- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Business Processes
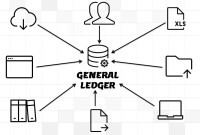
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- Five Core General Ledger Accounts
Five Core General Ledger Accounts
Typically, the accounts of the general ledger are sorted into five categories within a chart of accounts. Double-entry accounting uses five and only five account types to record all the transactions that can possibly be recorded in any accounting system. These five accounts are the basis for any accounting system, whether it is a manual or an automated accounting system. These five categories are assets, liabilities, owner's equity, revenue, and expenses.
The Five Account Types:
The five fundamental account types are the following:
Balance Sheet Accounts:
Funds can be invested by owners or outsiders known as equity & liabilities and can be used to acquire assets to perform business activities. In accounting, the economic resources of a business are categorized under the terms of assets, liabilities, and owner's equity. These terms also refer to the three types of accounts in which a business records its transactions.
1. Asset Accounts:
Assets are the things of value that are owned and used by the business. Examples of assets include cash, land, buildings, and equipment. According to the Financial Accounting Standards Board, assets are “probable future economic benefits obtained or controlled by a particular entity as a result of past transactions or events.” According to “The Institute of Management Accountants” assets is “any owned physical object (tangible) or right (intangible) having economic value to its owners; an item or source of wealth with continuing benefits for future periods, expressed, for accounting purposes, in terms of its cost, or other value, such as current replacement cost. Future periods refer to the following year or years.” An asset is anything that will probably bring future economic benefits. Every employee is responsible to follow policies and procedures to safeguard the company's assets.
2. Liability Accounts:
Liability accounts are debts that are owed by the business. These are the rights of the creditors or third parties over the assets of the business. Examples of liabilities include amounts due to suppliers, loans payable back to banks. The number of funds contributed by outsiders other than owners that are payable to them in the future. Liability is an obligation of an entity arising from past transactions or events, the settlement of which may result in the transfer or use of assets, provision of services, or another yielding of economic benefits in the future. Liabilities are generally classified as Short Term (Current) and Long Term Liabilities. Current liabilities are debts payable within one year, while long-term liabilities are debts payable over a longer period. Liabilities can be from a lot of sources like Loans, External Borrowings, Debt – Secured and Unsecured, Obligation for services received Balance Due or Credit due to Creditors. Some generally known examples of liabilities are any type of borrowing or loans from persons or banks or wages or salaries paid to employees or amounts payable to creditors for their goods and services and taxes payable to Governments.
3. Equity Accounts:
Equity is the owner's claim to business assets. These are the rights of the owners over the assets of the business. Examples include capital invested by the owners, the shares subscribed by the public, or the residual profit made by the business last year. The amount of the funds contributed by the owners (the stockholders) added or subtracted by accumulated gains and losses. Equity is the residual value of the business enterprise that belongs to the owners or shareholders. Funds contributed by owners in any business are different from all other types of funds. Generally, they don’t have any cost of carrying for the business and in the event of winding up of the business, shareholders are entitled to the residual value of the business after discharging all other liabilities. They are expected to remain invested in the business for a long period of time and no immediate payback is anticipated in case of a going concern. Equity accounts are also referred to as “Capital Account”, “Shareholder’s Funds” or “Accounts”, “Stock, Stake” and “Shareholder Equity”. Normally they have a credit balance and are reflected on the left side of the balance sheet. Profits and losses from each accounting year are added to Equity at the end of each year. Balances in the Retained Earnings Account are transferred to “Equity” at the end of each accounting year. While running a revaluation of balances, equity is revalued using the historical rates in accordance with the accounting standards. Equity is a separate account type in ERP’s to segregate funds from owners and others.

Profit and Loss Accounts:
Business operations may result in financial benefits or losses that arise as a difference in revenue gained from business activity and expenses, costs, and taxes needed to sustain the business activity. Any resultant profit or loss goes to the business owner. The operations of the business can either result in profit or loss. It may increase the economic value over a period of time in case of profit or might decrease the economic worth in case of loss. All such activities can be recorded using two types of profit and loss accounts:
4. Revenue Accounts:
Revenue is the increase in benefits during the accounting period. Revenue or income is measured from period to period and provides economic benefits to the company. The amounts earned from the sale of goods and services. Examples include sales, interest received on bank deposits, a commission earned by the business. Revenue accounts are credited when services are performed or billed and therefore will usually have credit balances. On the income statement, net income is computed by deducting all expenses from all revenues. Revenues are presented at the top part of the income statement, followed by the expenses.
5. Expense Accounts:
Expenses refer to costs incurred in conducting business. Technically, expenses are "decreases in economic benefits during the accounting period. Costs incurred in the course of business. Examples include purchases made for material, payment of rent, expenses for employee costs. The normal expense account balance is a debit.
Importance of Core Accounts
All general ledger accounts can be classified as belonging to either one of these categories – Equity, Liabilities, Assets, Revenue, and Expenses. These are the fundamental account types from the perspective of automated accounting systems. Based on this classification, closing balances are never carried forward in automated GL systems for Revenue and Expense Accounts. In ERP’s every account needs to be classified as belonging to one of these classifications.
Whenever IT professional starts working on any financial project, they encounter certain accounts and account types that are always seeded in the system, they are able to perform setups for those accounts after going through the manual of the software package, but usually explanation about the need and role of these accounts is not available in the product manual/guide. In this tutorial we have understood the minimum accounts types that need to be seeded in any financial system and "why" certain accounts have to be mandatory in nature before the automated accounting process can start.
The intended audience for this tutorial is anybody who has a need to work on any financial IT system. This will be helpful to everyone who wants to understand how to design and implement effective automated accounting systems like ERP. This tutorial focuses on these concepts from the perspective of an IT professional that is expected to work on any project involving design, build or interface to an automated GL system, rather than a student of accounting.
There can be thousands of sub-types; known as natural accounts which help in further classifying the nature of the transaction, but they all belong to one of the above lists, as practically all financial transactions can be recorded using these five types of accounts.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
In this article, we will explain the general Ledger journal processing flow from entering journals to running the final financial reports. Understand the generic general ledger process flow as it happens in automated ERP systems. The accounting cycle explains the flow of converting raw accounting data to financial information whereas general ledger process flow explains how journals flow in the system.
-
Although technically a general ledger appears to be fairly simple compared to other processes, in large organizations, the general ledger has to provide many functionalities and it becomes considerably large and complex. Modern business organizations are complex, run multiple products and service lines, leveraging a large number of registered legal entities, and have varied reporting needs.
-
There are five types of core accounts to capture any accounting transaction. Apart from these fundamental accounts, some other special-purpose accounts are used to ensure the integrity of financial transactions. Some examples of such accounts are clearing accounts, suspense accounts, contra accounts, and intercompany accounts. Understand the importance and usage of these accounts.
-
The sole trader organization (also called proprietorship) is the oldest form of organization and the most common form of organization for small businesses even today. In a proprietorship the enterprise is owned and controlled only by one person. This form is one of the most popular forms because of the advantages it offers. It is the simplest and easiest to form.
-
Operational Structures in Business
Large organizations grow through subsidiaries, joint ventures, multiple divisions and departments along with mergers and acquisitions. Leaders of these organizations typically want to analyze the business based on operational structures such as industries, functions, consumers, or product lines.
-
This article explains the process of entering and importing general ledger journals in automated accounting systems. Learn about the basic validations that must happen before the accounting data can be imported from any internal or external sub-system to the general ledger. Finally, understand what we mean by importing in detail or in summary.
-
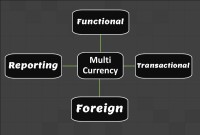
Multi Currency - Functional & Foriegn
Currency is the generally accepted form of money that is issued by a government and circulated within an economy. Accountants use different terms in the context of currency such as functional currency, accounting currency, foreign currency, and transactional currency. Are they the same or different and why we have so many terms? Read this article to learn currency concepts.
-
Global Business Services (GBS) Model
Global business services (GBS) is an integrated, scalable, and mature version of the shared services model. Global Business Services Model is a result of shared services maturing and evolving on a global scale. It is represented by the growth and maturity of the Shared services to better service the global corporations they support.
-
Horizontal or Flat Organizational Structures
Flat organizational structure is an organizational model with relatively few or no levels of middle management between the executives and the frontline employees. Its goal is to have as little hierarchy as possible between management and staff level employees. In a flat organizational structure, employees have increased involvement in the decision-making process.
-
Legal Structures for Multinational Companies
A multinational company generally has offices and/or factories in different countries and a centralized head office where they coordinate global management. A multinational company (MNC)is a corporate organization that owns or controls the production of goods or services in at least one country other than its home country.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved