- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Business Processes
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- Trial Balance in General Ledger
Trial Balance in General Ledger
One of the greatest benefits of using a double-entry accounting system is the capability to generate a trial balance. What do we mean by trial balance? As the name suggests a trial balance is a report that must have its debits equals to credits. Understand the importance of trial balance and why it is balanced. Learn how it is prepared and in which format.
Double Entry Accounting System:
In the preceding tutorials, we illustrated the rules of debit and credit for recording transactions in accounts using journal entries. We also discussed the accounting equation and established that, in doing so, the sum of the debits is always equal to the sum of the credits for each journal entry. This equality of debits and credits for each transaction is built into the accounting equation and because of this double equality; this system of recording transactions is called the double-entry accounting system. In the double-entry accounting system, each accounting entry results in two nominal accounts being debited and credited with equal amounts.
What is a Trial Balance?
The practice of recording the same debit amount to one account and an equal credit amount to another account results in total debits being equal to total credits for all accounts in the general ledger. If the accounting entries are recorded without error, the aggregate balance of all accounts having positive balances (Debit Balances) will be equal to the aggregate balance of all accounts having negative balances (Credit Balances). Trial Balance is the compilation of balances of all accounts in the general ledgers into debit and credit columns. In a double-entry accounting system the total debits equal the total credits hence a compilation of all the accounts will be balanced, that is Sum of Debits will be equal to the sum of credits and hence the sum of the trial balance will always be zero if debit balances are represented by positive amounts and credit balances are represented by negative amounts.
How trial balance is prepared?
The first step to prepare a trial balance is to extract the account balances from each account in the general ledger in a columnar form. Thus, before the trial balance can be prepared, each account balance in the ledger must be determined. When the standard account form is used, the balance of each account appears in the balance column on the same line as the last posting to the account. The next step is to calculate the debits and then the credits in the respective columns. In short, the trial balance procedure involves five steps:
- Identify the accounts and their balances.
- List the accounts and enter their balances in columnar format.
- Add the debit balances.
- Add the credit balances.
- Compare the sum of the debits and the credits; they should match in a double-entry accounting system.
All automated accounting systems and ERPs come with trial balance as a standard report and it can be generated for each accounting period.

Format of Trial Balance:
The important concept to understand is that a trial balance is a statement, not an account. It is the extraction of all balances from all accounts in a general ledger. It is valid for a particular date. It is always prepared with reference to an accounting period with reference to a particular date. Trial Balance is true for the date for which it has been drawn. The traditional format of trial balance includes the following columns:
- Serial Number
- Name of the General Ledger Account
- Ledger Folio or Account Number
- Debit Balance
- Credit Balance
Trial Balance and Error Prevention:
Because of the volume of data manipulated when bookkeeping, errors are easy to make, since numbers are constantly being added or subtracted. How can users be sure that they have not made an error in posting the debits and credits to the ledger? One way is to determine the equality of the debits and credits in the ledger. A trial balance checks the equality of the debits and credits. Taking a trial balance is done after posting to the ledger, but can also be performed throughout accounting activities. This equality should be proved at the end of each accounting period, if not more often.
Balances are Equal!
The trial balance does not provide complete proof of the accuracy of the ledger. It indicates only that the debits and the credits are equal. This proof is of value, however, because errors often affect the equality of debits and credits. If the balances equal in a trial balance, there still may be an error. Errors can easily be made because numbers are transferred so many times. During accounting activities, wrong amounts can be recorded, numbers transposed, and amounts debited instead of credited. Sometimes errors occur without affecting the balance.
Balances are not Equal !!
If the two totals of a trial balance are not equal, an error has occurred. If the trial balance shows that the debits do not equal the credits, then another trial balance should be taken. If the debits still do not equal the credits, then an error exists and must be found.
How to locate Errors?
There exist some techniques that are used by the accountants to locate the errors if the trial balance has resulted in unequal amounts. Some tips are given below:
- Take the trial balance in reverse order. This is known as backtracking and helps in locating the errors.
- Take the difference between the sum of the debits and the sum of the credits and analyze the difference.
- If the difference is equal to an account balance then an error in posting to the wrong side of the account has occurred.
- If the difference is divisible by nine then numbers have been transposed. To locate the error, compare the data in the trial balance against the data in the ledger to make sure numbers were copied correctly.
- If the difference is divisible by ten, then an error in addition or subtraction has occurred. In this case, recalculate the sums in the debits and credits in the trial balance.
Why we need Trial Balance?
Bookkeeping is the act of recording transactions, while accounting includes bookkeeping activities plus the preparation, analysis, and interpretation of financial information. Once we have recorded the transactions, the next step is to convert this data into meaningful information that can provide insights to the business stakeholders.
Trial Balance is usually drawn at the end of every reporting period. Trial Balance becomes the basis for advanced reports like Balance Sheet and Profit and Loss Accounts. The concept of “Balancing” and “Suspense Posting” ensures that Journals in an automated system and ERPs are always balanced resulting in a balanced trial balance. Trial Balance is used for financial reporting, management reporting, consolidation process, and reconciliation processes.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
In this article we will focus on and understand the accounting process which enables the accounting system to provide the necessary information to business stakeholders. We will deep dive into each of the steps of accounting and will understand how to identify accounting transactions and the process for recording accounting information and transactions.
-
This article explains the process of entering and importing general ledger journals in automated accounting systems. Learn about the basic validations that must happen before the accounting data can be imported from any internal or external sub-system to the general ledger. Finally, understand what we mean by importing in detail or in summary.
-
Business Metrics for Management Reporting
Business metric is a quantifiable measure of an organization's behavior, activities, and performance used to access the status of the targeted business process. Traditionally many metrics were finance based, inwardly focusing on the performance of the organization. Businesses can use various metrics available to monitor, evaluate, and improve their performance across any of the focus areas like sales, sourcing, IT or operations.
-
Hierarchical Organization Structures
Hierarchical structure is typical for larger businesses and organizations. It relies on having different levels of authority with a chain of command connecting multiple management levels within the organization. The decision-making process is typically formal and flows from the top down.
-
The purpose of the general ledger is to sort transaction information into meaningful categories and charts of accounts. The general ledger sorts information from the general journal and converts them into account balances and this process converts data into information, necessary to prepare financial statements. This article explains what a general ledger is and some of its major functionalities.
-
Introduction to Organizational Structures
Organizations are systems of some interacting components. Levitt (1965) sets out a basic framework for understanding organizations. This framework emphasizes four major internal components such as: task, people, technology, and structure. The task of the organization is its mission, purpose or goal for existence. The people are the human resources of the organization.
-
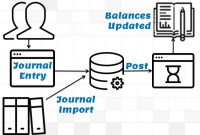
GL - Journal Posting and Balances
In this tutorial, we will explain what we mean by the posting process and what are the major differences between the posting process in the manual accounting system compared to the automated accounting systems and ERPs. This article also explains how posting also happens in subsidiary ledgers and subsequently that information is again posted to the general ledger.
-
Legal Structures in Businesses
Businesses not only vary in size and industry but also in their ownership. Most businesses evolve from being owned by just one person to a small group of people and eventually being managed by a large numbers of shareholders. Different ownership structures overlap with different legal forms that a business can take. A business’s legal and ownership structure determines many of its legal responsibilities.
-
Global Business Services (GBS) Model
Global business services (GBS) is an integrated, scalable, and mature version of the shared services model. Global Business Services Model is a result of shared services maturing and evolving on a global scale. It is represented by the growth and maturity of the Shared services to better service the global corporations they support.
-
Multitude of these legal and operational structures clubbed with accounting and reporting needs give rise to many reporting dimensions at which the organization may want to track or report its operational metrics and financial results. This is where business dimensions play a vital role.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved