- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Business Processes
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- Organizational Elements
Organizational Elements
McKinsey 7S Framework is most often used as an organizational analysis tool to assess and monitor changes in the internal situation of an organization. The model is based on the theory that, for an organization to perform well, seven elements need to be aligned and mutually reinforcing.
McKinsey 7S Framework is most often used as an organizational analysis tool to assess and monitor changes in the internal situation of an organization. The model is based on the theory that, for an organization to perform well, following seven elements need to be aligned and mutually reinforcing:
Hard Elements - Hardware of Organizational Success
-
Strategy: The integrated vision and direction of the company
A set of actions that the company starts with and which it must maintain. Strategy is the manner in which the organization derives, articulates, communicates and implements it's vision and direction. Strategy is the purpose of the business and the way the organization seeks to enhance its competitive positioning and competitive advantage.
Strategic thinking involves the understanding of basic economics of business; identifying one’s sources of competitive advantage, and allocating resources to ensure that ones distinctive capabilities remain strong.
-
Structure - The organizational chart of the company
Structure defines how people, tasks, work is organized and represents the way business divisions and units are organized and includes the information of who is accountable to whom. In other words, structure is the organizational chart of the firm. It is also one of the most visible and easy to change elements of the framework. Structure allow the firm to focus on areas that are deemed important for its evolution. This includes division of activities; integration and coordination mechanisms. Functional superiority can only be achieved if there is enough reliability and focus within each business unit.
-
Systems - The decision making procedures of the company
Systems refer to policies and procedures that govern the way in which the organization acts within itself and its external environment. These processes and information flows link the organization together and used by staff to get the work done. This includes computer systems, operational systems, HR systems, etc., which reveal business’ daily activities and how decisions are made. Systems do not only refer to hard copy reports and procedures but also to
informal mechanisms such as meetings and conflict management routines.
Soft Elements - Software of Organizational Success
-
Style - The management style of the company
Style represents the way the company is managed by top-level managers, how they interact, what actions do they take and their symbolic value. How managers behave, leadership style, unwritten norms of behavior and organizational culture etc.
-
Staff - The employees of the company
This element is concerned with how the company develops managers (current and future) and employees. Their selection, training, reward and recognition, retention, motivation and assignment to work etc. Identifying what type and how many employees an organization will need and how they will be recruited, trained and deployed.
-
Shared Values - The key beliefs and aspirations and guiding values of the company
These values define the firm's key beliefs and aspirations that form the core of its corporate culture. These values shapes the organizational culture as the employees share the same goals guiding values. Values act as an organization's conscience, providing guidance in times of crisis and are the foundation of every organization.
Values are intangibles that affects employees (treating them with dignity), customers (treating them with fairness) and society (making a social contribution).
-
Skills - The dominant capabilities of the company
Dominant attributes, competence or capabilities that exist in the organization. It refers to the fact that employees have the skills necessary to execute company’s strategy. Skills enables its employees to achieve its objectives.
Organization is a system of consciously coordinated activities of two or more persons in order to achieve a common goal. As per the model these seven internal aspects of an organization need to be aligned if it is to be successful. The 7Ss framework provides a useful framework for analyzing the strategic attributes of an organization. Whatever the type of change – restructuring, new processes, organizational merger, new systems, change of leadership, and so on – the model can be used to understand how the organizational elements are interrelated, and to ensure that the wider impact of changes made in one area is taken into consideration. The model can be applied to many situations and is a valuable tool when organizational design is at question.
The most common uses of the framework are:
- To facilitate organizational change
- To help implement new strategy
- To identify how each area may change in a future
- To facilitate the merger of organizations
Organizational structure aligns and relates parts of an organization, so it can achieve its maximum performance.
Organizational structure sets out who does what within a company and specifies who answers to whom.
A strategic, carefully planned organizational structure helps a business run effectively and efficiently.
It helps determine how your products are produced, distributed, marketed and sold.
Structure is also dependent on your company’s unique mission and goals.
Regardless of the type of structure you choose, you’ll find key elements that they all have in common.
One of the most important components of your organizational structure is defining who’s in charge.
It’s important that you have a clear defined chain of command.
How and where your products or services are produced is also considered within your business structure.
An organization’s structure also maps out how products are delivered to customers.
Each of these elements affects how workers engage with each other, management and their jobs in order to achieve the employer’s goals.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Concept of Representative Office
A representative office is the easiest option for a company planning to start its operations in a foreign country. The company need not incorporate a separate legal entity nor trigger corporate income tax, as long as the activities are limited in nature.
-
Multitude of these legal and operational structures clubbed with accounting and reporting needs give rise to many reporting dimensions at which the organization may want to track or report its operational metrics and financial results. This is where business dimensions play a vital role.
-
In some of the ERP tools, there are more than 12 accounting periods in a financial year. This article discusses the concept of accounting calendar and accounting periods. Learn why different companies have different accounting periods. Understand some of the commonly used periods across different organizations and the definition & use of an adjustment period.
-
The purpose of the general ledger is to sort transaction information into meaningful categories and charts of accounts. The general ledger sorts information from the general journal and converts them into account balances and this process converts data into information, necessary to prepare financial statements. This article explains what a general ledger is and some of its major functionalities.
-
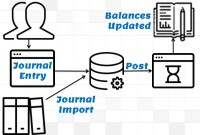
GL - Journal Posting and Balances
In this tutorial, we will explain what we mean by the posting process and what are the major differences between the posting process in the manual accounting system compared to the automated accounting systems and ERPs. This article also explains how posting also happens in subsidiary ledgers and subsequently that information is again posted to the general ledger.
-
A joint venture (JV) is a business agreement in which the parties agree to develop, for a finite time, a new entity and new assets by contributing equity. They exercise control over the enterprise and consequently share revenues, expenses and assets. A joint venture takes place when two or more parties come together to take on one project.
-
In this article, we explain some commonly used subsidiary ledgers like accounts receivable subsidiary ledger, accounts payable subsidiary ledger or creditors' subsidiary ledger, inventory subsidiary ledger, fixed assets subsidiary ledger, projects subsidiary ledger, work in progress subsidiary ledger, and cash receipts or payments subsidiary ledger.
-
Global Business Services (GBS) Model
Global business services (GBS) is an integrated, scalable, and mature version of the shared services model. Global Business Services Model is a result of shared services maturing and evolving on a global scale. It is represented by the growth and maturity of the Shared services to better service the global corporations they support.
-
Hierarchical Organization Structures
Hierarchical structure is typical for larger businesses and organizations. It relies on having different levels of authority with a chain of command connecting multiple management levels within the organization. The decision-making process is typically formal and flows from the top down.
-
GL - Recurring Journal Entries
A “Recurring Journal” is a journal that needs to be repeated and processed periodically. Recurring Entries are business transactions that are repeated regularly, such as fixed rent or insurance to be paid every month. Learn the various methods that can be used to generate recurring journals. See some examples and explore the generic process to create recurring journals in any automated system.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved