- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Business Processes
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- Organizational Design
Organizational Design
An organizational design is the process by which a company defines and manages elements of structure so that an organization can control the activities necessary to achieve its goals. Good organizational structure and design helps improve communication, increase productivity, and inspire innovation. Organizational structure is the formal system of task and activity relationships to clearly define how people coordinate their actions and use resources to achieve organizational goals.
An organizational design is the process by which a company defines and manages elements of structure so that an organization can control the activities necessary to achieve its goals. Good organizational structure and design helps improve communication, increase productivity, and inspire innovation. Organizational structure is the formal system of task and activity relationships to clearly define how people coordinate their actions and use resources to achieve organizational goals. It creates an environment where people can work effectively. Organizing ensures that objectives are achieved in the shortest possible time, in an orderly manner, with maximum utilization of the given resources.
Meaning of Organizational Design
The term ‘organizational design’ refers to how various parts of the organization and distinct organizational elements are brought together. It involves the creation of roles, processes and structures to ensure that the organization’s vision and objectives can be realized. Organization design includes defining arrangement of roles/positions and reporting lines on the organization chart. Decisions made with regard to formal structure, roles and processes directly impact the jobs and careers of employees – and the ability of the firm to realize its strategic objectives. Organization structure refers to the formal, established pattern of relationships amongst the various parts of a firm or any organization. The fact that these relationships are formal implies that they are deliberately specified and adopted and do not evolve on their own.
However, organization design is much more than just formal structures and includes:
- The overall organizational “architecture”
- The design of business areas and business units
- The design of departments and other sub-units within a business unit
- The design of individual roles
- System flows to handle and pass information
- Process and procedures to make decisions; produce results; manage quality;
- Planning, develop and management of resources;
- Innovation and continuous improvement
Why Organizational Design?
Broadly an organization is designed to realize a number of objectives.
These could be:
- To support the organization’s strategy;
- Realization of the organization’s goals and objectives;
- Arrange resources in the most efficient and effective way;
- Effective division of tasks and accountabilities
- Effective co-ordination of the organization’s activities
- Clarify the decision-making processes;
- Lines of communication up, down and across the organization;
- Effective monitoring and review of the organization’s activities;
- Coping with change in internal and external environments;
- Handling of crises and problems;
Considerations for Organizational Design
Following factors play a key role in the organization design:
History
The organization’s present structure may have developed over a number of years, as functions have been added,
changed or deleted. Obviously, the older the organization, the more significant history is likely to be. Initially individuals used to perform the entire operations. With the concept of specialization and division of work, organizations, instead of being designed around individuals, were structured on the basis of different people doing only a specialized part of the entire process.
Technology
The second important factor affecting the structure of your organization is the technology that the company has adopted. Technology refined the traditional individual based processes with the introduction of automation and assembly lines. Now with the introduction of computerization and robots, new structural designs are once again emerging. Entire plants are managed by a single operator who controls the plant operations using computers. Major human inputs are needed in designing computer controls and software rather than in performing repetitive jobs.
Span of Control:
Scalar principle and unity of command are two closely related principles. The scalar principle states that authority should flow in a straight line from the superior to the subordinate in a hierarchical manner. The principle of unity of command states that ideally each subordinate should have only one superior. These two principles establish the basic hierarchical nature of an organization.
The number of levels in the structure, sometimes referred to as the scalar chain, should be as few as possible.
As an organization adds on levels of management it becomes vertical and the span of control at each level becomes narrow. In a flat organization, the span of control is relatively wider and levels of management are few. The span of control, i.e., the number of subordinates directly managed, will vary according to the nature of the jobs and the organization, but it should not be so narrow that it results in a structure with too many levels, or too broad to allow effective management. There should be what has been described as unity of command. For this the reporting positions and authority need to be clearly defined. Every post in the structure should have a clear role and add value to the way the organization functions.
Centralized or Decentralized:
Centralization refers to the concentration of authority and decision-making in one single position in the organization. In a one-man enterprise, the entrepreneur makes all the decisions and all the authority and decision-making power is vested in him. With the expansion of business, it may no longer be possible for one man to control all the operations and may become necessary for him to delegate some responsibility and authority to another person. Delegation implies that you are acting on behalf of your boss by virtue of the power which he has given to you. The greater the delegation of power the greater is the extent of decentralization in the organization.
The extent to which the organization should be centralized or decentralized will need to be determined by reference to a number of factors. These include, the nature and type of industry, geographical dispersion, history, environment, resources available etc.
Some jobs are routine, meaning that employees perform the same tasks all of the time and rely on set rules (standard operating procedures) when exceptions do occur. Almost everything is predictable. These situations, such as automobile assembly lines, have high formalization and centralization as well as standardization of work processes. When employees perform tasks with high variety and low analyzability, they apply their skills to unique situations with little opportunity for repetition. Research project teams operate under these conditions. These situations call for an organic structure, one with low formalization, highly decentralized decision-making authority, and coordination mainly through informal communication among team members.
Operating Environment:
All organizations operate within an environment which comprises economic, social, cultural, political and legal subsystems. A change in any of these sub-systems may force you to change the design of your structure. Organizations, as open systems, need to receive various inputs from the environment and to sell various outputs to their environment. Therefore, it is important to comprehend what the environment is and what elements are likely to be important. To be effective, the overall organization design must be aligned with the business strategy and the market environment in which the business operates.
Customers and Markets
The organization structure is also affected by the type of market and customers it serves, and in a customer-responsive environment this should be one of the main determinants of structure. If the organization is providing services to a broad range of customers in a large number of locations, it may need to have many branch officers, as do Banks, the Post Office and so on.
Processes
The processes used within the organization also affect the structure. A production line process consists of a number of distinct tasks carried out by people specializing in those tasks at different stages of the process. The underlying principle behind this approach is that specialization means people can develop high skills and speed, resulting in high output at low cost. The various parts of the structure could be divided into specialist areas. These specialist areas need to be interlinked.
People
People in the organization affect the structure in a number of ways. Structures do not just appear, they are the result of people’s views and beliefs and their approach to managing the organization. The structure is also be affected by
the types of jobs and people within the organization. Structures with a large number of professionals are more likely to involve team working, and therefore to be relatively flat compared with an organization that has to accommodate a range of jobs from the production line operative to the chairman.
Geography
The geographical spreading of an organization affects its structure mainly because of its need to be near raw materials or customers,. Where there is a significant degree of geographical distribution, there is likely to be more need for careful co-ordination and control than with a single site location. When there is a strong need to provide products or services within a particular geographical area, the organization may be divided into regions or areas, with each being a fully self-contained, miniature version of the parent organization.
Products and Services
The structure may be determined by the particular products and services provided. Large and diverse organizations have separate divisions because they are dealing with very different products and services. Similarly, the Post Office has separate organizations for the various services it provides such as mail delivery (Royal Mail), parcel delivery (Parcel force) and counter services (Post Office Counters Limited).
Summary
Organization design broadly includes how the organization is structured, the types and numbers of jobs , formal system of communication, division of labor, coordination, control, authority, and responsibility essential to attain an organization’s goals. An organization is designed to realize a number of objectives.
The primary factors that often affect organization design are size, environment, business strategy, and technology. However several other factors such as history of the organization, its products and services, processes, coverage of customers, people, geographical spreading etc. also affect the organization design.
An organizational design is the process by which a company defines and manages elements of structure so that an organization can control the activities necessary to achieve its goals. Good organizational structure and design helps improve communication, increase productivity, and inspire innovation. Organizational structure is the formal system of task and activity relationships to clearly define how people coordinate their actions and use resources to achieve organizational goals. It creates an environment where people can work effectively. Organizing ensures that objectives are achieved in the shortest possible time, in an orderly manner, with maximum utilization of the given resources.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
In this article we will help you understand the double-entry accounting system and state the accounting equation and define each element of the equation. Then we will describe and illustrate how business transactions can be recorded in terms of the resulting change in the elements of the accounting equation.
-
A Company (also called corporation) may be understood as an association of persons in which money is contributed by them, to carry on some business or undertaking. Persons who contribute the money are called the shareholders or the members of the company. A corporation is an artificial being, invisible, intangible and existing only in contemplation of law. Being the mere creature of law, it possesses only those properties which the charter of its creation confers upon it.
-
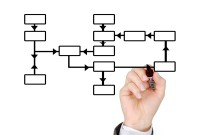
Divisional Organizational Structures
The divisional structure or product structure consists of self-contained divisions. A division is a collection of functions which produce a product. It also utilizes a plan to compete and operate as a separate business or profit center. Divisional structure is based on external or internal parameters like product /customer segment/ geographical location etc.
-
In this article we will discuss various types of "Management Entities". Various types of operational units, are created by management, to effectively run, manage and control their business. Different types of functional units, and divisional units, are widely used across industry.
-
Understand what we mean by GAAP to STAT adjustments. This article discusses the different standards that are used for multiple representations of the financial results for global organizations. Understand the meaning of US GAAP, Local GAAP, STAT, IFRS, and STAT. Finally, understand why accounting differences arise and how they are adjusted for different financial representations.
-
GL - Different Type of Journals
Two basic types of journals exist: general and special. In this article, the learner will understand the meaning of journalizing and the steps required to create a journal entry. This article will also discuss the types of journals and will help you understand general journals & special journals. In the end, we will explain the impact of automated ERPs on the Journalizing Process.
-
In this article, we explain some commonly used subsidiary ledgers like accounts receivable subsidiary ledger, accounts payable subsidiary ledger or creditors' subsidiary ledger, inventory subsidiary ledger, fixed assets subsidiary ledger, projects subsidiary ledger, work in progress subsidiary ledger, and cash receipts or payments subsidiary ledger.
-
In this article, we will describe how to determine if an account needs adjustment entries due to the application of the matching concept. Learners will get a thorough understanding of the adjustment process and the nature of the adjustment entries. We will discuss the four types of adjustments resulting from unearned revenue, prepaid expenses, accrued expenses, and accrued revenue.
-
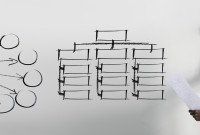
Hierarchical Organization Structures
Hierarchical structure is typical for larger businesses and organizations. It relies on having different levels of authority with a chain of command connecting multiple management levels within the organization. The decision-making process is typically formal and flows from the top down.
-
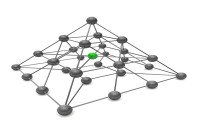
Network Organizational Structures
The newest, and most divergent, team structure is commonly known as a Network Structure (also called "lean" structure) has central, core functions that operate the strategic business. It outsources or subcontracts non-core functions. When an organization needs to control other organizations or agencies whose participation is essential to the success, a network structure is organized.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved