- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Business Processes
- Procure to Pay
- Account Payable Process
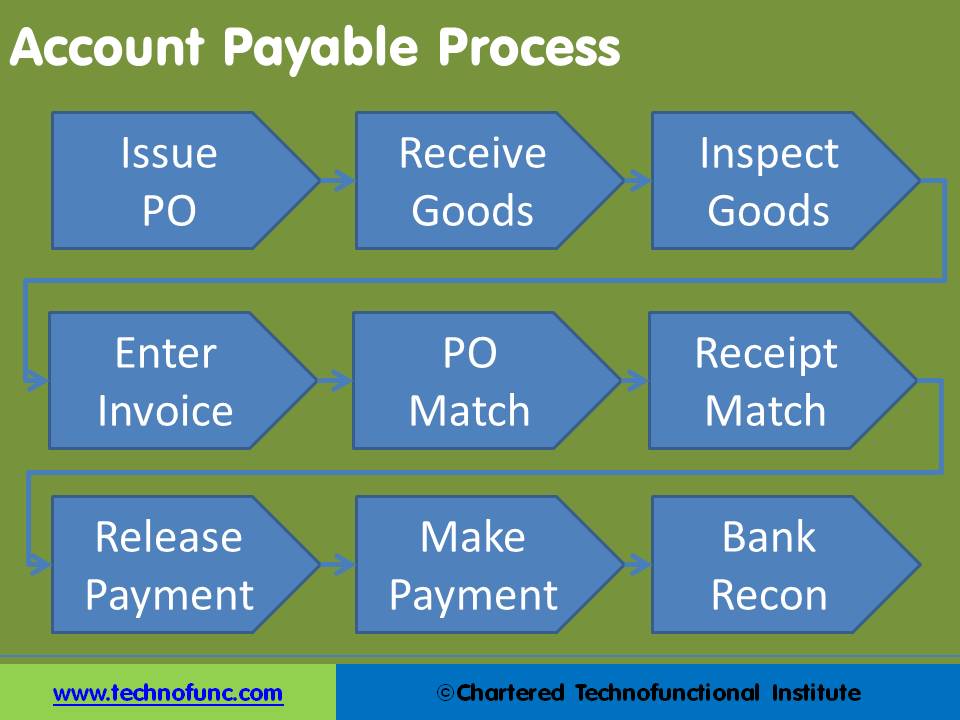
Account Payable Process
Understand the Accounts Payable process. Understand the AP cycle and the various tasks that need to be completed during AP transaction processing. Learn the key activities and setups that are done in any typical system during the AP processing.
Given below is the complete Accounts Payable Process:
1. Issue Purchase Order:
The AP Process starts with the issue of Purchase order to the Supplier. The purchase order specifies what you intend to buy, the make and the quality of the goods. In some cases it also specifies the agreed quantity and the price.
2. Receive Goods:
Based on the purchase order the supplier will ship a product. Till goods have been received by the customer, the ownership generally lies with the supplier. Once the goods are received at your go down, you become the owner of the goods.
3. Inspect Goods:
Most organizations have the internal control processes to inspect the goods to ensure the quantity and quality of the supplied material.
4. Enter Invoice:
Supplier issues an credit invoice, and collects payment later. This describes a cash conversion cycle, a period of time during which the supplier has already paid for raw materials but hasn't been paid in return by the final customer. Received invoice is accounted for in the books of the customer.
5. PO Match and Receipt Match:
When the invoice is received by the purchaser it is matched to the packing slip and purchase order, and if all is in order, the invoice is paid. This is referred to as the three-way match. The three-way match can slow down the payment process, so three-way matching may be limited solely to large-value invoices, or the matching is automatically approved if the received quantity is within a certain percentage of the amount authorized in the purchase order.
6. Release and Make Payment:
Once the matching is done and accounts payable department is satisfied to the accuracy and validity of purchase, the refer to the payments terms. Companies may have negotiated different payment terms with different suppliers. Payment is released based on the agreed payment terms and amount is issued to the supplier.
7. Bank Reconciliation:
Generally the payment is made through the bank. There is a slight delay between the date when the payment is released and when it reaches to the account of the supplier. The bank entry is reconciled to the original payment entry in the Payments Register to reconcile the both accounts and this completes the account payable process.
In the next video tutorial we will take you through the accounting entries in the payable process.
Given below are some other activities that happen during the AP processing cycle:
- Define and maintain supplier information to be used at the time of invoicing and payment
- Enter invoice information
- Match invoices to Purchase Orders
- Define, enter and import employee expense reports as expenses are also part of payables to employees
- Set up bank accounts for payment to Vendors
- Enter manual payments or use EDI to make automated payments
- Pay invoices
- Stop and void payments in case any holds are required
- Enter and apply prepayments to invoices, adjust advances
- Enter and apply employee advances
- Create recurring invoices for same type of invoices
- Transfer invoices and payment details to General Ledger to ensure proper accounting
- Before any ERP System works, you might need to define the tax defaulting rules and principles
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
This article discusses the key documents that gets generated during the import/export process. These documents may apply to both invoice to cash as well as order to cash cycles. Also learn the major custom docments for India.
-
This article discusses the documents that gets generated during the procure to pay process. Undestand why these documents are created, what is their business significance and how they are handled and generated using ERP or automated systems.
-
Types of Inventory Count Processes
While dealing with lots of inventory in a warehouse, lots of things can go wrong. Shipments may not have the right number of units in them, or they could get damaged somewhere along the supply chain. Discrepancies in the stock may arise as part of every inventory control, and need to be corrected immediately after the inventory control procedure has been finished.
-
We need a strong payables process so that it provides us with a high-productivity accounting solution to process vendor payments. An integrated payables process provides strong financial control so you can prevent duplicate payments, pay for only the goods and services you order and receive, and maximize supplier discounts. Understand the key features of an effective accounts payable system.
-
Overview of Warehouse Processes
The basic function of a warehouse is to store goods. This means that they receive deliveries from suppliers, do any necessary checking and sorting, store the materials until it is dispatched to customers. Traditionally warehouses were seen as places for the long-term storage of goods. Now organizations want to optimize their customer experience and try to move materials quickly through the supply chain, so the role of warehousing has changed.
-
Resource Planning is the process of planning for expected workload and determining the number of resources required to complete each activity in the warehouse. There are many types of warehouse positions, and they also vary by the employer, the scale of operations and location. Discussed here are generic positions applicable to warehouse management processes.
-
After products have been received and passed a quality inspection, they need to be stored so that you can find them when you need them. This process is called putaway. The spot where you store a particular product is called a location. One section of a warehouse might have small locations for light items; another area may have large locations on the floor for heavy items.
-
To stay competitive in today’s tough market, the location of your warehouse is vital. To grow retail business need to offer to customers faster and affordable shipping time, which is dependent on the warehousing location as the location of the warehouse affects the transit time to ship orders to customers.
-
Accounts Payable Journal Entry
Although in the large organizations the Procure to Pay Accounting process starts when the purchase order for supply of goods is released to the supplier. To keep things simple in the beginning we will discuss the core accounting entries related to the Accounts Payables process.
-
Large companies have huge number of suppliers. To remain competitive they need to manage their procure to pay process very effectively. They create specialized division to handle these operations.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved