- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Industry Knowledge
- Banking Domain
- Types of Banks: Different Banks & their Classifications (Global)
Types of Banks: Different Banks & their Classifications (Global)
The banking industry caters to various sections of society thus the focus of banking becomes varied, catering to the diverse needs of clients through different products, services, and methods. To meet this, we need distinctive kinds of banks addressing complex business & social needs. In this article, we will explain various types of banking institutions ranging from retail banks, commercial banks, co-operative banks, investment banks, central banks to various other types of specialized banks.
The focus of banking is varied, the needs diverse and methods different. Banking institutions offer an assortment of services from deposits in savings accounts to housing and business loans to check clearing, underwriting, and credit cards. The world is fast-changing and globalization in conjunction with technological advances is changing the landscape of the banking industry. Both individuals and business customers are demanding faster and innovative products & services. The banking industry is also heavily regulated and has its own share of challenges to deliver financial objectives to people and organizations.
Thus, distinctive kinds of banks are evolving to cater to various business demands, social needs, and global complexities. These different banking institutions conduct their operations in a different manner. However, on the basis of their functions, clientele served and products or services offered, we can classify banks as follows:
Basis of Products/Services
Retail Banks
Commercial banks
Investment Banks
Basis of Statue
Cooperative banks
Central banks
Specialized banks
1. Retail Banks:
 Retail banks provide basic banking services to individual consumers. Examples include savings accounts, recurring and fixed deposits and secured and unsecured loans. Products and services offered by retail banks include safe deposit boxes, checks and savings accounting, certificates of deposit (CDs), mortgages, consumer and car loans, personal credit cards, etc. The objective of retail banks is to provide services to individuals rather than commercial clients. They can be found in highly residential areas catering to the day to day banking needs of the public. They may additionally offer wealth management and consultancy to their clients. Some common examples of retail banks are community development banks, private banks, savings banks, and postal saving banks. They are explained below:
Retail banks provide basic banking services to individual consumers. Examples include savings accounts, recurring and fixed deposits and secured and unsecured loans. Products and services offered by retail banks include safe deposit boxes, checks and savings accounting, certificates of deposit (CDs), mortgages, consumer and car loans, personal credit cards, etc. The objective of retail banks is to provide services to individuals rather than commercial clients. They can be found in highly residential areas catering to the day to day banking needs of the public. They may additionally offer wealth management and consultancy to their clients. Some common examples of retail banks are community development banks, private banks, savings banks, and postal saving banks. They are explained below:
-
Community Development Banks
Provide services to underserved markets or populations, example Rural Banks in India, generally incentivized and regulated by the government.
-
Private Banks:
Some private retail banks manage the assets of high-net-worth individuals and provide specialized services like wealth management.
-
Savings Banks:
These are deposit oriented branches, also could be an extension counter of an existing bank branch that accept savings deposits and provide basic banking.
-
Postal Saving Banks:
Postal banks are the banks operated and controlled by National Postal Departments and provide basic banking services to retail customers. These banks are very effective in small towns and villages and provide financial inclusion to a section of society which otherwise would not have been catered by other banks.
2. Commercial Banks:
 Banking means accepting deposits of money from the public for the purpose of lending or investment. Deposit-taking institutions take the form of commercial banks, which accept deposits and make commercial, real estate, and other loans. Commercial banks in modern capitalist societies act as financial intermediaries, raising funds from depositors and lending the same funds to borrowers. The depositors’ claims against the bank, their deposits, are liquid, meaning banks are expected to redeem deposits on demand, instantly. Banks’ claims against their borrowers are much less liquid, giving borrowers a much longer span of time to repay money owed banks. Because a bank cannot immediately reclaim money lent to borrowers, it may face bankruptcy if all its depositors show up on a given day to withdraw all their money. The commercial bank serves the interests of its depositors by utilizing the funds collected in profitable ventures and in-return offers a variety of services to its customers.
Banking means accepting deposits of money from the public for the purpose of lending or investment. Deposit-taking institutions take the form of commercial banks, which accept deposits and make commercial, real estate, and other loans. Commercial banks in modern capitalist societies act as financial intermediaries, raising funds from depositors and lending the same funds to borrowers. The depositors’ claims against the bank, their deposits, are liquid, meaning banks are expected to redeem deposits on demand, instantly. Banks’ claims against their borrowers are much less liquid, giving borrowers a much longer span of time to repay money owed banks. Because a bank cannot immediately reclaim money lent to borrowers, it may face bankruptcy if all its depositors show up on a given day to withdraw all their money. The commercial bank serves the interests of its depositors by utilizing the funds collected in profitable ventures and in-return offers a variety of services to its customers.
Services provided by commercial banks include credit and debit cards, bank accounts, deposits and loans, and deposit mobilization. They also provide secured and unsecured loans. These commercial banks are the oldest institutions in banking history and generally have a wide network of branches spread throughout the area of their operations.
Commercial banks may either be owned by the government or maybe run in the private sector. Based on their ownership structure they can be classified as public sector and private sector banks.
Public Sector Banks:
 Public sector banks are those in which the government has a major stake and they usually need to emphasize social objectives than on profitability. The main objectives of public sector banks is to ensure there is no monopoly and control of banking and financial services by few individuals or business houses and to ensure compliance with regulations and promote the needs of the underprivileged and weaker sections of society, cater to the needs of agriculture and other priority sectors and prevent the concentration of wealth and economic power. These banks play a revolutionary role in lending, particularly to the priority sector, constituting of agriculture, small-scale industries, and small businesses. In India, there are 27 public sector banks that have been nationalized by the government to protect the interests of the majority of the citizens. Some examples are State Bank of India, Union Bank of India, etc.
Public sector banks are those in which the government has a major stake and they usually need to emphasize social objectives than on profitability. The main objectives of public sector banks is to ensure there is no monopoly and control of banking and financial services by few individuals or business houses and to ensure compliance with regulations and promote the needs of the underprivileged and weaker sections of society, cater to the needs of agriculture and other priority sectors and prevent the concentration of wealth and economic power. These banks play a revolutionary role in lending, particularly to the priority sector, constituting of agriculture, small-scale industries, and small businesses. In India, there are 27 public sector banks that have been nationalized by the government to protect the interests of the majority of the citizens. Some examples are State Bank of India, Union Bank of India, etc.
Private sector banks:
 The private-sector banks are banks where the majority of their ownership is held by private shareholders and not by the government. Private sector banks are owned, managed and controlled by private promoters and they are free to operate as per market forces. To ensure their safety and smooth functioning there are generally entry barriers and regulatory criteria set like the minimum net worth etc. This ensures safety of public deposits entrusted with such institutions and they are also regulated by guidelines issued by Central Banks from time to time. Some examples of private sector banks in India are ICICI Bank, Yes Bank and Axis Bank.
The private-sector banks are banks where the majority of their ownership is held by private shareholders and not by the government. Private sector banks are owned, managed and controlled by private promoters and they are free to operate as per market forces. To ensure their safety and smooth functioning there are generally entry barriers and regulatory criteria set like the minimum net worth etc. This ensures safety of public deposits entrusted with such institutions and they are also regulated by guidelines issued by Central Banks from time to time. Some examples of private sector banks in India are ICICI Bank, Yes Bank and Axis Bank.
Importance of Commercial Banks:

Commercial banks play a very important role in the economic development of any country as they mobilize deposits that inculcates saving habit in the public. Commercial banks also facilitate payments through cheques and help happening of financial transactions without actual movement of cash providing a layer of security to comfort to such transactions. They also offer variety of business services like offering loans and credit facilities, allowing overdraft facilities, issuing letters of credit & guarantee (LC’s and LG’s). They also provide clearing services like discounting of bills, collection of cheques, drafts & bills of exchange etc. and facilitates remittance and receiving of money on behalf of its customers. The term “bank” has become synonymous nowadays and most often refers to these commercial banks.
The emerging environment offers ample opportunities for banks to venture into new and profitable areas. Also, due to deregulation, commercial banks are also now competing more with investment banks in money market operations, bond underwriting, and financial advisory work.
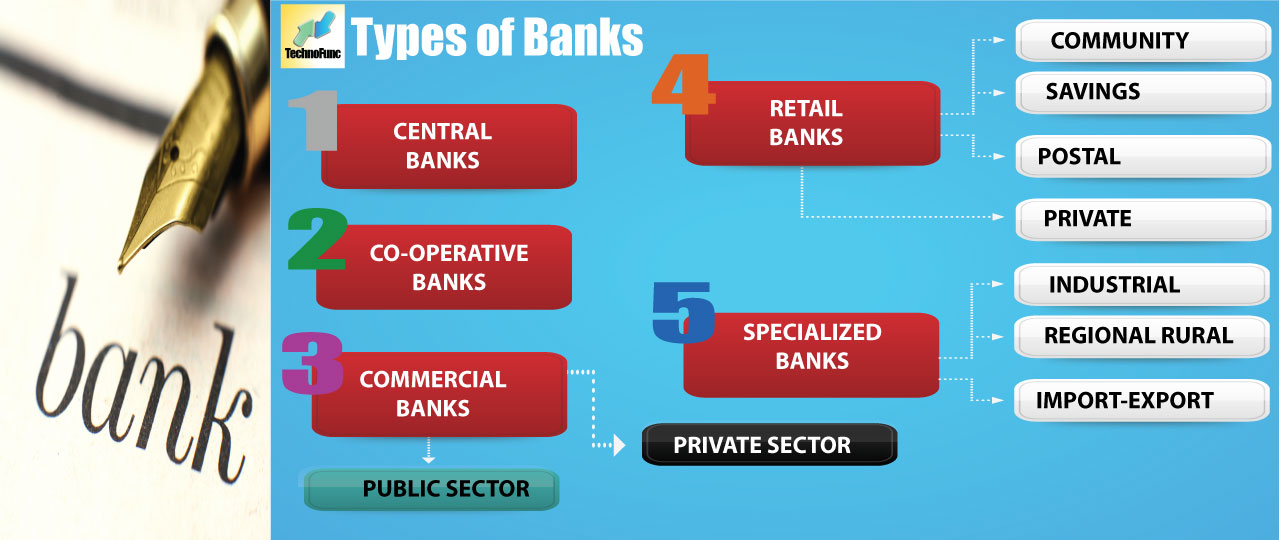
3. Cooperative Banks:
 Cooperative banks are private sector banks. Co-operative banks are also mutual savings banks meant essentially for providing cheap credit to their members. A cooperative bank is a voluntary association of members for self-help and caters to their financial needs on a mutual basis. They accept deposits and make mortgages and other types of loans to their members. These banks are also subject to control and inspection by the Reserve Bank of India but they are generally governed by a different statue, which is more flexible and easy to comply with compared to central bank acts. In India, they are governed by the provisions of the State Cooperative Societies Act. Another type is credit unions, which are cooperative organizations that issue share certificates and make member (consumer) and other loans.
Cooperative banks are private sector banks. Co-operative banks are also mutual savings banks meant essentially for providing cheap credit to their members. A cooperative bank is a voluntary association of members for self-help and caters to their financial needs on a mutual basis. They accept deposits and make mortgages and other types of loans to their members. These banks are also subject to control and inspection by the Reserve Bank of India but they are generally governed by a different statue, which is more flexible and easy to comply with compared to central bank acts. In India, they are governed by the provisions of the State Cooperative Societies Act. Another type is credit unions, which are cooperative organizations that issue share certificates and make member (consumer) and other loans.
These institutions are an important source of rural credit i.e., agricultural financing in India. Co-operative banks get their resources from the issuance of their shares, accepting public deposits, and also taking loans from the state cooperative banks. They also get short and medium-term loans from the Reserve Bank of India. To enhance safety and public confidence in cooperative banks, the Reserve Bank of India has extended the Credit Guarantee Scheme to cooperative banks.
4. Investment Banks:
 An investment bank is a financial institution that assists individuals, corporations, and governments in raising capital by underwriting and/or acting as the client's agent in the issuance of securities. An investment bank may also assist companies involved in mergers and acquisitions, and provide ancillary services such as market making, trading of derivatives, fixed income instruments, foreign exchange, commodities, and equity securities. Investment banks aid companies in acquiring funds and they provide advice for a wide range of transactions. These banks also offer financial consulting services to companies and give advice on mergers and acquisitions and management of public assets.
An investment bank is a financial institution that assists individuals, corporations, and governments in raising capital by underwriting and/or acting as the client's agent in the issuance of securities. An investment bank may also assist companies involved in mergers and acquisitions, and provide ancillary services such as market making, trading of derivatives, fixed income instruments, foreign exchange, commodities, and equity securities. Investment banks aid companies in acquiring funds and they provide advice for a wide range of transactions. These banks also offer financial consulting services to companies and give advice on mergers and acquisitions and management of public assets.
5. Central Banks:
 Every country has a Central Bank of its own generally regulated by a special act. Central banks are bankers’ banks, and these banks trace their history from the Bank of England. It is called a Central Bank because it occupies a central position in the banking system and acts as the highest financial authority. The main function of this bank is to regulate and supervise the whole banking system in the country. It is a banker's bank and controller of credit in the country. They guarantee stable monetary and financial policy from country to country and play an important role in the economy of the country. Typical functions include implementing monetary policy, managing foreign exchange and gold reserves, making decisions regarding official interest rates, acting as banker to the government and other banks, and regulating and supervising the banking industry.
Every country has a Central Bank of its own generally regulated by a special act. Central banks are bankers’ banks, and these banks trace their history from the Bank of England. It is called a Central Bank because it occupies a central position in the banking system and acts as the highest financial authority. The main function of this bank is to regulate and supervise the whole banking system in the country. It is a banker's bank and controller of credit in the country. They guarantee stable monetary and financial policy from country to country and play an important role in the economy of the country. Typical functions include implementing monetary policy, managing foreign exchange and gold reserves, making decisions regarding official interest rates, acting as banker to the government and other banks, and regulating and supervising the banking industry.
These banks buy government debt, have a monopoly on the issuance of paper money, and often act as a lender of last resort to commercial banks. The Central bank of any country supervises controls and regulates the activities of all the commercial banks of that country. It also acts as a government banker. It controls and coordinates the currency and credit policies of any country. In India, the Reserve Bank of India is the central bank. It is the apex bank and the statutory institution in the money market of the country.
6. Specialized Banks:
 Specialized banks are dedicated banks that excel in a particular product, service, or sector and provide mission-based services to a section of society. Some examples of specialized banks are industrial banks, land development banks, regional rural banks, foreign exchange banks, and export-import banks, etc. addressing the specific needs of these unique areas. These banks provide distinctive services or products like financial aid to industries, heavy turnkey projects, and foreign trade. Some specialized banks are discussed below:
Specialized banks are dedicated banks that excel in a particular product, service, or sector and provide mission-based services to a section of society. Some examples of specialized banks are industrial banks, land development banks, regional rural banks, foreign exchange banks, and export-import banks, etc. addressing the specific needs of these unique areas. These banks provide distinctive services or products like financial aid to industries, heavy turnkey projects, and foreign trade. Some specialized banks are discussed below:
Industrial Banks:
 Industrial banks target to promote rapid industrial development. They provide specialized medium and long term loans to the industrial sector backed by consultancy, supervision, and expertise. They support industrial growth by rendering other services like project identification, preparation of project reports, providing technical advice and managerial services, etc. They also do underwriting of public issues by the corporate sector or help industrial units get finance through a consortium or provide a guarantee to other financial institutions. We have a number of such banks in India like the Industrial Development Bank of India (IDB), Industrial Finance Corporation of India (IFCI), Industrial Credit and Investment Corporation of India Ltd. (ICICI), Industrial Reconstruction Bank of India (IRBI), etc.
Industrial banks target to promote rapid industrial development. They provide specialized medium and long term loans to the industrial sector backed by consultancy, supervision, and expertise. They support industrial growth by rendering other services like project identification, preparation of project reports, providing technical advice and managerial services, etc. They also do underwriting of public issues by the corporate sector or help industrial units get finance through a consortium or provide a guarantee to other financial institutions. We have a number of such banks in India like the Industrial Development Bank of India (IDB), Industrial Finance Corporation of India (IFCI), Industrial Credit and Investment Corporation of India Ltd. (ICICI), Industrial Reconstruction Bank of India (IRBI), etc.
Land Development Banks:
 These banks support the development of agriculture and land. They provide long term credit to agriculture for purposes such as pump sets, tractors, digging up wells, land improvement, etc.
These banks support the development of agriculture and land. They provide long term credit to agriculture for purposes such as pump sets, tractors, digging up wells, land improvement, etc.
These banks get funding by issuing debentures, which are generally subscribed by the State Bank Group, other commercial banks, LIC, and Reserve Bank of India. These banks grant loans to farmers against the security of their land.
Regional Rural Banks:
 These banks support small and marginal farmers by extending credit to them in rural areas. They cater to the credit needs of small and marginal farmers, agricultural laborers, artisans, and small entrepreneurs in rural areas. The RRB's are sponsored by scheduled banks, usually a nationalized commercial bank.
These banks support small and marginal farmers by extending credit to them in rural areas. They cater to the credit needs of small and marginal farmers, agricultural laborers, artisans, and small entrepreneurs in rural areas. The RRB's are sponsored by scheduled banks, usually a nationalized commercial bank.
Import – Export Banks:
 Import-Export banks are generally set up by government like central banks to promote trade activities in import and export. They support exporters and importers by providing financial assistance, acting as principal financial institutions, coordinating the working of other institutions engaged in export and import to facilitate the growth of international trade. They provide traditional export finance and also do financing of export-oriented units. The bank finances and insures foreign purchases of goods for customers unable or unwilling to accept credit risk. Some examples are Export-Import Bank of India (Exim Bank), Export-Import Bank of the United States, etc.
Import-Export banks are generally set up by government like central banks to promote trade activities in import and export. They support exporters and importers by providing financial assistance, acting as principal financial institutions, coordinating the working of other institutions engaged in export and import to facilitate the growth of international trade. They provide traditional export finance and also do financing of export-oriented units. The bank finances and insures foreign purchases of goods for customers unable or unwilling to accept credit risk. Some examples are Export-Import Bank of India (Exim Bank), Export-Import Bank of the United States, etc.
Banking Domain Knowledge - Resources
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Definition of Bank: Meaning of the term Bank and the Business of Banking
What do we mean by the word bank? How did the word bank originate? What is the most simple and concise definition of a bank that explains the fundamentals of the banking process? Does the definition of banking vary from country to country? What are the key differentiators between any other business and a Bank? Get answers to all these questions and explore the basics of bank and banking as an industry.
-
History of Banking: Evolution of Banking as an Industry
Banking is one of the oldest industries and banking in the form that we know of began at about 2000BC of the ancient world. It started with merchants making grain loans to farmers and traders while carrying goods between cities. Since then, the banking industry has evolved from a simplistic barter system and gift economies of earlier times to modern complex, globalized, technology-driven, and internet-based e-banking model. In this article, we will take you through the major events and developments in the history of the banking industry.
-
History of Banking: Famous Banks from the Past
Seven hundred years ago a bank was established in Venice, which made transactions resembling modern banking. In 1407, another bank was founded in Italy under the name of Banco di San Giorgio which was one of the oldest chartered banks in Europe. Sveriges Riksbank (Riksbanken), is the central bank of Sweden and the world's oldest central bank. The Bank of England is the second oldest central bank in the world, and most modern central banks have been based on that model. Let us explore some interesting events as we learn more about these early banking institutions.
-
History of Banking: The Gold Standard & Fractional Reserve Banking
Gold has always been considered as a safe economic investment and treated like a currency. All of the economically advanced countries of the world were on the gold standard for a relatively brief time. Under a gold standard, the value of a unit of currency, such as a dollar, is defined in terms of a fixed weight of gold and banknotes or other paper money are convertible into gold accordingly. Explore the fascinating history of the gold standard through the lens of history and also learn why banks hold back a certain fraction of deposits as reserves.
-
Overview of Banking Industry: The Industry Basics
Banks play a key role in the entire financial system by mobilizing deposits from households spread across the nation and making these funds available for investment, either by lending or buying securities. Today the banking industry has become an integral part of any nation’s economic progress and is critical for the financial wellbeing of individuals, businesses, nations, and the entire globe. In this article, we will provide an overview of key industry concepts, main sectors, and key aspects of the banking industry’s business model and trends.
-
Banking Sector, Segments & It's Classifications
The banking industry players deal in a variety of products from savings accounts to loans and mortgages, offer various services from check cashing to underwriting, caters to different types of customers from individuals to large corporates, serve diverse geographies from rural villages to cross-border operations. Thus the banking industry is made up of several types of banks, with their own objectives, roles, and functions. In this article, we will explore the various sectors, segments, and classifications of banking based on parameters like products, customers, types, etc.
-
Type of Banks: Different Types of Banks in India & their Functions
This article explains the banking structure in India and how different banks are classified as per RBI Norms. The Indian banking industry has been divided into two parts, organized and unorganized sectors. The organized sector consists of Reserve Bank of India, Commercial Banks and Co-operative Banks, and Specialized Financial Institutions (IDBI, ICICI, IFC, etc.). The unorganized sector, which is not homogeneous, is largely made up of money lenders and indigenous bankers. Learn what we mean by nationalized banks, scheduled banks, public sector banks, private banks, and foreign banks.
-
Types of Banks: Different Banks & their Classifications (Global)
The banking industry caters to various sections of society thus the focus of banking becomes varied, catering to the diverse needs of clients through different products, services, and methods. To meet this, we need distinctive kinds of banks addressing complex business & social needs. In this article, we will explain various types of banking institutions ranging from retail banks, commercial banks, co-operative banks, investment banks, central banks to various other types of specialized banks.
-
Banking Operations: Understanding Various Transactions & Activities
Banks perform a variety of operations ranging from basic or primary functions like day to day transactions at a branch to others that maybe the agency or general utility services in nature. The transactions that are incidental to revenue/sales or sustaining the business are an important element of the banking industry value chain. In this article, we will look at the key operations performed in the course of banking.
-
Banking Industry Business Model - Understanding How the Banking System Works
Banks are commercial profitable institutions and need to increase their business, grow their revenue, and provide returns to their owners. Unlike other stores and shops, banks are providing services rather than selling their products. Learn how banks get their funds and how they make money on services. Read more to learn how the banks earn their profit!
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved