- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Business Processes
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- GL - Errors & Reversals
GL - Errors & Reversals
Explore the concept of journal reversals and understand the business scenarios in which users may need to reverse the accounting entries that have been already entered into the system. Understand the common sources of errors resulting in the reversal of entries and learn how to correct them. Discuss the reversal of adjustment entries and the reversal functionalities in ERPs.
Discovery of Errors in Accounting Books:
It is obvious that care should be used in recording transactions in the journal and in posting to the accounts. The need for accuracy in determining account balances and reporting them to the business stakeholders is also evident.
In the practical world, errors will sometimes occur in journalizing and posting transactions. In some cases, however, an error might not be significant enough to affect the decisions of management or others. In such cases, the materiality concept implies that the error may be treated in the easiest possible way. For example, an error of a few dollars in recording an asset as an expense for a business with millions of dollars in assets would be considered immaterial, and a correction would not be necessary. However, in case the error is significant and material then it needs to be corrected. In the case of automated systems and ERPs, the general practice is to correct all identified errors.
Causes of Errors:
Some of the most common errors in the recording and posting steps are described below:
- Failure to record a transaction or to post a transaction.
- Recording the same erroneous amount for both the debit and the credit parts of a transaction.
- Recording the same transaction more than once.
- Posting a part of a transaction correctly as a debit or credit but to the wrong account.
- Posting the transaction not in accordance with the accounting principles
- Source system errors creating wrong transactions in General Ledger
- Wrong period errors, prior period items getting posted in the current period
- Interface errors, sub-ledger feed is omitted or is posted twice
- Coding errors – erroneous data is automatically created and posted.
- Exchange Rate Errors- the system has picked up a wrong exchange rate that needs to be corrected
- Account balance errors
- The wrong amount posted to an account.
- Debit posted as credit, or vice versa.
- Debit or credit posting omitted.
- Posting errors
Correction of Errors by Reversals:
The procedures used to correct an error vary according to the nature of the error, when the error is discovered, and whether a manual or computerized accounting system is used. Oftentimes, an error is discovered as it is being journalized or posted. In such cases, the error is simply corrected. For example, computerized accounting systems automatically verify for each journal entry whether the total debits equal the total credits. If the totals are not equal, an error report is created and the computer program will not proceed until the journal entry is corrected.
Occasionally, however, an error is not discovered until after a journal entry has been recorded and posted to the accounts. Correcting this type of error is more complex. In the automated systems the journal cannot be edited or deleted once it has been posted. After the posting process has happened, the only way to correct the errors is to reverse the original transaction that nullifies the accounting impact of the wrong Journal and create a new journal with the correct accounting data.
In Automated Accounting Systems, it is not possible to delete transactions once the posting has been made. In such systems reversals is the recommended way to correct the erroneous entries. An example is that one interface feed has been posted by mistake twice. This has inflated many income expense accounts. A reversing entry with opposite debit and credit amounts to all the impacted accounts will nullify the impact of the mistake.
Reversal of Adjustment Entries:
At the beginning of each accounting period, there is an accounting practice to use reversing entries to cancel out the adjusting/accrual entries that were made to accrue revenues and expenses at the end of the previous accounting period. The use of Reversing Entries makes it easier to record subsequent transactions by eliminating the possibility of duplication.
- Reversing entries are made on the first day of an accounting period in order to offset adjusting accrual/provision entries made in the previous accounting period.
- Reversing entries are used to avoid the double booking of revenues or expenses when the accruals/provisions are settled in cash.
- A reversing entry is linked to the original adjusting entry and is written by reversing the position of debits with credits and vice versa.
- The net impact of Original Entry and Reversing Entry on the accounting books is always zero.
Automatic Reversals:
Large organizations need to routinely generate and post large numbers of journal reversals as part of their month-end closing and opening procedures. Automated journal reversals save time and reduce entry errors by automatically generating and posting journal reversals. Users generally need to define journal reversal criteria which are the reversal business rules for journal categories or classes along with the reversal method, period and date. The journal will be reversed based on the method, period, and date criteria defined for that journal category/class when a new accounting period is opened.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
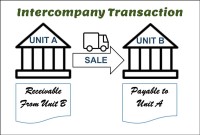
After reading this article the learner should be able to understand the meaning of intercompany and different types of intercompany transactions that can occur. Understand why intercompany transactions are addressed when preparing consolidated financial statements, differentiate between upstream and downstream intercompany transactions, and understand the concept of intercompany reconciliations.
-
GL - Different Type of Journals
Two basic types of journals exist: general and special. In this article, the learner will understand the meaning of journalizing and the steps required to create a journal entry. This article will also discuss the types of journals and will help you understand general journals & special journals. In the end, we will explain the impact of automated ERPs on the Journalizing Process.
-
In this article we will discuss various types of "Management Entities". Various types of operational units, are created by management, to effectively run, manage and control their business. Different types of functional units, and divisional units, are widely used across industry.
-
Legal Structures for Multinational Companies
A multinational company generally has offices and/or factories in different countries and a centralized head office where they coordinate global management. A multinational company (MNC)is a corporate organization that owns or controls the production of goods or services in at least one country other than its home country.
-
Global Business Services (GBS) Model
Global business services (GBS) is an integrated, scalable, and mature version of the shared services model. Global Business Services Model is a result of shared services maturing and evolving on a global scale. It is represented by the growth and maturity of the Shared services to better service the global corporations they support.
-
Matrix Organizational Structures
In recent times the two types of organization structures which have evolved are the matrix organization and the network organization. Rigid departmentalization is being complemented by the use of teams that cross over traditional departmental lines.
-
A Company (also called corporation) may be understood as an association of persons in which money is contributed by them, to carry on some business or undertaking. Persons who contribute the money are called the shareholders or the members of the company. A corporation is an artificial being, invisible, intangible and existing only in contemplation of law. Being the mere creature of law, it possesses only those properties which the charter of its creation confers upon it.
-
A subsidiary is a company that is completely or partly owned by another corporation that owns more than half of the subsidiary's stock, and which normally acts as a holding corporation which at least partly or wholly controls the activities and policies of the daughter corporation.
-
Introduction to Legal Entities Concept
Modern business organizations operate globally and leverage a large number of registered legal entities, and operate through complex matrix relationships. To stay competitive in the current global business environment, they must often develop highly diverse and complex organizational structures that cross international borders. Learn more about Legal Entities and their importance for businesses.
-
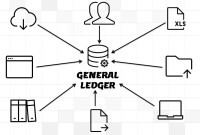
This article explains the process of entering and importing general ledger journals in automated accounting systems. Learn about the basic validations that must happen before the accounting data can be imported from any internal or external sub-system to the general ledger. Finally, understand what we mean by importing in detail or in summary.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved