earth, considers new way of doing something if convinced. Not known for creativity or curiosity, but appreciates innovation and efficiency. |
|||
|
Preserver/ |
Prefer familiar territory, more practical, down to earth and comfortable with repetitive activities. May be considered conservative, narrow in thinking by others. |
|||
|
A |
Agreeableness |
A refers to one’s accommodation ability, negotiation, agreeableness or adaptability. Estimate of point at which person gets tire of being defiant and turn to acts of submission. |
|
Tends to accommodate the wishes and needs of others, is tolerant, humble and accepting. May be considered as naïve, submissive and conflict-averse by others. |
|
Negotiator / |
Can shift between competitive and cooperative situations and usually push for a win-win strategy. |
|||
|
Challenger/ |
Tends to cater to his or her own personal priorities, relate to authority by being skeptical, tough, guarded, persistent and competitive. May be considered as hostile, rude, self-centered or combative by others. |
|||
|
C |
Conscientiousness |
C refers to one’s consolidation, conscientiousness, will to achieve or goal-oriented. Capacity to focus attention on sustained, repetitive, goalfocused behavior. |
|
Tends to consolidate energy, time and resources. Works in disciplined, dependable, linear, sequential manner, with a strong will to achieve goals. |
|
Balanced / |
Keep work demands and personal needs in balance. Can switch from focused activities to spontaneous tasks. |
|||
|
Flexible/ |
Prefers multitasking and spontaneous work, approaches goals in a relaxed, spontaneous, open-ended way. Can be considered casual about responsibilities or unorganized by others. |
|||
Study to Examine Big Five Personality Dimensions:
To assess the links between the Big Five and leadership, Judge, Bono, Ilies, and Gerhardt (2002) conducted a major meta-analysis of 78 leadership and personality studies and found a strong relationship between the Big Five traits and leadership.
This model of leadership was result of a study to examine the relationship between the “Big Five” personality dimensions (neuroticism, conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness, and openness) with respect to career success. A sample of few hundred employees was surveyed in a diverse set of occupations and organizations. Hierarchical regression analysis was used to examine the incremental variance contributed by the five personality traits after controlling for several career-related variables.
Results showed that, extraversion was related positively to salary level, promotions, and career satisfaction and that neuroticism was related negatively to career satisfaction. Agreeableness was related negatively only to career satisfaction and openness was related negatively to salary level. It was confirmed as expected that having certain personality traits is associated with being an effective leader.
Is the Big Five personality assessment valid?
Researchers have pointed to reliability studies that are consistent enough to approach the status of law and for the corporate world; this model provides a reliable, standard vocabulary with which to discuss personality differences. Although the Big Five model gives us a uniform language based on standard definitions, but the fact remains that a combination of forces shape an individual. The Five Factors can be thought as being the main infrastructure as human individuality is too complex for any one system to explain adequately.
This personality assessment can be practically applied to identify the needs of a specific role prior to selecting or appointing a leader and performing a match of factors to determine success of the individual in the role.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
There are four characteristics of leadership that help us to understand the character of leadership as a concept. 1. Leadership is a process, 2. Leadership involves influence, 3. Leadership always occurs in a group context and 4. Leadership involves goal attainment. These are the four components that make up the character of the 'leadership' term and help us to define the leadership concept. All of these components of leadership have common characteristics.
-
Communication has as its central objective the transmission of meaning. The process of communication is successful only when the receiver understands an idea as the sender intended it. How does a message or an idea travel from one person to another? To transmit our message, we engage in a sensitive and complex process of communication, with different elements like sender, message, channels, receiver, noise, and feedback.
-
Normative leadership theories are built on moral principles and tell leaders how they ought to act. Victor Vroom formulated the normative model of leadership that specifically address leader behavior explicitly built on moral principles or norms. Normative leadership theories tell leaders how they should act to raise the moral performance inside the working group and manage their different responsibilities.
-
Theory Z also called the "Japanese Management" style is a leadership theory of human motivation focused on organizational behavior, communication, and development. It assumes that employees want to enter into long term partnerships with their employers and peers. Offering stable jobs with an associated focus on the well-being of employees results in increased employee loyalty to the company.
-
Attribution Theory of Leadership
The attribution theory of leadership deals with the formation of individual opinions about the reasons for particular events or observations. People will always try to understand why people do what they do. The leader will make a judgment about his employees based on his attribution of the causes of the employees' performance. Individuals will also make inferences about the leader and react to poor performance by the leader.
-
Symbolic Interaction and Social Change
George Herbert Mead, an American philosopher, affiliated with the University of Chicago founded the theory of symbolic interactionism. A major aspect of this is that people interact by symbols both verbal and non-verbal signals and every interaction makes a contribution to the mental make-up of the mind thus every interaction with someone, changes you and you go away a different person signifying that humans and change go together.
-
Certain generally accepted truths or principles of communication are important to consider when communicating with others. These principles hold true for all people in every culture. By understanding these principles, you will experience greater communication effectiveness. An effective communication system is one that achieved its objectives. Communication is effective where there are no barriers to communication.
-
Idiosyncrasy Credit Model of Leadership builds upon the awareness that when the emergent leader meets the team's expectations, idiosyncrasy credits are awarded. These credits depend on how the leader fulfilled follower's expectations and what is the impact of the leader's decisions on the follower. When the balance of credits shifts, another leader will emerge.
-
The two-factor theory also known as Herzberg's motivation-hygiene theory and dual-factor theory. This motivator-hygiene theory states that certain factors cause job satisfaction whereas certain separate factors cause dissatisfaction in the workplace. An organization can adjust these factors to influence motivation. These factors are respectively termed as motivators and hygiene factors.
-
Early studies on leadership were done at Ohio State University using the Leader Behavior Description Questionnaire to identify the leader's observable behaviors. Ohio State study on leadership found two behavioral characteristics of leadership - people-oriented (consideration) and task-oriented (initiating structure) leadership style.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved










