- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Business Processes
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- GL - Recurring Journal Entries
GL - Recurring Journal Entries
A “Recurring Journal” is a journal that needs to be repeated and processed periodically. Recurring Entries are business transactions that are repeated regularly, such as fixed rent or insurance to be paid every month. Learn the various methods that can be used to generate recurring journals. See some examples and explore the generic process to create recurring journals in any automated system.
What is a Recurring Journal?
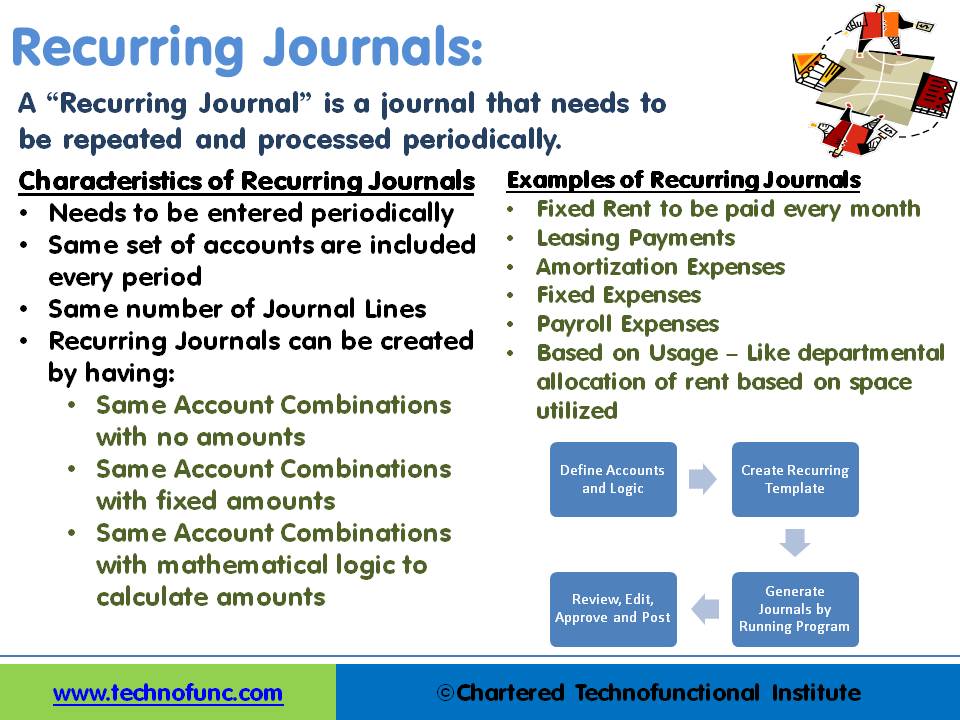
A “Recurring Journal” is a journal that needs to be repeated and processed periodically. Recurring Entries are business transactions that are repeated regularly, such as fixed rent or insurance to be paid every month. Each accounting period the journal should have the same accounts but the amounts could be different. A recurring journal entry enables you to automate similar or repeating entries. For users who need to post certain transactions frequently with few or no changes, it is an advantage to use recurring journals.
Recurring entries allow for common repeatable transactions to be saved in a template and created in multiple accounting periods upon request, making it unnecessary to retype the entire transaction thereby improving productivity. The Auto-generation of recurring accounting entries minimizes the occurrence of errors and omissions. Systems allow the generation of recurring entries at weekly, monthly, or any other frequency.
Characteristics of Recurring Journals:
-
Needs to be entered periodically
-
The same set of accounts are included every period
-
The same number of Journal Lines
-
Logic exists to define the line selection criteria
-
Simplifies the process of recording repetitive journal entries
-
Creates same journal entries with varying or same amounts in different accounting periods
Methods to Create Recurring Journals:
1. Same Account Combinations with no amounts:
This is useful when the same accounts need to be used every period however the amounts get changed every time. In this scenario, the template is defined with no amounts, and amounts are entered manually every accounting period for which the entry needs to be generated.
2. Same Account Combinations with fixed amounts:
This is useful when both accounts and amounts can be pre-determined. A good example of this scenario is fixed rent payable each month on a specific date. In this case, the template is defined with actual amounts, and journals are created and posted for relevant accounting periods.
3. Same Account Combinations with mathematical logic to calculate amounts:
This is useful when accounts can be pre-determined and amounts will be based on some logic or pre-defined formula. A good example of this scenario could be defining salesmen accounts as the pre-determined accounts. The commission is to be paid to these salesmen as a fixed percentage of sales made by each salesman during the month and sales for each salesman are recorded in separate accounts. A recurring journal can be defined that can look for the balance in respective sales accounts at the end of the period and automatically calculate the commission and create the required accounting entry for commission payable.
Examples of Recurring Journals:
This method works best for repeatable transactions. For example annual expenses that can be charged through twelve equal monthly entries such as, rent or insurance expense allocation or annual lease rentals. Each month 1/12th of the total annual expense can be debited and credited to the appropriate accounts and appear as the current month’s actual transaction. Users can benefit by creating a recurring entry for some of the business scenarios listed below:
- Fixed Rent to be paid every month
- Fixed Insurance to be paid every month
- Leasing Payments
- Amortization Expenses
- Fixed Expenses
- Payroll Expenses
- Based on Usage – Like departmental allocation of rent based on space utilized
- Depreciation
- Allocations
Generic Process to Create Recurring Journals:
Users need to define recurring journal formulas for transactions that they want to repeat every accounting period, such as accruals, depreciation charges, and allocations. The formulas can be simple or complex but need to have some logic of ascertaining the amounts for each of the accounts that need to be repeated. Each formula can use fixed amounts and/or account balances and period-to-date or year-to-date balances from the current period, prior period, or same period last year. Given below is a generic process flow to define recurring journals:
- Define Accounts, Amounts or Formula or Logic
- Create Recurring Template
- Define the accounting periods for which the recurring journals need to be created
- Generate Journals by Running automated recurring journals creation program
- Enter missing data in case of Skelton journals – missing amounts
- Review, Edit, Approve and Post recurring journals
Allocations V/s Recurring Journals:
Recurring Journals are for transactions that repeat every accounting period as explained above and allocation Journals are for single journal entry using an accounting or mathematical formula to allocate revenues and expenses across a group of accounting dimensions like cost centers, departments, divisions, locations, or product lines depending upon usage factors.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Defining Organizational Hierarchies
A hierarchy is an ordered series of related objects. You can relate hierarchy with “pyramid” - where each step of the pyramid is subordinate to the one above it. One can use drill up or down to perform multi-dimensional analysis with a hierarchy. Multi-dimensional analysis uses dimension objects organized in a meaningful order and allows users to observe data from various viewpoints.
-
There are five types of core accounts to capture any accounting transaction. Apart from these fundamental accounts, some other special-purpose accounts are used to ensure the integrity of financial transactions. Some examples of such accounts are clearing accounts, suspense accounts, contra accounts, and intercompany accounts. Understand the importance and usage of these accounts.
-
In this article we will focus on and understand the accounting process which enables the accounting system to provide the necessary information to business stakeholders. We will deep dive into each of the steps of accounting and will understand how to identify accounting transactions and the process for recording accounting information and transactions.
-
Period End Accruals, Receipt Accruals, Paid Time-Off Accruals, AP Accruals, Revenue Based Cost Accruals, Perpetual Accruals, Inventory Accruals, Accruals Write Off, PO Receipt Accrual, Cost Accrual, etc. are some of the most complex and generally misconstrued terms in the context of general ledger accounting. In this article, we will explore what is the concept of accrual and how it impacts general ledger accounting.
-
Matrix Organizational Structures
In recent times the two types of organization structures which have evolved are the matrix organization and the network organization. Rigid departmentalization is being complemented by the use of teams that cross over traditional departmental lines.
-
GL - Accrued / Unbilled Revenue
Accrued revenues (also called accrued assets) are revenues already earned but not yet paid by the customer or posted to the general ledger. Understand what we mean by the terms accrued revenue, accrued assets, and unbilled revenue. Explore the business conditions that require recognition of accrued revenue in the books of accounts and some industries where this practice is prevalent.
-
In this article, we will explain the general Ledger journal processing flow from entering journals to running the final financial reports. Understand the generic general ledger process flow as it happens in automated ERP systems. The accounting cycle explains the flow of converting raw accounting data to financial information whereas general ledger process flow explains how journals flow in the system.
-
Internally, an organization can be structured in many different ways, depending on their objectives. The internal structure of an organization will determine the modes in which it operates and performs. Organizational structure allows the expressed allocation of responsibilities for different functions and processes to different entities such as the branch, department, workgroup and individual.
-
Team-Based Organizational Structure
Team-based structure is a relatively new structure that opposes the traditional hierarchical structure and it slowly gaining acceptance in the corporate world. In such a structure, employees come together as team in order to fulfill their tasks that serve a common goal.
-
An organizational design is the process by which a company defines and manages elements of structure so that an organization can control the activities necessary to achieve its goals. Good organizational structure and design helps improve communication, increase productivity, and inspire innovation. Organizational structure is the formal system of task and activity relationships to clearly define how people coordinate their actions and use resources to achieve organizational goals.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved