- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Leadership Skills
- Leadership Theories
- Five-Factor Personality Model
Five-Factor Personality Model
Five Factors Model (FFM) also known as Five-Factor Personality Model is based on five broad personality traits which are extraversion, neuroticism, openness to experience, agreeableness, and conscientiousness represented by acronym OCEAN, these traits are often referred to as the “Big Five”.
What are Big Five Personality Traits:
Over the past 25 years, a consensus has emerged among researchers regarding the basic factors that make up what we call personality. Psychologists now believe that of all the various methods for classifying personality dimensions, only one stands out as the most statistically robust: the Big Five. These factors, commonly called the Big Five, are neuroticism, extraversion, openness, agreeableness and conscientiousness.
N = Neuroticism = Need for stability, negative emotionality
E = Extraversion = Positive emotionality, sociability
O = Openness = Originality, imagination
A = Agreeableness = Accommodation, adaptability
C = Conscientiousness = Consolidation, will to achieve, goal-oriented
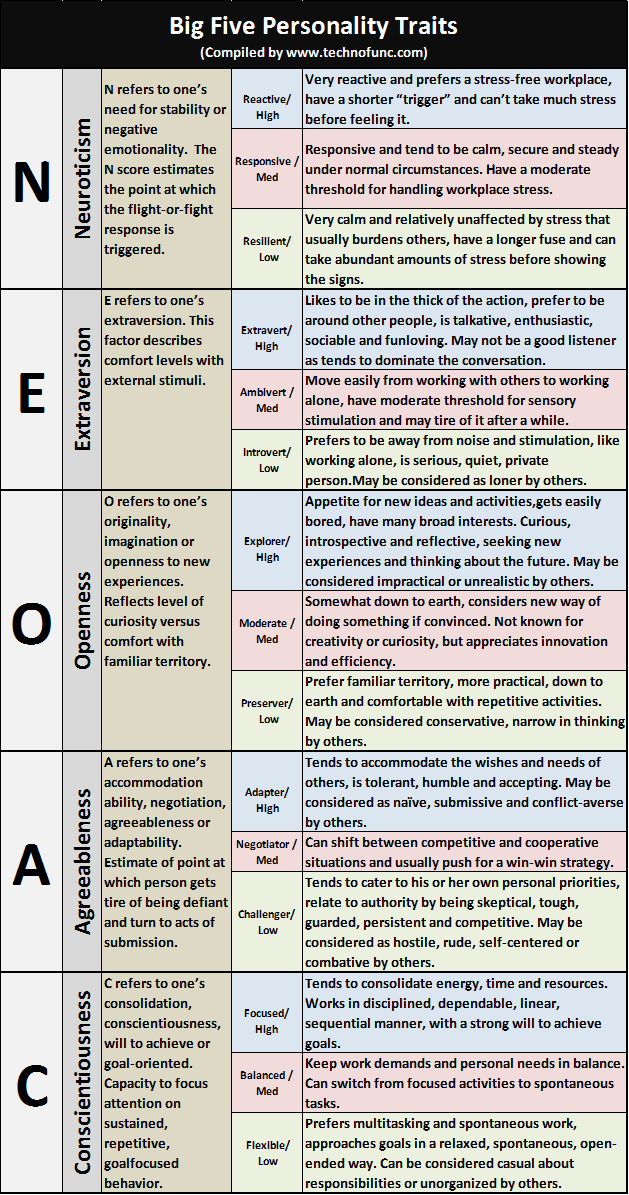
Table below provides the description, attributes and explanations for each of the factors listed above. These five personality factors are the most reliable for differentiating personality traits. The Big Five synonym clusters appear to account for most differences among individual personalities, describing five universal dimensions. We score a high, low or mid-range rating in each dimension and interpretations of the scores is given below:
|
Big Five Personality Traits |
||||
|
N |
Neuroticism |
N refers to one’s need for stability or negative emotionality. The N score estimates the point at which the flight-or-fight response is triggered. |
|
Very reactive and prefers a stress-free workplace, have a shorter “trigger” and can’t take much stress before feeling it. |
|
Responsive / |
Responsive and tend to be calm, secure and steady under normal circumstances. Have a moderate threshold for handling workplace stress. |
|||
|
Resilient/ |
Very calm and relatively unaffected by stress that usually burdens others, have a longer fuse and can take abundant amounts of stress before showing the signs. |
|||
|
E |
Extraversion |
E refers to one’s extraversion. This factor describes comfort levels with external stimuli. |
|
Likes to be in the thick of the action, prefer to be around other people, is talkative, enthusiastic, sociable and funloving. May not be a good listener as tends to dominate the conversation. |
|
Ambivert / |
Move easily from working with others to working alone, have moderate threshold for sensory stimulation and may tire of it after a while. |
|||
|
Introvert/ |
Prefers to be away from noise and stimulation, like working alone, is serious, quiet, private person.May be considered as loner by others. |
|||
|
O |
Openness |
O refers to one’s originality, imagination or openness to new experiences. Reflects level of curiosity versus comfort with familiar territory. |
|
Appetite for new ideas and activities,gets easily bored, have many broad interests. Curious, introspective and reflective, seeking new experiences and thinking about the future. May be considered impractical or unrealistic by others. |
|
Moderate / |
Somewhat down to earth, considers new way of doing something if convinced. Not known for creativity or curiosity, but appreciates innovation and efficiency. |
|||
|
Preserver/ |
Prefer familiar territory, more practical, down to earth and comfortable with repetitive activities. May be considered conservative, narrow in thinking by others. |
|||
|
A |
Agreeableness |
A refers to one’s accommodation ability, negotiation, agreeableness or adaptability. Estimate of point at which person gets tire of being defiant and turn to acts of submission. |
|
Tends to accommodate the wishes and needs of others, is tolerant, humble and accepting. May be considered as naïve, submissive and conflict-averse by others. |
|
Negotiator / |
Can shift between competitive and cooperative situations and usually push for a win-win strategy. |
|||
|
Challenger/ |
Tends to cater to his or her own personal priorities, relate to authority by being skeptical, tough, guarded, persistent and competitive. May be considered as hostile, rude, self-centered or combative by others. |
|||
|
C |
Conscientiousness |
C refers to one’s consolidation, conscientiousness, will to achieve or goal-oriented. Capacity to focus attention on sustained, repetitive, goalfocused behavior. |
|
Tends to consolidate energy, time and resources. Works in disciplined, dependable, linear, sequential manner, with a strong will to achieve goals. |
|
Balanced / |
Keep work demands and personal needs in balance. Can switch from focused activities to spontaneous tasks. |
|||
|
Flexible/ |
Prefers multitasking and spontaneous work, approaches goals in a relaxed, spontaneous, open-ended way. Can be considered casual about responsibilities or unorganized by others. |
|||
Study to Examine Big Five Personality Dimensions:
To assess the links between the Big Five and leadership, Judge, Bono, Ilies, and Gerhardt (2002) conducted a major meta-analysis of 78 leadership and personality studies and found a strong relationship between the Big Five traits and leadership.
This model of leadership was result of a study to examine the relationship between the “Big Five” personality dimensions (neuroticism, conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness, and openness) with respect to career success. A sample of few hundred employees was surveyed in a diverse set of occupations and organizations. Hierarchical regression analysis was used to examine the incremental variance contributed by the five personality traits after controlling for several career-related variables.
Results showed that, extraversion was related positively to salary level, promotions, and career satisfaction and that neuroticism was related negatively to career satisfaction. Agreeableness was related negatively only to career satisfaction and openness was related negatively to salary level. It was confirmed as expected that having certain personality traits is associated with being an effective leader.
Is the Big Five personality assessment valid?
Researchers have pointed to reliability studies that are consistent enough to approach the status of law and for the corporate world; this model provides a reliable, standard vocabulary with which to discuss personality differences. Although the Big Five model gives us a uniform language based on standard definitions, but the fact remains that a combination of forces shape an individual. The Five Factors can be thought as being the main infrastructure as human individuality is too complex for any one system to explain adequately.
This personality assessment can be practically applied to identify the needs of a specific role prior to selecting or appointing a leader and performing a match of factors to determine success of the individual in the role.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Bass's Transformational Leadership Theory
Bass Transformational Leadership Theory is based on performance beyond expectations approach which defines four elements of transformational leadership. The 4 elements described by Bernard A. Bass in 1985 are Idealised Influence, Intellectual Stimulation, Individualised Consideration, and Inspirational Motivation. This study highlights four key insights about performance beyond expectations and associated criteria to measure it.
-
Robert Katz identified three leadership skills called - technical skills, human skills, and conceptual skills as the basic personal skills essential for leadership. Leaders must possess these three skills that assist them in optimizing a leader's performance. Technical skills are related to the field, human skills are related to communicating with people and conceptual skills related to setting the vision.
-
Transactional Theory of Leadership
Transactional leadership theory is based on the concept of rewards and punishments. The transactional management approach assumes that the desires of the leader and follower are different and leaders give followers something in exchange for getting something they want. Transactional leaders expect followers to be compliant and focuses on structure, instruction, monitoring, organization, or performance to get tasks completed on time.
-
Jung first introduced his personality theory and explained that all humans have a natural impulse to relate meaningfully to the world through productive work and people through significant relationships. He used four psychological functions - thinking and feeling (rational functions) and sensation and intuition (irrational functions). He also used introversion and extraversion and its impact on appropriate leader behaviors.
-
Maslow's hierarchy of needs is a motivational theory that explains that people are motivated by five basic categories of human needs. These needs are physiological, safety, love and belonging, esteem, and self-actualization. There is a little scientific basis for this concept of a hierarchy of needs.
-
Social learning theory is a theory of learning process that states that most human behavior is learned observationally through modeling. Behavior change can occur in response to leader modeling and learning occurs through the observation of rewards and punishments. The focus of this approach has been teaching leadership across formal and informal settings.
-
Hawthorne Studies - Leadership
The Hawthorne studies were conducted on workers at the Hawthorne plant of the Western Electric Company by Elton Mayo and Fritz Roethlisberger in the 1920s. This study established the behavioral change that happened due to an awareness of being observed, resulting in active compliance with the supposed wishes of researchers, because of special attention received, or positive response to the stimulus being introduced.
-
Leadership traits refer to personal qualities that define effective leaders. Here are the major leadership qualities that can make someone a good leader. Five key traits that are common in leaders can be learned and sharpened with time.
-
There are four major factors in leadership called Leader, Follower, Communication, and Situation. The success of the leader is dependent on how the leader is effectively able to communicate and motivate followers to perform desired tasks using the appropriate leadership style best suited for the given situation. Interdependencies and dynamics of these four factors of leadership must be considered by a leader to be effective.
-
Five Factors Model (FFM) also known as Five-Factor Personality Model is based on five broad personality traits which are extraversion, neuroticism, openness to experience, agreeableness, and conscientiousness represented by acronym OCEAN, these traits are often referred to as the “Big Five”.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved










