- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Business Processes
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- GL - Review & Approve Journals
GL - Review & Approve Journals
Review and Approval mechanisms ensure that the accounting transaction is reasonable, necessary, and comply with applicable policies. Understand why we need review and approval processes, what are they, and how they are performed in automated general ledger systems. Learn the benefits of having journal approval mechanisms in place.
What is Internal Control?
Internal control plays an important role in the prevention and detection of fraud and errors to ensure the accuracy of financial results. Internal control is the process designed to ensure reliable financial reporting, effective and efficient operations, and compliance with applicable laws and regulations. This needs to be supplemented by an effective control environment that ensures that established policies and procedures are followed.
What are the principles of Internal Control?
Management defines specific policies and procedures to achieve its objectives and run the day to day operations in the organization. The most important control activities involve segregation of duties, proper authorization of transactions and activities, adequate documents and records, physical control over assets and records, and independent checks on performance. These controls and checks ensure that financial statements are complete and accurate.
Principle 1: Segregation of Duties:
The internal control principle of segregation of duties requires that different individuals be assigned responsibility for different elements of related activities, particularly those involving authorization, custody, or recordkeeping. Some examples in the context of general ledger transactions are; the same person who is responsible for recording a transaction should not be responsible for posting the same in the general ledger. The recorded transaction should be checked and reviewed by someone else as having different individuals perform these functions creates a system of checks and balances.
Principle 2: Authorization of Transactions:
Proper authorization of transactions and activities helps ensure that all company activities adhere to established guidelines unless responsible managers authorize exceptions granting another course of action. In the context of the general ledger for example, Journals with different levels of amounts should go to various officers in the company for official authorization before they can be posted in General Ledger. Another example could be that any journal necessitating a debit to Revenue Account must be approved by the accounts manager before it can be posted, to allow the accounts manager to authorize and verify the reversal of revenue.
Principle 3: Adequate Documentation & Physical Control:
Adequate documents and records provide evidence that financial statements are accurate and based on genuine business transactions pertaining to the entity. Controls designed to ensure adequate recordkeeping include the creation of journals and other supporting documents that are easy to use and sufficiently informative. Document sequencing is another functionality that is used to pre-number consecutive journals. It is also very important to document the review and approval process to make it available for audit staff subsequently. The simplest way to do this is to print out the journal entries and have the reviewer initial them. This should then be saved as support. In the automated general ledgers, each user is associated with a user id and transactions can flow to the reviewer and approver before posting and a system audit trail is sufficient audit evidence if such a process has been established.
Physical control over assets and records helps protect the company's assets. These control activities may include electronic or mechanical controls. Journals should be physically safeguarded in case they are on paper and guarded with access privileges & established backup and recovery procedures in case of automated systems.

What is the need for Journal Review and Approval?
Under the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, companies are required to perform a fraud risk assessment and assess related controls. This typically involves identifying scenarios in which theft or loss could occur and determining if existing control procedures effectively manage the risk to an acceptable level. The risk that senior management might override important financial controls to manipulate financial reporting is also a key area of focus in fraud risk assessment. Top managers of publicly held companies must sign a statement of responsibility for internal controls and include this statement in their annual report to stockholders. Review and approval in the accounting process are independent checks on performance, which are carried out by employees who did not do the work being checked. These processes help ensure the reliability of accounting information and the efficiency of operations. Internal auditors and external auditors rely on established processes to gaze at the extent of their audit procedures.
Having the journal review and approval process in place ensures that all general journal entries get reviewed. This review is done to help prevent errors such as adjusting the wrong accounts and transposing numbers. It also helps protect against fraud by making sure there is a valid reason for the journal entry and someone is not manipulating the accounts for vested interests.
1. Review Transactions/Edit Transactions:
The transactions can be reviewed for accuracy and completeness once they have been entered into the automated accounting system. If a review is done by another person who is not responsible or involved in recording the transaction it can help to ensure that financial information in the journals accurately reflects actual activity.
A review of transactions is done to ensure that the transaction is within the guidelines of the purpose of the accounts used and is appropriately charged to the account following the concepts defined in the accounting equation. In the case of manual journals, one must ensure that the transaction is consistent with available supporting documents. If any errors are found in the transaction, they can be edited and corrected at this stage.
2. Journal Approval:
In the case of journal recording the journal entered by one person needs to be approved by another person in this step. This ensures having more than one person to complete the “Journal Creation Task”. In GL the separation by getting the financial transaction approved by more than one individual prevents fraud and error.
3. Journal Approval Workflow:
Automated accounting systems provide you with the functionality of sending the journals for approval to the designated person. The system will validate the journal batch, determine if approval is required, and submit the batch to approvers (if required), then notifies appropriate individuals of the approval results. Review and Approval must happen before the journal is posted and balances are updated.
ERP Systems provide review capabilities by providing a workflow framework to route these transactions to appropriate users based on the rules defined in the system. Automatic notifications are sent to the person who needs to take action.
Benefits of Journal Review and Approve:
Review and Approval mechanisms ensure:
- The transaction is reasonable, necessary, and complies with applicable policies
- The amounts are correct, allowable for the account, allocable, and properly coded
- Charges are appropriately documented and are recorded in a consistent manner
- Funds are available in the account being charged
- Reduces the risk of error, waste, or wrongful acts or inappropriate, unauthorized, or fraudulent activities
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Different Types of Organizational Structures
Modern business organizations run multiple product and service lines, operate globally, leverage large number of registered legal entities, and operate through complex matrix relationships. To stay competitive in the current global business environment, they must often develop highly diverse and complex organizational structures that cross international borders.
-
An account inquiry is a review of any type of financial account, whether it be a depository account or a credit account. In this tutorial, you learn what we mean by drill through functionality in the context of the general ledger system. We will explain the concept of drill-down and how it enables users to perform account and transaction inquiry at a granular level and the benefits of using this functionality.
-
Multitude of these legal and operational structures clubbed with accounting and reporting needs give rise to many reporting dimensions at which the organization may want to track or report its operational metrics and financial results. This is where business dimensions play a vital role.
-
Shared Services is the centralization of service offering at one part of an organization or group sharing funding and resourcing. The providing department effectively becomes an internal service provider. The key is the idea of 'sharing' within an organization or group.
-
GL - Unearned / Deferred Revenue
Unearned revenue is a liability to the entity until the revenue is earned. Learn the concept of unearned revenue, also known as deferred revenue. Gain an understanding of business scenarios in which organizations need to park their receipts as unearned. Look at some real-life examples and understand the accounting treatment for unearned revenue. Finally, look at how the concept is treated in the ERPs or automated systems.
-
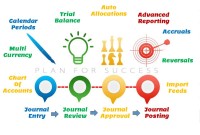
General Ledger - Advanced Features
Modern automated general ledger systems provide detailed and powerful support for financial reporting and budgeting and can report against multiple legal entities from the single system. These systems offer many advanced functionalities right from journal capture to advanced reporting. This article will provide an overview of some advanced features available in today's General Ledgers.
-
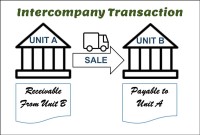
After reading this article the learner should be able to understand the meaning of intercompany and different types of intercompany transactions that can occur. Understand why intercompany transactions are addressed when preparing consolidated financial statements, differentiate between upstream and downstream intercompany transactions, and understand the concept of intercompany reconciliations.
-
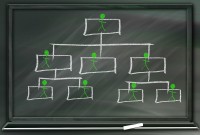
Defining Organizational Hierarchies
A hierarchy is an ordered series of related objects. You can relate hierarchy with “pyramid” - where each step of the pyramid is subordinate to the one above it. One can use drill up or down to perform multi-dimensional analysis with a hierarchy. Multi-dimensional analysis uses dimension objects organized in a meaningful order and allows users to observe data from various viewpoints.
-
Period End Accruals, Receipt Accruals, Paid Time-Off Accruals, AP Accruals, Revenue Based Cost Accruals, Perpetual Accruals, Inventory Accruals, Accruals Write Off, PO Receipt Accrual, Cost Accrual, etc. are some of the most complex and generally misconstrued terms in the context of general ledger accounting. In this article, we will explore what is the concept of accrual and how it impacts general ledger accounting.
-
Team-Based Organizational Structure
Team-based structure is a relatively new structure that opposes the traditional hierarchical structure and it slowly gaining acceptance in the corporate world. In such a structure, employees come together as team in order to fulfill their tasks that serve a common goal.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved