- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Business Processes
- Cash Management
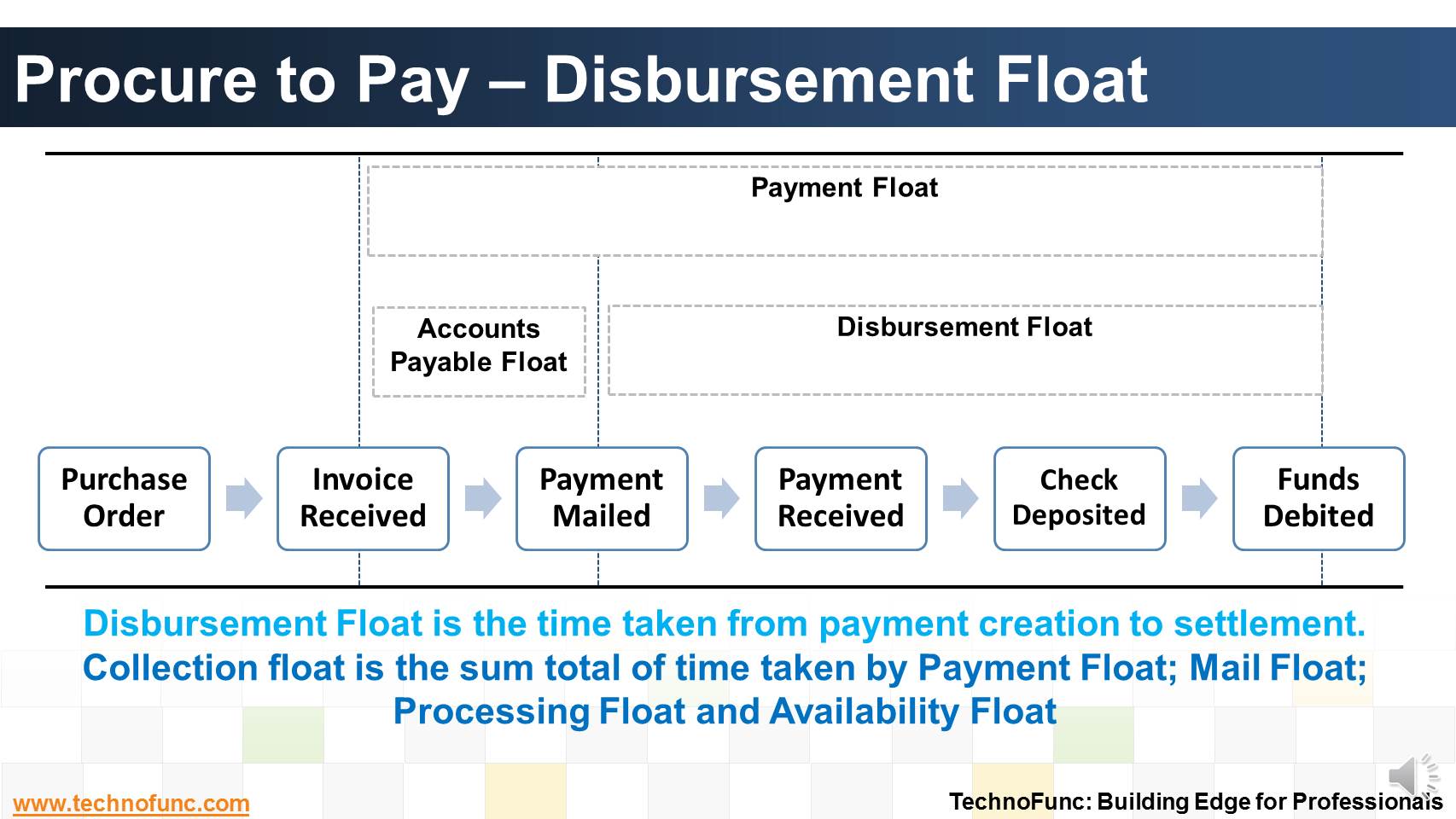
- Disbursement Float
Disbursement Float
Disbursement Float is the time taken from payment creation to settlement. Collection float is the sum total of time taken by Payment Float; Mail Float; Processing Float and Availability Float. Learn more!
Disbursement Float is the time it takes a company's payment to be created, mailed, received, deposited and presented to the drawee bank for settlement.
Thus collection float and disbursement float refer to the same processes and time intervals depending on point of view; one as a customer and another as a supplier.
For the company receiving a payment, collection float represents the time it takes an invoice to be prepared, to reach the customer, to receive payment and for the payment to clear the bank.
For the company making the payment, that same interval is disbursement float.Disbursement float consists of the following four components:
1. Invoicing and payment processing float includes both the time it takes the supplier to prepare and send the invoice, as well as the time the accounts payable department requires to process the invoice and create the payment.
2. Mail float is the time taken by postal or courier service to deliver the payment to the vendor.
3. Processing float is the time it takes the vendor to record the payment and deposit it into the bank.
4. Availability float is the time it takes the bank to clear the check and deduct the funds from the payee's bank balance.
Cash management focuses on shortening collection float and extending disbursement float, without impacting the positive customer and vendor relationships.
The skillful management of float contributes real bottom-line impact and benefit to the company.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
The objective of Financial risk management is to protect assets and cash flows from any risk. Treasury function works to accurately assess financial risks by identifying financial exposures including foreign exchange, interest rate, credit, commodity and other enterprise risks. Learn about the various risks that are managed by treasury.
-
Introduction to Bank Reconciliation Process
These set of articles provide a brief introduction to Bank Reconciliation Process. This topic not only discusses the meaning of bank reconciliation process but also discusses how this process in handled in new age ERPs and Automated Reconciliation Systems.
-
Before we dive into cash management, let us fist understand what we mean by cash and what constitutes cash in context of cash management process.
-
Bank reconciliation process is targeted to validate the bank balance in the general ledger and explain the difference between the bank balance shown in an organization's bank statement. Learn the reasons for existence of differences between the two.
-
Cash Clearing – Accounting Entries
The Cash Clearing process enables you to track amounts that have actually cleared your bank. Learn the steps and accounting entries that gets generated during the cash clearing process.
-
In manual clearing, Bank statement details are to be matched manually considering certain rules. Learn the steps involved in manual clearing of bank transactions.
-
What is Account Reconciliation?
Before you understand the Bank Reconciliation Process it is important to understand what is account reconciliation and why it is carried out.
-
In automated clearing, Bank statement details are automatically matched and reconciled with system transactions. Learn how this process works and what are the perquisites to enable the same.
-
The Cash Clearing process enables you to track amounts that have actually cleared your bank. Till reconciliation happens the amounts are parked in 'Cash Clearing Account'.
-
Technology has enabled the treasury function by providing various solutions to manage it's complicated tasks. This article explains various types of treasury management systems available in the market.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved











