- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Business Processes
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- Prepayments and Prepaid Expenses
Prepayments and Prepaid Expenses
Prepayments are the payment of a bill, operating expense, or non-operating expense that settle an account before it becomes due. Learn the concept of prepaid expenses. Understand the accounting treatment for prepaid expenses. Understand the concept by looking at some practical examples and finally learn the adjusting entry for these expenses.
What are Prepaid Expenses?
Prepaid expenses, sometimes referred to as deferred expenses, are the amounts that have been paid in advance to a vendor or creditor for goods and services. These payments initially get recorded as assets but are expected to become expenses over time or through the normal operations of the business. Supplies, prepaid insurance, prepaid advertising, advance rental, advance tuition fee, and prepaid interest are some examples of prepaid expenses that may require adjustment at the end of an accounting period.
What is the accounting treatment for prepaid expenses?
Prepaid Expenses are the expenses that are paid before the time period in which the benefit will be consumed. The payment is a current asset on the balance sheet and this amount paid is then amortized, as the consumption or utilization happens by charging proportionate amounts to expense accounts. Because the advance payments are to obtain benefits for the organization over a period of time, the cost of these assets is charged against profits throughout the period, usually on a monthly basis. Prepaid expenses are treated as current assets because the company has paid for something and someone owes services or goods in exchange in the future.
Although the prepaid expenses are generally classified as Current Assets in the balance sheet, however, it’s an unusual classification as prepaid expenses will never, except in rare cases, be turned into cash in the practical world. Prepaid expenses are expenses that have been paid in advance and therefore won't have to be paid again, in a way they create cash by enabling the company to avoid paying out towards the expense for the benefit period.
What are some examples of Prepaid Expenses?
Every business buys insurance of various kinds to manage and mitigate risk and to buy insurance the organization needs to pay the premium to the insurance company, which is generally paid in advance, typically for a year at a time, and covers the organization for specified risks for the policy period. For some businesses, insurance can be a very costly item. The policy cover may extend many accounting periods and hence companies allocate the cost of that protection over the period of time that is being protected, based on the allocation per accounting period. Proper accounting treatment, matching, and accrual concepts demand that the premium benefits all 12 months and should therefore be charged to profits over the benefit period, not just the month in which you paid the premium.
So, if the company has defined its accounting period as a calendar month and the policy period is for 12 months, then the company will charge the insurance amount to expense over the 12 months that it protects, usually by simply charging 1/12 of the total to expense each month. The balance of the advance premium payment is considered prepaid and it rests in a prepaid expense account until it has been entirely written off to expense. Other examples of prepaid expenses might be property taxes, advance rentals, or advance income tax installments.
Adjusting Entry for Prepaid Expenses:
Prepaid expenses (or deferred expenses) are expenses paid in cash and recorded as assets prior to being used. The most common form of an adjusting entry for prepaid expenses would be to create a current asset at the time of payment for the expense and charge it to the expense account over the accounting periods for which the benefit will be in place. These types of adjusting entries are usually permanent.
In the case of prepaid expenses, there is a timing difference between the cash-flow and the actual charge to the expense spread over the period of coverage of the advance. In case these cash-flows are not matched to the accounting periods in which the expenses will actually happen, it will adversely affect the profits of the period in which the cash flow has been recorded. Therefore prepaid expenses are treated as assets to reflect the true state of affairs for the current accounting period.
Many business managers often overlook these timing differences because they think that the effects will equal and compensate each other over time. But such differences can be very significant in the short term and can impact the critical cash flow planning.
Prepayment accounting entries:
Given below is a set of accounting entries that generally take place in automated systems and ERPs:
Step 1: Raise a Prepayment Invoice
Debit: Prepaid Expense A/c
Credit: Liability A/c
(Example: Performa invoice of the total insurance period for the year has been received and the company has decided to purchase the policy)
Step 2: Prepayment is release to the vendor:
Debit: Liability A/c
Credit: Bank/cash A/c
(Example: The payment has been released to the vendor)
Step 3: When the Invoice is raised for Expense:
Debit: Expense Charge A/c
Credit: Prepaid Expense A/c
(Example: During the accounting period one, the charge for the expense is made and prepaid expense is reduced by the same amount)
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
GL - Different Accounting Methods
The accounting method refers to the rules a company follows in reporting revenues and expenses. Understand the two common systems of bookkeeping, single, and double-entry accounting systems. Learners will also understand the two most common accounting methods; cash and accrual methods of accounting and the advantages and disadvantages of using them.
-
Introduction to Legal Entities Concept
Modern business organizations operate globally and leverage a large number of registered legal entities, and operate through complex matrix relationships. To stay competitive in the current global business environment, they must often develop highly diverse and complex organizational structures that cross international borders. Learn more about Legal Entities and their importance for businesses.
-
In this article we will discuss various types of "Management Entities". Various types of operational units, are created by management, to effectively run, manage and control their business. Different types of functional units, and divisional units, are widely used across industry.
-
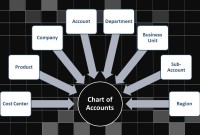
GL - Understanding Chart of Accounts
A chart of accounts (COA) is a list of the accounts used by a business entity to record and categorize financial transactions. COA has transitioned from the legacy accounts, capturing just the natural account, to modern-day multidimensional COA structures capturing all accounting dimensions pertaining to underlying data enabling a granular level of reporting. Learn more about the role of COA in modern accounting systems.
-
A legal entity is an artificial person having separate legal standing in the eyes of law. A Legal entity represents a legal company for which you prepare fiscal or tax reports. A legal entity is any company or organization that has legal rights and responsibilities, including tax filings.
-
In this article, we will describe how to determine if an account needs adjustment entries due to the application of the matching concept. Learners will get a thorough understanding of the adjustment process and the nature of the adjustment entries. We will discuss the four types of adjustments resulting from unearned revenue, prepaid expenses, accrued expenses, and accrued revenue.
-
Learn the typical accounting cycle that takes place in an automated accounting system. We will understand the perquisites for commencing the accounting cycle and the series of steps required to record transactions and convert them into financial reports. This accounting cycle is the standard repetitive process that is undertaken to record and report accounting.
-
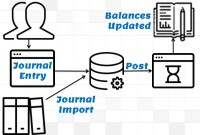
GL - Journal Posting and Balances
In this tutorial, we will explain what we mean by the posting process and what are the major differences between the posting process in the manual accounting system compared to the automated accounting systems and ERPs. This article also explains how posting also happens in subsidiary ledgers and subsequently that information is again posted to the general ledger.
-
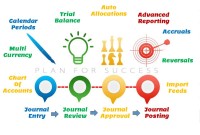
General Ledger - Advanced Features
Modern automated general ledger systems provide detailed and powerful support for financial reporting and budgeting and can report against multiple legal entities from the single system. These systems offer many advanced functionalities right from journal capture to advanced reporting. This article will provide an overview of some advanced features available in today's General Ledgers.
-
McKinsey 7S Framework is most often used as an organizational analysis tool to assess and monitor changes in the internal situation of an organization. The model is based on the theory that, for an organization to perform well, seven elements need to be aligned and mutually reinforcing.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved