- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Business Processes
- Procure to Pay
- Define Accounts Payable
Define Accounts Payable
Payables are often categorized as “Trade Payables” & “Expense Payables”. “Trade Payables” are the monies due for the purchase of physical goods that are recorded in Inventory. “Expense Payables” are the monies due for the purchase of goods or services that are expensed.
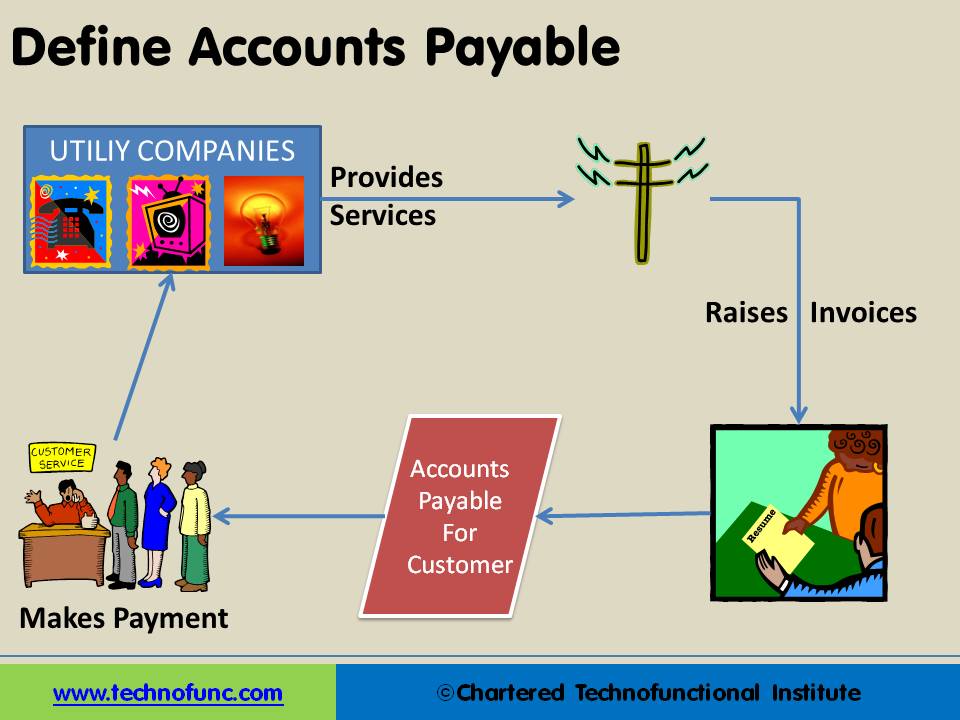
How do we define Accounts Payables:
We all use utilities. For example we take various services from the phone company, the gas company and the cable company. They provide us the goods and services first and as the end of the agreed billing period they raise an invoice on the customer. In this case the Utility Company is our Creditor and they have provided us the service on credit. The amount payable to the utility company is the “Account Payable” for us, which needs to be paid in very short-term to the utility company (Supplier/Creditor) to enjoy continued services.
Similarly credit is extended in the normal course of business to the customers on purchase of goods and services and needs to be paid off within a given period of time in order to avoid default.
Payables are often categorized as “Trade Payables” & “Expense Payables”. “Trade Payables” are the monies due for the purchase of physical goods that are recorded in Inventory. “Expense Payables” are the monies due for the purchase of goods or services that are expensed. Common examples of Expense Payables are utilities like telephone and electricity.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
To stay competitive in today’s tough market, the location of your warehouse is vital. To grow retail business need to offer to customers faster and affordable shipping time, which is dependent on the warehousing location as the location of the warehouse affects the transit time to ship orders to customers.
-
Warehouses may seem like a simple, straightforward concept, but they actually include a variety of different types of warehouses that all have their own niche. The type of warehousing that’s right for you depends on your specific industry, location, and needs. From private warehousing, distribution centers, and climate-controlled warehouses, there’s an option to suit every business.
-
Transport operations are often divided into full load and part load and due to economies of scale, the unit costs are higher for part loads. Our customer needs several part loads delivering, so it can reduce costs by consolidating these into full loads. Then it gets all the part loads delivered to a warehouse near the suppliers, consolidates them into full loads, and pays the lower costs of full-load transport to its operations.
-
Miscellaneous Warehouse Processes
At the end of each inventory control, the Contractor provides the Ordering Person with an inventory report which contains a list of all stock adjustments. The Ordering Person uses the report to create, by use of his/her own means, necessary value and accounting adjustments related to the stock. Let us look at some to the mislaneous warehouse processes not covered earlier.
-
Accounts Payable Journal Entry
Although in the large organizations the Procure to Pay Accounting process starts when the purchase order for supply of goods is released to the supplier. To keep things simple in the beginning we will discuss the core accounting entries related to the Accounts Payables process.
-
The Outbound process starts with routing the shipments. The Outbound execution process starts from the point when pick tasks are completed for an outbound shipment and ends at the point where the outbound packages are loaded into trailers. The Warehouse Outbound process includes managing and controlling outgoing materials starting from the download of orders through to the shipping of products from the warehouse.
-
Companies and businesses have huge transactions pertaining to their accounts payable process. They receive goods and services from various suppliers and they need to manage timely payments to these creditors to avoid default and adhere to the payment terms.
-
Payables are often categorized as “Trade Payables” & “Expense Payables”. “Trade Payables” are the monies due for the purchase of physical goods that are recorded in Inventory. “Expense Payables” are the monies due for the purchase of goods or services that are expensed.
-
After products have been received and passed a quality inspection, they need to be stored so that you can find them when you need them. This process is called putaway. The spot where you store a particular product is called a location. One section of a warehouse might have small locations for light items; another area may have large locations on the floor for heavy items.
-
This article discusses the documents that gets generated during the procure to pay process. Undestand why these documents are created, what is their business significance and how they are handled and generated using ERP or automated systems.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved










