- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Leadership
- Leadership Theories
- Behavioral Theories of Leadership
Behavioral Theories of Leadership
Behavioral Theory of leadership is a big leap from Trait Theory, as it was developed scientifically by conducting behaviour focused studies. The theory emphasizes that leadership capability can be learned, rather than being inherent. This theory is based on the principle that a leader's behaviors can be conditioned in a manner that one can have a specific response to specific stimuli.
Behavioral Theories of Leadership, also known as “The style approach to leadership” focuses on the behavior of the leader and what leaders do and how they act. In the 1940s, two parallel studies on leadership were in progress, one based on traits displayed by leaders, another on the behaviours exhibited by leaders.
- Traits theory assumes that leaders are born, rather than made
- Trait theory concentrates on, what the leaders are
- Great Man Theory and Traits Theory are focused on intrinsic personal characteristics
- Behavioural theories are based upon the belief that great leaders are made, not born
- Behavioural theories concentrate on, what leaders do
- Behavioral approach is based on the leader's beliefs, values, and interpersonal relations
- Considers the Leader's attitude, behavior, opinion, and concern about his followers/organization
- Studies leadership behavior from the point of view of motivation, supervision, and authority
- Behavioural theories assume that specific behavioral patterns of leaders can be acquired
- People can learn to become leaders through teaching and observation.
What are Behaviors?
Behavior is the range of actions and mannerisms made by organisms, systems, or artificial entities in conjunction with their environment, which includes the other systems or organisms around as well as the physical environment.
What is Human Behaviors?
Human behavior refers to the range of behaviors exhibited by humans and which are influenced by culture, attitudes, emotions, values, ethics, authority, rapport, hypnosis, persuasion, coercion and/or genetics. In humans, behavior is believed to be controlled primarily by the endocrine system and the nervous system. Behaviors can be either innate or learned.
Human behavior is experienced throughout an individual’s entire lifetime. It includes the way they act based on different factors such as genetics, social norms, core faith, and attitude. Behavior is impacted by certain traits each individual has. The traits vary from person to person and can produce different actions or behavior from each person.
As the questions about how to measure traits continued to challenge trait theory, researchers began thinking about measuring behavior. While you can’t easily measure confidence or honesty in a person, they noted, you can define a behavior or a set of behaviors that seem to embody the trait.
Beliefs are ideas that people have about the world around them and how it operates. People tend to behave according to their beliefs. Values are assessments of the goodness or badness of various features of one's life. Values form attitudes that guide a person's conduct. Beliefs and values have close interaction. Beliefs become values when they lead to certain favorable or unfavorable consequences.
Researchers define behaviors as observable actions, which makes measuring them more scientifically valid than trying to measure a human personality trait. In this theory, we will focus on two general kinds of behaviors by leaders called task behaviors and relationship behaviors.
What is Behavioral Theory of Leadership?
Behavioral Theory of Leadership is a leadership theory that considers the observable actions and reactions of leaders and followers in a given situation. Behavioral theories focus on how leaders behave and assume that leaders can be made, rather than born, and successful leadership is based on definable, learnable behavior. Behavioral theories of leadership are classified as such because they focus on the study of specific behaviors of a leader. For behavioral theorists, a leader behavior is the best predictor of his leadership influences and as a result, is the best determinant of his or her leadership success.
These theories concentrate on what leaders actually do rather than on their qualities. Different patterns of behavior are observed and categorized as 'styles of leadership'. This area has probably attracted the most attention from practicing managers.
Quotes on behaviors:
“No one really knows why humans do what they do.”
David K. Reynolds
“If you want to change attitudes, start with a change in behavior.”
William Glasser
““Behavior is the mirror in which everyone shows their image.”
Johann Wolfgang von Goethe
“It's better to hang out with people better than you. Pick out associates whose behavior is better than yours and you'll drift in that direction.”
Warren Buffett
Overview of Behavioral Theory of Leadership:
Behavioral Theory of leadership is a big leap from Trait Theory, in that it assumes that leadership capability can be learned, rather than being inherent. This theory is based on the principle that behaviors can be conditioned in a manner that one can have a specific response to specific stimuli. Rather than seeking inborn traits this theory looks at what leaders actually do by studying their behaviors in response to different situations, assessing leadership success by studying their actions, and then correlating significant behaviors with success.
The practical application of the theory is that leader’s behavior affects their performance and different leadership behaviors could be appropriate at different times. The best leaders are those who have the adaptability to flex their behavioral style and choose the right style suitable for each situation.
According to this theory, people can learn to become leaders through teaching and observation and certain behavioral patterns may be identified as leadership styles.
Advantages of Behavioral Theory of Leadership:
Behavioral theory promotes the value of leadership styles with an emphasis on concern for people and collaboration. It promotes participative decision making and team development by supporting individual needs and aligning individual and group objectives.
It helps managers evaluate and understand how their behavioral style as a manager affects their relationship with the team and promotes commitment and contribution towards organizational goals.
This theory helps managers find the right balance between different styles of leadership, and helps them decide how to behave as a leader, depending on concerns for people and for productivity.
Criticism / Arguments against - Behavioral Theory of Leadership:
As there were inherent limitations with the Trait approach to leadership, when early researchers ran out of steam in their search for traits, they turned to what leaders did, how they behaved, and came with behavioral theory of leadership. This became the dominant way of approaching leadership within organizations in the 1950s and early 1960s but this theory too had its own limitations.
Behavioral Theory of Leadership proposes leadership styles but a specific leadership style may not be best in all circumstances. When researchers really got to work on this it didn’t seem to validate their assumptions. While behavioral theories may help managers develop particular leadership behaviors but they provide little guidance as to what constitutes effective leadership in different situations.
There were lots of differences and inconsistencies between studies. It was difficult to say which style of leadership was significant in enabling one group to work better than another. The styles that leaders can adopt are far more affected by those they are working with, and the environment they are operating within than had been originally thought. Most researchers today conclude that no one leadership style is right for every manager under all circumstances.
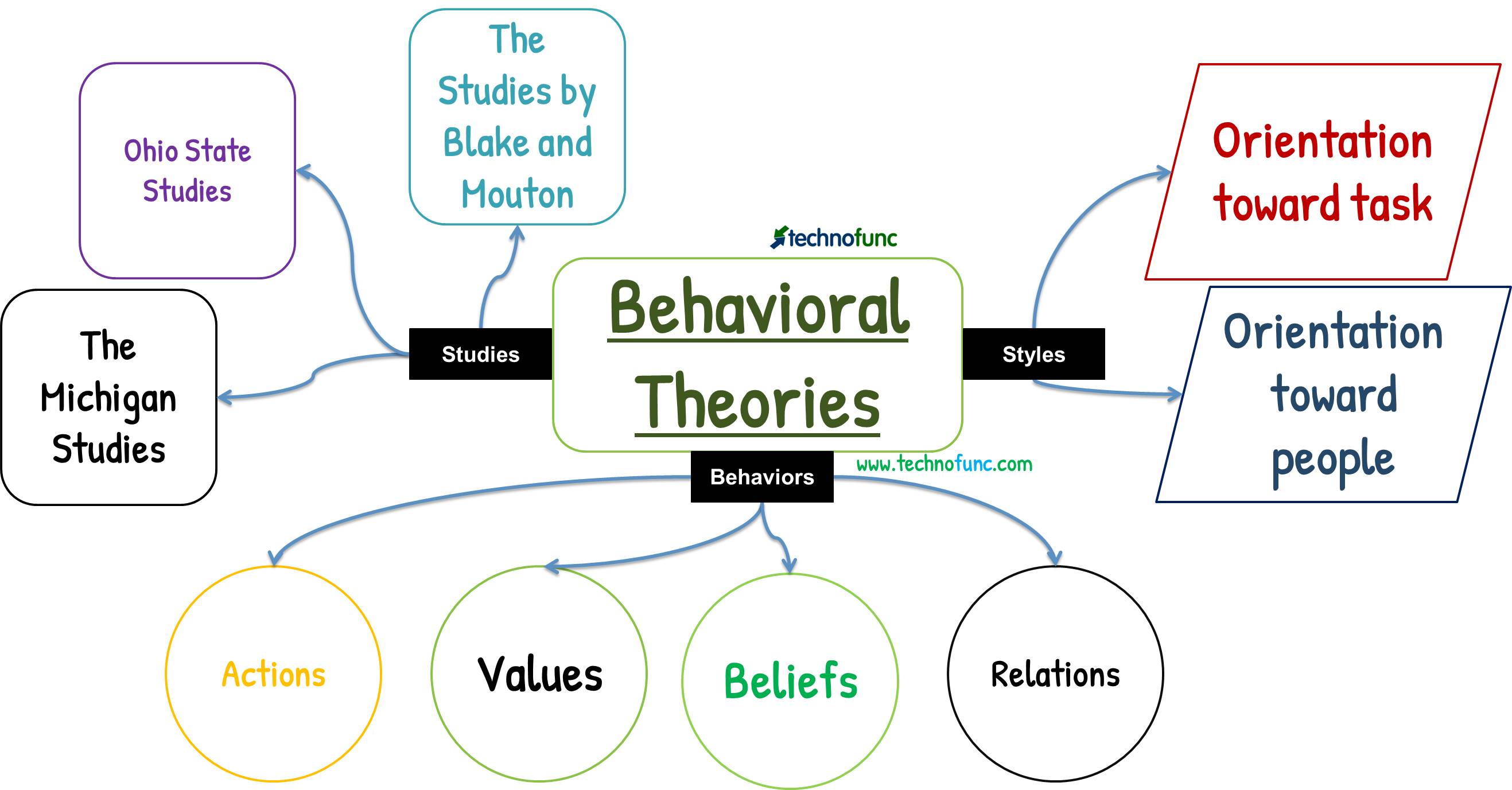
Two Important Behavioral Studies:
The first and foremost study on leadership was carried out by a psychologist, Kurt Lewin, and his associates in 1939 and identified different styles of leadership, viz. autocratic, democratic, and laissez-faire leadership. Subsequently, many research studies could be categorized under the heading of the behavioral approach leading to the identification of various leadership styles and their correlation with measures of effectiveness. The following three studies are strongly representative of the ideas in this approach:
By looking closely at each of these groups of studies, we can draw a clearer picture of the key concepts and implications of the style/behavioral approach to leadership.
Of these three the two Key Studies in behavioral theory at the University of Michigan and Ohio State University became famous in the next generation of leadership research. These studies identified two key behavioral categories
- Orientation toward task: Task behaviors facilitate goal accomplishment and help the team to achieve its objectives.
- Orientation toward people: Relationship behaviors help team members feel comfortable with themselves, with each other, and with the situation in which they find themselves.
List of Behavioral Theories:
Given below is a list of theories and articles that are also classified under behavioral theories or should be read to understand behavioral theories:
- Action Centered Leadership
- Continuum of leadership
- Four Factor Leadership Theory
- Freud Personality Types
- Functional leadership theory
- Iowa Studies
- Jung Personality Types
- Katz’s Three-Skill Approach
- Lewin’s Change Management Model
- Likerts Management System
- Managerial Grid Theory
- McGregor's Theory X and Theory Y
- Michigan Studies
- Ohio State Studies
- Psychodynamic Approach
- Skills Approach to Leadership
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
McGregor's Theory X and Theory Y
McGregor created Theory X and Theory Y of human work motivation and explained two styles of management known as authoritarian (Theory X) and participative (Theory Y). Theory X management assumes most people will attempt to avoid work whereas Theory Y managers trust their people to take ownership of their work.
-
In this study of power, Raven identified five bases of power as coercive, reward, legitimate, referent, and expert. The 5 Types of Power can help you decide when it is appropriate to use a particular type of power in important situations. Leadership involves authority and it is very important for leaders to understand what type of power they're using.
-
The open systems model of leadership acknowledges the influence of the environment on organizations. An open system regularly exchanges feedback with its external environment. The environment also provides key resources that are necessary to sustain and lead to change and survival. Leadership in an open system should focus on influence, open communication, and patterns to control expanding the number of variables created by external dynamics.
-
University of Iowa Studies was the first leadership study to analyze leadership using scientific methodology. The study was conducted by Lewin, Lippitt, and White and worked on different styles of leadership. The studies explored three leadership styles - authoritarian, democratic, and laissez-fair leaders. This early study was very influential and established three major leadership styles.
-
Action Centered Leadership is a model developed by John Adair and focuses on the three responsibilities of a leader which are achieving the task, managing the team, and managing individuals. All these action elements are mutually dependent and important for any leader.
-
Have you ever resonated that there seem to be as many different ways to lead people as there have been great leaders? When we recall the success of Mahatma Gandhi, Nelson Mandela, Abraham Lincoln, Napoleon Bonaparte to Steve Jobs and Jack Welch, we also notice that they all used different approaches that were suitable to their specific situations and circumstances. Over the last century, researchers and psychologists have developed simple ways to describe the “Styles of leadership” and in this section, we will explore these commonly known leadership styles.
-
The two-factor theory also known as Herzberg's motivation-hygiene theory and dual-factor theory. This motivator-hygiene theory states that certain factors cause job satisfaction whereas certain separate factors cause dissatisfaction in the workplace. An organization can adjust these factors to influence motivation. These factors are respectively termed as motivators and hygiene factors.
-
Leadership traits refer to personal qualities that define effective leaders. Here are the major leadership qualities that can make someone a good leader. Five key traits that are common in leaders can be learned and sharpened with time.
-
Role theory is a concept in sociology and the role theory of leadership borrows these concepts to explain how people adapt to specific organizational and leadership roles. How the leaders and followers in an organizational context define their own roles, define the roles of others, how people act in their roles and how people expect people to act in their roles within the organization.
-
Power is the ability to exercise influence or control over others. Leadership involves authority and it is very important for leaders to understand what type of power they're using. The 5 Types of Power in Leadership are Coercive power, expert power, legitimate power, referent power, and reward power. Authority is the right to command and extract obedience from others. It comes from the organization and it allows the leader to use power.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved










