- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Business Processes
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- GL - Journal Posting and Balances
GL - Journal Posting and Balances
In this tutorial, we will explain what we mean by the posting process and what are the major differences between the posting process in the manual accounting system compared to the automated accounting systems and ERPs. This article also explains how posting also happens in subsidiary ledgers and subsequently that information is again posted to the general ledger.
What is Journal Posting?
As we discussed in the preceding tutorials, a transaction is first recorded in a journal. The journal is a chronological listing of the accounting events. Periodically, the journal entries are transferred to the accounts in the ledger. An organization's ledgers contain each and every account the organization uses, organized by account code. The final step of the bookkeeping phase is, posting to the general ledger. The process of transferring the debits and credits from the journal entries to the accounts is called posting. The ledger is a history of transactions by account. The purpose of posting is to maintain and be able to determine the balance of each specific account.
In practice, businesses use a variety of formats for recording journal entries. The journals may be part of either a manual accounting system or a computerized accounting system. The posting of a journal entry to a ledger account is a straightforward process. Posting transfers information already in the journal, requiring no further analysis. Remember, the key information in the ledger is the same as what's in the journal. The date, description, account names, account codes, and debit and credit amounts are all there in the ledger account, just in a different format.
Posting – Process Difference between Manual and Computerized Accounting Systems:
Manual Accounting Systems: As discussed earlier the preceding steps in the accounting cycle are to identify and analyze the transaction and record by making journal entries. Each single-line journal entry affects two ledger accounts. A typical bookkeeping process records transactions chronologically to a journal, posts daily to subsidiary ledgers, and posts periodically to the general ledger. After posting the transaction to the general ledger, you return to the journal entry and put in the reference number of each ledger account affected by the debit and credit. This indicates to anyone looking at the journal that the entry has been posted to the ledger.
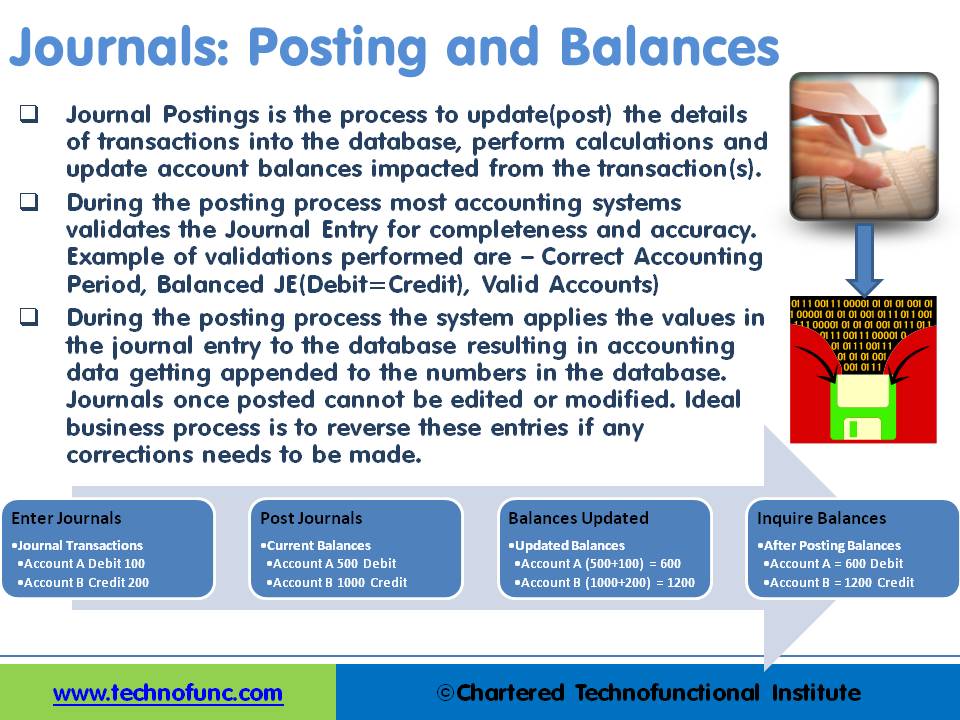
Automated Accounting Systems: In automated accounting systems posting can be understood as the process to update (post) the details of transactions into the database, perform calculations and update account balances impacted by the transaction(s). During the posting process, most accounting systems validate the Journal Entry for completeness and accuracy. Example of validations performed are – Correct Accounting Period, Balanced JE (Debit=Credit), or Valid Accounts
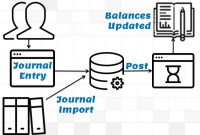
Posting in Automated Systems:
During the posting process, the system applies the values in the journal entry to the database resulting in accounting data getting appended to the numbers in the database. Journals once posted cannot be edited or modified. The ideal business process is to reverse these entries if any corrections need to be made. To verify accounts, total balances from subsidiary ledgers are compared to the totals in each general ledger account.
In the example shown in the figure, in the first step, the journals are entered. Once the journals are entered, they are available in the systems for Review, Approval, and Posting. At this point, current balances in the accounts are not impacted. The next three boxes depict that as the journal gets posted, the current balances are updated to show the impact of the entered transaction. Hence posting is the process to update account balances with the transaction amount.
Posting from Subsidiary Ledgers:
As discussed in earlier tutorials, it is common for businesses to use subsidiary ledgers to track information with similar characteristics. The number and types of subsidiary ledgers and the level of detail contained in each varies substantially with the needs of the organization. There are many possible subsidiary ledgers as explained in examples on subsidiary ledgers article. At the end of a given period – such as a week or a month – the sub-ledger journal information can be posted to the ledgers in summary form, making the process of posting more efficient. Posting to subsidiary ledgers in addition to the general ledger is a good option for when more detail is required.
The relationship between journals, subsidiary ledgers, and the general ledger is slightly more complex than that between general ledger journals and general ledgers. Each subsidiary journal has entries that share the same characteristics, but the listing still reflects changes to two or more accounts in the general ledger. Subsidiary ledgers correspond to the control accounts in the ledger, the journal transaction is entered in sub-ledgers first, usually on a daily basis. Subsequently, these also get posted from the sub-ledgers to the general ledger, usually weekly or monthly.
The general ledger control account balances are checked against the totals in the subsidiary ledgers to ensure correctness at the end of the accounting period. To verify a subsidiary ledger such as the Accounts Receivable ledger, you begin by calculating the sum of the accounts with balances in the subsidiary ledger. You then compare that to the running balance in the accounts receivable control account of the general ledger. If the totals match, you can assume that the ledgers are accurate.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
GL - Journal Posting and Balances
In this tutorial, we will explain what we mean by the posting process and what are the major differences between the posting process in the manual accounting system compared to the automated accounting systems and ERPs. This article also explains how posting also happens in subsidiary ledgers and subsequently that information is again posted to the general ledger.
-
GL - Unearned / Deferred Revenue
Unearned revenue is a liability to the entity until the revenue is earned. Learn the concept of unearned revenue, also known as deferred revenue. Gain an understanding of business scenarios in which organizations need to park their receipts as unearned. Look at some real-life examples and understand the accounting treatment for unearned revenue. Finally, look at how the concept is treated in the ERPs or automated systems.
-
GL - Different Accounting Methods
The accounting method refers to the rules a company follows in reporting revenues and expenses. Understand the two common systems of bookkeeping, single, and double-entry accounting systems. Learners will also understand the two most common accounting methods; cash and accrual methods of accounting and the advantages and disadvantages of using them.
-
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles define the accounting procedures, and understanding them is essential to producing accurate and meaningful records. In this article we emphasize on accounting principles and concepts so that the learner can understand the “why” of accounting which will help you gain an understanding of the full significance of accounting.
-
Introduction to Organizational Structures
Organizations are systems of some interacting components. Levitt (1965) sets out a basic framework for understanding organizations. This framework emphasizes four major internal components such as: task, people, technology, and structure. The task of the organization is its mission, purpose or goal for existence. The people are the human resources of the organization.
-
What is Accounting & Book Keeping
Accounting is a process designed to capture the economic impact of everyday transactions. Each day, many events and activities occur in an entity, these events and activities are in the normal course of business; however, each of these events may or may not have an economic impact. Events or activities that have an effect on the accounting equation are accounting events.
-
Defining Organizational Hierarchies
A hierarchy is an ordered series of related objects. You can relate hierarchy with “pyramid” - where each step of the pyramid is subordinate to the one above it. One can use drill up or down to perform multi-dimensional analysis with a hierarchy. Multi-dimensional analysis uses dimension objects organized in a meaningful order and allows users to observe data from various viewpoints.
-
Five Core General Ledger Accounts
Typically, the accounts of the general ledger are sorted into five categories within a chart of accounts. Double-entry accounting uses five and only five account types to record all the transactions that can possibly be recorded in any accounting system. These five accounts are the basis for any accounting system, whether it is a manual or an automated accounting system. These five categories are assets, liabilities, owner's equity, revenue, and expenses.
-
What is a Business Eco System?
The goal of a business is to generate capital appreciation and profits for its owners or stakeholders by engaging in provision of goods and services to customers within the eco system/framework governed by respective laws(local/international). The eco system involves various entities that the business works with for delivery of a product or service.
-
In this article we will help you understand the double-entry accounting system and state the accounting equation and define each element of the equation. Then we will describe and illustrate how business transactions can be recorded in terms of the resulting change in the elements of the accounting equation.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved