- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Functional
- HRMS & Payroll
- Digital Age and Dynamic Business Environment
Digital Age and Dynamic Business Environment
The digital age, as per yourdictionary.com is also called the information age, is defined as the time period starting in the 1970s with the introduction of the personal computer with subsequent technology introduced providing the ability to transfer information freely and quickly.
The digital age, as per yourdictionary.com is also called the information age, is defined as the time period starting in the 1970s with the introduction of the personal computer with subsequent technology introduced providing the ability to transfer information freely and quickly.
The time period in which we live now where Internet and email are available is an example of the digital age.
The digital age technologies have displaced established technology resulting in a completely new way of doing business and creating opportunities for emergence of a new industry.
These technologies have disrupted the way traditional companies have conducted businesses and both old and new businesses must embrace these disruptive technologies to stay relevant and to meet customer needs.
Here are a few examples of disruptive technologies in 1990’s that transformed established businesses to newer ways of working:
- personal computer replaced typewriter
- Internet enabled Email replaced letter-writing disrupting greeting card industries.
- Cell phones enabled people to call anywhere disrupting telecom industry.
- Laptop and mobile computing made mobile workforce possible.
- Smartphones disrupted pocket cameras, MP3 players, calculators and GPS devices,
- Social networking disrupted telephone, email, instant messaging and event planning.
The last decade has seen an increased intensity in industrial competition, in which cycle times are shrinking and the volatility, uncertainty, complexity, and ambiguity have opened opportunities and challenges alike
The above listed are just a few examples of disruptions in the 1990’s that have set the stage for continuous evolution in technology to what is observed today. Business services functions – finance, human resources, procurement and IT – are under pressure to adapt the way they deliver services to the demands of the digital age.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Legal Structures for Multinational Companies
A multinational company generally has offices and/or factories in different countries and a centralized head office where they coordinate global management. A multinational company (MNC)is a corporate organization that owns or controls the production of goods or services in at least one country other than its home country.
-
Multitude of these legal and operational structures clubbed with accounting and reporting needs give rise to many reporting dimensions at which the organization may want to track or report its operational metrics and financial results. This is where business dimensions play a vital role.
-
In this article, we explain some commonly used subsidiary ledgers like accounts receivable subsidiary ledger, accounts payable subsidiary ledger or creditors' subsidiary ledger, inventory subsidiary ledger, fixed assets subsidiary ledger, projects subsidiary ledger, work in progress subsidiary ledger, and cash receipts or payments subsidiary ledger.
-
Divisional Organizational Structures
The divisional structure or product structure consists of self-contained divisions. A division is a collection of functions which produce a product. It also utilizes a plan to compete and operate as a separate business or profit center. Divisional structure is based on external or internal parameters like product /customer segment/ geographical location etc.
-
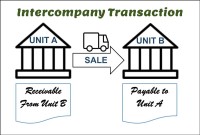
After reading this article the learner should be able to understand the meaning of intercompany and different types of intercompany transactions that can occur. Understand why intercompany transactions are addressed when preparing consolidated financial statements, differentiate between upstream and downstream intercompany transactions, and understand the concept of intercompany reconciliations.
-
Although technically a general ledger appears to be fairly simple compared to other processes, in large organizations, the general ledger has to provide many functionalities and it becomes considerably large and complex. Modern business organizations are complex, run multiple products and service lines, leveraging a large number of registered legal entities, and have varied reporting needs.
-
In this article, we will explain the general Ledger journal processing flow from entering journals to running the final financial reports. Understand the generic general ledger process flow as it happens in automated ERP systems. The accounting cycle explains the flow of converting raw accounting data to financial information whereas general ledger process flow explains how journals flow in the system.
-
GL - Different Accounting Methods
The accounting method refers to the rules a company follows in reporting revenues and expenses. Understand the two common systems of bookkeeping, single, and double-entry accounting systems. Learners will also understand the two most common accounting methods; cash and accrual methods of accounting and the advantages and disadvantages of using them.
-
Team-Based Organizational Structure
Team-based structure is a relatively new structure that opposes the traditional hierarchical structure and it slowly gaining acceptance in the corporate world. In such a structure, employees come together as team in order to fulfill their tasks that serve a common goal.
-
Hierarchical Organization Structures
Hierarchical structure is typical for larger businesses and organizations. It relies on having different levels of authority with a chain of command connecting multiple management levels within the organization. The decision-making process is typically formal and flows from the top down.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved