- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Business Processes
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- Functional Organizational Structures
Functional Organizational Structures
A functional organizational structure is a structure that consists of activities such as coordination, supervision and task allocation. The organizational structure determines how the organization performs or operates. The term organizational structure refers to how the people in an organization are grouped and to whom they report.
A functional organizational structure is a structure that consists of activities such as coordination, supervision and task allocation. The organizational structure determines how the organization performs or operates. The term organizational structure refers to how the people in an organization are grouped and to whom they report. One traditional way of organizing people is by function. Some common functions within an organization include production, marketing, human resources, and accounting. This organizing of specialization leads to operational efficiency, where employees become specialists within their own realm of expertise. Business functions are the external directed activity systems of an organization. They are often referred to as business processes or throughput functions. These business functions are concerned with the provision of goods and services to the external customers of the organization. They express the main purpose of the organization, why the business exists.
Example: A motorcar manufacturer could have parallel process lines for different types of cars (e.g. passenger cars, heavy duty vehicles, microbuses, sports cars, etc.). Other examples are the different degree courses and research programs at a university, the different types of projects in an engineering company, different shops in a region, different types of services of a consultant etc.
Functional organizational structures - Differentiation by Function
The grouping of activities according to the type of function performed is the most commonly used structure. This is the most traditional way of organizing people. You would find this not only being widely used in business organization but also in non-commercial organization such as hospitals, universities etc. Some common functions within an organization include production, marketing, human resources, information technology and finance. This organizing of specialization leads to operational efficiencies where employees become specialists within their own realm of expertise. This structure enhances the experience of each function.
Depending on the nature of the organization and its scope of activities, the functions it has to perform may differ vastly from those of another organization. For instance, one company which undertakes both manufacturing and marketing may have departments engaged in purchase, production, marketing and finance. If it is selling a product such as TV or refrigerator it may also have an after-sale-service department.
On the other hand, a company which is an ancillary to a parent company may have only departments for purchase, manufacturing and finance. Since it is selling its entire production to the mother company there is no need for a marketing department.
Business Support Functions:
The provision of a good or service involves processing, namely the transformation of inputs into outputs. This occurs in phases. For example, the business of producing cars involves procurement of parts, the assembly of different parts into a car, other processing (e.g. painting), as well as marketing, selling and delivery. Likewise, a university course involves different disciplines and subjects. Each phase is a sub-activity system or sub-function with its own expertise or functional specialization. These are provided by the business support systems.
Inward-directed activity systems of an organization are known as business support functions. They are concerned with providing resources (e.g. human, material, technological, knowledge and energy) for the different specializations required by the business functions.
Coordinating/Governance Functions:
All functions have their own internal governance, as well as being governed by coordinating organizational governance. Coordinating governance is self-referring activity systems and includes planning, performance management and various regulatory activities. They coordinate all functions within the organization, the business, business support and organization support functions.
Organization Support Functions:
Self-directed activity systems of an organization are known as organization support functions. They are concerned with establishing and maintaining the organization as an entity. Each organization support function provides support to all functions, business, business support and other organization support functions.
For example, corporate finance provides budgets and accounting services to all functions (even to itself). Likewise, the IT function coordinates the flow of data within and between all functions (including its own data flow). Other organization support functions are administration, knowledge management, human resource development, organizational development, legal services and auditing, amongst others.
Center of Excellence Functions:
Another extension to this model could be creation of center of excellence (COE) centers within the organization. COE refers to a team, a shared facility or an entity that provides leadership, evangelization, best practices, research, support and/or training for a focus area. The focus area in this case might be a technology, a business concept, a skill (e.g. negotiation) or a broad area of study. A center of excellence may also be aimed at revitalizing stalled initiatives. It may also be known as a competency center or a capability center. Such a center may bring together faculty members from different disciplines and provide shared facilities.
Main Features
- The functional structure is most suited when an organization is dealing with a single product or service.
- Functional structure allows for specialization of work
- Ensures the most efficient utilization of human resources.
- There is concentration of authority and responsibility in the top man
- Ensures there are no conflicts arising from different authorities
- The hierarchical line of responsibility is very clearly delineated
- Functional specialists may lose sight of the overall organizational objectives and focus only on functional objectives
- Co-ordination among functional departments is needed due to unique set of constraints and problems
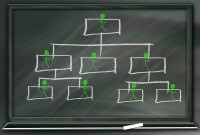
Example - Given below is the functional structure for a Services Organization:
Service Organizations are outsourcing providers of functions that have traditionally been performed and audited within the client (user) organization. Their functional organizational structure is usually divided into :
-
Human Resource( HR)
In most companies, HR is split into Recruitment, Training & Talent management. If the scales of operation are very wide Recruitment, Training and Talent management function like different Departments and the job profiles do not overlap at all.
-
Operations
Operations is the most important part of the actual functioning of the company . It is the main earner of the business because it can ‘billed’ for. All other expenses go as ‘costs’ to the company. This category includes employees who actually execute the processes for the customers.
-
Administration
Administration is again a wide function which looks after the day to day functioning of the company starting from transport ,office maintenance, security and running the cafeteria. Some of these are often called transaction processing.
-
Finance
Finance is a back office function that includes a number of services including billing, account payables, general accounting etc.
-
Business Development(BD)/Marketing
Business development includes marketing and other strategic planning. Important decisions with respect to Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A’s) are taken by this department in close coordination with the Finance department. Scanning the market and drawing a map for the company’s future growth depends largely on the efficiency of this Department.
-
Technical
The Technical Department is also a support function .Unlike in an IT Company, this Department ensures systems are in place. As there is extensive use of technology, the Technical Department has the responsible job of ensuring that all software is running smoothly.
Each of these can function as a separate company in terms of the structure. The C-level Executives have the tough job of coordination between different Departments for a smooth and effective functioning. Roles for each Department are quite clearly defined generally.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
The sole trader organization (also called proprietorship) is the oldest form of organization and the most common form of organization for small businesses even today. In a proprietorship the enterprise is owned and controlled only by one person. This form is one of the most popular forms because of the advantages it offers. It is the simplest and easiest to form.
-
In most of the automated financial systems, you can define more than 12 accounting periods in a financial year. This article will explain the concept of the adjustment period and the benefits of having adjustment periods. Adjustment periods have their inherent challenges for the users of financial statements and there is a workaround for those who don’t want to use adjustment periods.
-
GL - Accrued / Unbilled Revenue
Accrued revenues (also called accrued assets) are revenues already earned but not yet paid by the customer or posted to the general ledger. Understand what we mean by the terms accrued revenue, accrued assets, and unbilled revenue. Explore the business conditions that require recognition of accrued revenue in the books of accounts and some industries where this practice is prevalent.
-
An allocation is a process of shifting overhead costs to cost objects, using a rational basis of allotment. Understand what is the meaning of allocation in the accounting context and how defining mass allocations simplifies the process of allocating overheads to various accounting segments. Explore types of allocations and see some practical examples of mass allocations in real business situations.
-
A legal entity is an artificial person having separate legal standing in the eyes of law. A Legal entity represents a legal company for which you prepare fiscal or tax reports. A legal entity is any company or organization that has legal rights and responsibilities, including tax filings.
-
There are five types of core accounts to capture any accounting transaction. Apart from these fundamental accounts, some other special-purpose accounts are used to ensure the integrity of financial transactions. Some examples of such accounts are clearing accounts, suspense accounts, contra accounts, and intercompany accounts. Understand the importance and usage of these accounts.
-
Defining Organizational Hierarchies
A hierarchy is an ordered series of related objects. You can relate hierarchy with “pyramid” - where each step of the pyramid is subordinate to the one above it. One can use drill up or down to perform multi-dimensional analysis with a hierarchy. Multi-dimensional analysis uses dimension objects organized in a meaningful order and allows users to observe data from various viewpoints.
-
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles define the accounting procedures, and understanding them is essential to producing accurate and meaningful records. In this article we emphasize on accounting principles and concepts so that the learner can understand the “why” of accounting which will help you gain an understanding of the full significance of accounting.
-
In this article we will focus on and understand the accounting process which enables the accounting system to provide the necessary information to business stakeholders. We will deep dive into each of the steps of accounting and will understand how to identify accounting transactions and the process for recording accounting information and transactions.
-
Hierarchical Organization Structures
Hierarchical structure is typical for larger businesses and organizations. It relies on having different levels of authority with a chain of command connecting multiple management levels within the organization. The decision-making process is typically formal and flows from the top down.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved