- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Functional
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
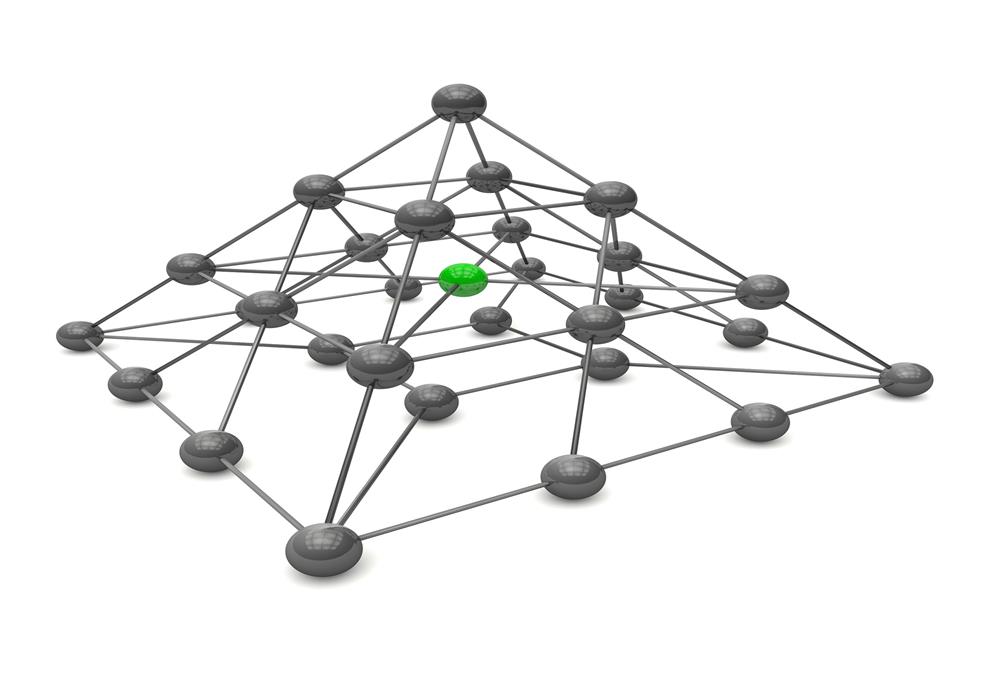
- Network Organizational Structures
Network Organizational Structures
The newest, and most divergent, team structure is commonly known as a Network Structure (also called "lean" structure) has central, core functions that operate the strategic business. It outsources or subcontracts non-core functions. When an organization needs to control other organizations or agencies whose participation is essential to the success, a network structure is organized.
The newest, and most divergent, team structure is commonly known as a Network Structure (also called "lean" structure) has central, core functions that operate the strategic business. It outsources or subcontracts non-core functions. When an organization needs to control other organizations or agencies whose participation is essential to the success, a network structure is organized. In this, the main organization creates a network of relevant agencies and it influences in different ways.
A network structure has little bureaucracy and features decentralized decision making. This structure is very flexible, and it can adapt to new market challenges almost immediately. Flexibility is one of the main reasons why firms pursue network organizational structure in the first place. This allows them to change its production techniques, quantity, products’ designs or stop the production completely without facing any major problems.
Such an organization works like an advanced computer network where many autonomous organizational units interact with each other and the external world to deliver outcomes. Goals and strategy is set by central management but there involvement is limited to building on the capabilities of network units and monitoring progress. Network structure is widely used in non-business organizations which have sociopolitical objectives.
For instance, the National Industrial Development Corporation assigned with the task of rapid industrial development in the country may resort to a network structure in their objective to build an industrial estate. They will act as the lead agency and involve the various other agencies like Electricity Boards, Municipal Authorities, Land Development Authorities, Authorities for Water & Sewage Control, Department for communication facilities etc. They will also need to establish a network with people who would ultimately be using the industrial estate. It would also use the services of an advertising agency to promote the industrial estate and attract maximum number of entrepreneurs. For the construction of sheds and factories they may have to utilize the services of private construction agencies. Thus, a network structure envisages the utilization of a number of different services offered by different agencies. There is need to coordinate the different inputs and synchronize them towards the ultimate objective.
A network structure is meant to promote communication and the free flow of information between different parts of the organization as needed. Managers coordinate and control relations both internal and external to the firm. A social structure of interactions is fostered to build and manage formal and informal relationships. The goal of this structure is to achieve rapid organizational evolution and adaptation to constantly changing external and internal environments. But there's an almost inevitable loss of control due to its dependence on third parties, and all the potential problems that come from managing outsourced or subcontracted teams.
An organization that has been using network structure is H&M (Hennes & Mauritz), a very popular brand that has followers world over. H&M has outsourced the production and processing of their goods to different countries majorly Asian and South East Asian countries. H&M is the core company in its case. As it can be seen, the core company distributes its functions to different companies which, in this case, are present in different countries: product development company in Australia, Call center company in New Zealand, the Accounting company in Australia, Distribution company in Singapore and Manufacturing company in Malaysia.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
A subsidiary is a company that is completely or partly owned by another corporation that owns more than half of the subsidiary's stock, and which normally acts as a holding corporation which at least partly or wholly controls the activities and policies of the daughter corporation.
-
Learn the typical accounting cycle that takes place in an automated accounting system. We will understand the perquisites for commencing the accounting cycle and the series of steps required to record transactions and convert them into financial reports. This accounting cycle is the standard repetitive process that is undertaken to record and report accounting.
-
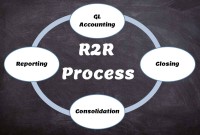
Record to report (R2R) is a finance and accounting management process that involves collecting, processing, analyzing, validating, organizing, and finally reporting accurate financial data. R2R process provides strategic, financial, and operational feedback on the performance of the organization to inform management and external stakeholders. R2R process also covers the steps involved in preparing and reporting on the overall accounts.
-
In this article, we will describe how to determine if an account needs adjustment entries due to the application of the matching concept. Learners will get a thorough understanding of the adjustment process and the nature of the adjustment entries. We will discuss the four types of adjustments resulting from unearned revenue, prepaid expenses, accrued expenses, and accrued revenue.
-
For any company that has a large number of transactions, putting all the details in the general ledger is not feasible. Hence it needs to be supported by one or more subsidiary ledgers that provide details for accounts in the general ledger. Understand the concept of the subsidiary ledgers and control accounts.
-
In some of the ERP tools, there are more than 12 accounting periods in a financial year. This article discusses the concept of accounting calendar and accounting periods. Learn why different companies have different accounting periods. Understand some of the commonly used periods across different organizations and the definition & use of an adjustment period.
-
Business Metrics for Management Reporting
Business metric is a quantifiable measure of an organization's behavior, activities, and performance used to access the status of the targeted business process. Traditionally many metrics were finance based, inwardly focusing on the performance of the organization. Businesses can use various metrics available to monitor, evaluate, and improve their performance across any of the focus areas like sales, sourcing, IT or operations.
-
In this article we will help you understand the double-entry accounting system and state the accounting equation and define each element of the equation. Then we will describe and illustrate how business transactions can be recorded in terms of the resulting change in the elements of the accounting equation.
-
General Ledger - Advanced Features
Modern automated general ledger systems provide detailed and powerful support for financial reporting and budgeting and can report against multiple legal entities from the single system. These systems offer many advanced functionalities right from journal capture to advanced reporting. This article will provide an overview of some advanced features available in today's General Ledgers.
-
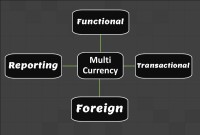
Multi Currency - Functional & Foriegn
Currency is the generally accepted form of money that is issued by a government and circulated within an economy. Accountants use different terms in the context of currency such as functional currency, accounting currency, foreign currency, and transactional currency. Are they the same or different and why we have so many terms? Read this article to learn currency concepts.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved