- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Business Processes
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- GL - Using Adjustment Period
GL - Using Adjustment Period
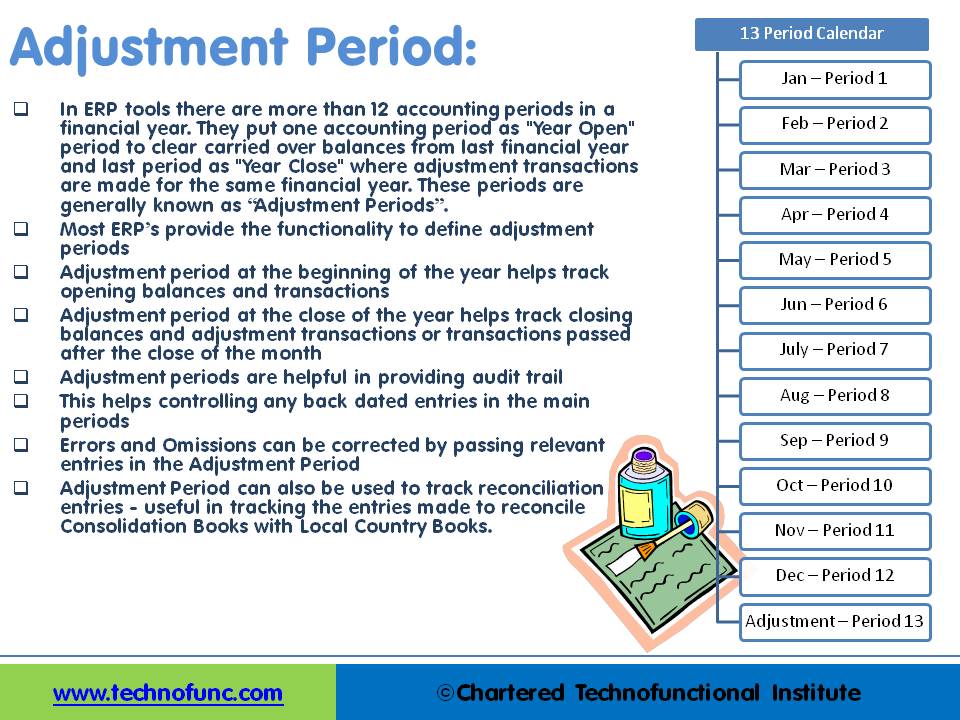
In most of the automated financial systems, you can define more than 12 accounting periods in a financial year. This article will explain the concept of the adjustment period and the benefits of having adjustment periods. Adjustment periods have their inherent challenges for the users of financial statements and there is a workaround for those who don’t want to use adjustment periods.
What is the Adjustment Period?
Any accounting period created specifically for entering adjustment and closing entries is known as adjustment period. The dates in the adjustment period overlap with the normal accounting periods in automated systems. Organizations create one accounting period as "Year Open Period” which is the first period in the accounting calendar to clear “carried over balances” from last financial year. Similarly accountants may define the last period of the accounting calendar as "Year Close Period" where adjustment transactions and closing entries are posted for the current accounting calendar. These periods are generally known as “Adjustment Periods”, sometimes are also referred to as “Zero Periods”. Most ERP’s and automated general ledger systems provide the functionality to define adjustment periods.
Benefits of Adjustment Periods:
Opening Adjustment Period: Adjustment period at the beginning of the year helps tracks opening balances and transactions. At the beginning of the year user can create journals to transfer their opening balances for the current accounting year. Generally there is an time overlap between the opening of the new financial year and finalization of audit of the previous year. This results in creation of many adjustment entries in the previous year that has an impact on the opening balances of the current year. Users are able to capture those adjustments in a separate “opening adjustment period” to keep a complete track of their normal and adjustment entries. The starting period “Zero” is used to store the starting balance for each balance sheet account.
Closing Adjustment Period:
Similarly, defining an adjustment period at the close of the year helps track closing balances and adjustment transactions. Multiple closing periods allow generation of financial statements reflecting various stages of closing and are helpful in providing complete audit trail. This also helps controlling any back dated entries in the main accounting periods.
Tracking of Errors & Omissions:
Errors and Omissions discovered after the year close can be corrected by passing relevant entries in the Adjustment Period. This will not impact your reported balances; however will create an audit trail for the transactions that need to be take care of next year.
Stat to Management Reconciliation:
Adjustment Period can also be used to track reconciliation entries. Large corporations need to pass many reconciliation entries to tally their Statutory and Main Consolidation Books. Adjustment period is useful in tracking the entries made to reconcile the consolidation books with the Local Country Books.
Exclusion for Management Reporting:
After the close of the books, a large number of entries like accounting entries for accrual or provisions need to be made in the accounting books to comply with the accounting standards and legal regulations. Management however is generally interested in operational data to do their planning and forecasting activities. By limiting adjustment and statutory entries to adjustment period management reports can be driven from same accounting books by excluding adjustment periods from the reports.
Challenges of using Adjustment Periods:
Adjustment periods have some inherent challenges which have been discussed below:
- Automated Accounting Packages comes with many standard reports. You might need to evaluate the impact of adjustment periods on these reports.
- While reversing journal entries; users need to take precaution to select the period in which they want the reversals to happen. ERPs by default might select the adjustment period.
- You may need to decide whether adjustment period should be included or excluded in your comparative reports.
- Similarly you may need to decide whether adjustment period need to be included in any management reports, especially the ones that can be compared with your statutory published results.
How to track adjustment entries without adjustment period?
Defining adjustment periods is totally optional and decision must be based on company’s requirement on the factors discussed above. Alternate solution to defining adjustment periods could be to define a separate cost center (department, division, profit center etc.). All year-end adjustment entries are made using this cost center and this unit is included for statutory consolidation but excluded for management reporting.
Diagram: Figure given at bottom gives a pictorial representation of a calendar with 13 effective periods having one adjustment period at the year end. While reporting your financial results you need to include your beginning of the year adjustment period with the first calendar period and your last adjustment period with the last reporting period.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
An account inquiry is a review of any type of financial account, whether it be a depository account or a credit account. In this tutorial, you learn what we mean by drill through functionality in the context of the general ledger system. We will explain the concept of drill-down and how it enables users to perform account and transaction inquiry at a granular level and the benefits of using this functionality.
-
Introduction to Organizational Structures
Organizations are systems of some interacting components. Levitt (1965) sets out a basic framework for understanding organizations. This framework emphasizes four major internal components such as: task, people, technology, and structure. The task of the organization is its mission, purpose or goal for existence. The people are the human resources of the organization.
-
There are two commonly used methods of accounting - Cash Basis and the Accruals Basis. Understand the difference between accruals and reversals. Recap the earlier discussion we had on accruals and reversals and see the comparison between these two different but related accounting concepts. Understand how the action of accruing results in reversals subsequently in the accounting cycle.
-
Five Core General Ledger Accounts
Typically, the accounts of the general ledger are sorted into five categories within a chart of accounts. Double-entry accounting uses five and only five account types to record all the transactions that can possibly be recorded in any accounting system. These five accounts are the basis for any accounting system, whether it is a manual or an automated accounting system. These five categories are assets, liabilities, owner's equity, revenue, and expenses.
-
In this article we will discuss various types of "Management Entities". Various types of operational units, are created by management, to effectively run, manage and control their business. Different types of functional units, and divisional units, are widely used across industry.
-
Learn the typical accounting cycle that takes place in an automated accounting system. We will understand the perquisites for commencing the accounting cycle and the series of steps required to record transactions and convert them into financial reports. This accounting cycle is the standard repetitive process that is undertaken to record and report accounting.
-
In some of the ERP tools, there are more than 12 accounting periods in a financial year. This article discusses the concept of accounting calendar and accounting periods. Learn why different companies have different accounting periods. Understand some of the commonly used periods across different organizations and the definition & use of an adjustment period.
-
A joint venture (JV) is a business agreement in which the parties agree to develop, for a finite time, a new entity and new assets by contributing equity. They exercise control over the enterprise and consequently share revenues, expenses and assets. A joint venture takes place when two or more parties come together to take on one project.
-
GL - Unearned / Deferred Revenue
Unearned revenue is a liability to the entity until the revenue is earned. Learn the concept of unearned revenue, also known as deferred revenue. Gain an understanding of business scenarios in which organizations need to park their receipts as unearned. Look at some real-life examples and understand the accounting treatment for unearned revenue. Finally, look at how the concept is treated in the ERPs or automated systems.
-
Concept of Representative Office
A representative office is the easiest option for a company planning to start its operations in a foreign country. The company need not incorporate a separate legal entity nor trigger corporate income tax, as long as the activities are limited in nature.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved