- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Business Processes
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- Concept of Subsidiaries
Concept of Subsidiaries
A subsidiary is a company that is completely or partly owned by another corporation that owns more than half of the subsidiary's stock, and which normally acts as a holding corporation which at least partly or wholly controls the activities and policies of the daughter corporation.
A subsidiary is a company that is completely or partly owned by another corporation that owns more than half of the subsidiary's stock, and which normally acts as a holding corporation which at least partly or wholly controls the activities and policies of the daughter corporation. The controlling entity is called its parent company, parent, or holding company. Subsidiaries are a common feature of business life, and all multinational corporations organize their operations in this way.
A subsidiary may itself have subsidiaries, and these, in turn, may have subsidiaries of their own. A parent and all its subsidiaries together are called a "group", although this term can also apply to cooperating companies and their subsidiaries with varying degrees of shared ownership. Examples include holding companies such as Berkshire Hathaway, Time Warner, or Citigroup; as well as more focused companies such as IBM or Xerox. These, and other MNCs, organize their businesses into national and functional subsidiaries, often with multiple levels of subsidiaries.
Subsidiaries are separate, distinct legal entities for the purposes of taxation, regulation, and liability. For this reason, they differ from divisions, which are businesses fully integrated within the main company, and not legally or otherwise distinct from it. A parent company may own one or more subsidiaries, in which case each of its subsidiaries are known as ‘sister’ companies to one another.
For the purposes of liability, taxation and regulation, subsidiaries are distinct legal entities. A subsidiary can sue and be sued separately from its parent and its obligations will not normally be the obligations of its parent. If a parent company owns a foreign subsidiary, the company under which the subsidiary is incorporated must follow the laws of the country where the subsidiary operates, and the parent company still carries the foreign subsidiary's financials on its books (consolidated financial statements).
Foreign Subsidiary:
In subsidiary structure the inbound company incorporates a wholly owned subsidiary in the foreign country, making it a distinct legal entity separate from the parent company. Subsidiary incorporated by a foreign company generally is not subject to specific restrictions/limitations with respect to its activities other than the general limitations applicable to domestic entities as well. The profits earned by a foreign subsidiary are liable to tax as per the local laws and regulations of the country of operation.
The Walt Disney Company has more than 50 Subsidiaries (https://www.sec.gov/Archives/edgar/data/1001039/000100103917000198/fy2017_q4x10kxex21.htm).
Given below are some of its foreign subsidiaries:
- Disney FTC Services (Singapore) Pte. Ltd, Singapore
- Euro Disney Associes S.C.A. France
- Hong Kong Disneyland Management Limited, Hong Kong
- Shanghai International Theme Park Company Limited, China
- UTV Software Communications Limited, India
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Multitude of these legal and operational structures clubbed with accounting and reporting needs give rise to many reporting dimensions at which the organization may want to track or report its operational metrics and financial results. This is where business dimensions play a vital role.
-
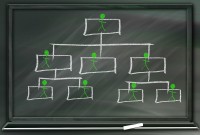
Introduction to Organizational Structures
Organizations are systems of some interacting components. Levitt (1965) sets out a basic framework for understanding organizations. This framework emphasizes four major internal components such as: task, people, technology, and structure. The task of the organization is its mission, purpose or goal for existence. The people are the human resources of the organization.
-
An organizational design is the process by which a company defines and manages elements of structure so that an organization can control the activities necessary to achieve its goals. Good organizational structure and design helps improve communication, increase productivity, and inspire innovation. Organizational structure is the formal system of task and activity relationships to clearly define how people coordinate their actions and use resources to achieve organizational goals.
-
Functional Organizational Structures
A functional organizational structure is a structure that consists of activities such as coordination, supervision and task allocation. The organizational structure determines how the organization performs or operates. The term organizational structure refers to how the people in an organization are grouped and to whom they report.
-
Funds contributed by owners in any business are different from all other types of funds. Equity is the residual value of the business enterprise that belongs to the owners or shareholders. The funds contributed by outsiders other than owners that are payable to them in the future. Liabilities are generally classified as Short Term (Current) and Long Term Liabilities. Current liabilities are debts payable within one year.
-
Operational Structures in Business
Large organizations grow through subsidiaries, joint ventures, multiple divisions and departments along with mergers and acquisitions. Leaders of these organizations typically want to analyze the business based on operational structures such as industries, functions, consumers, or product lines.
-
Different Types of Organizational Structures
Modern business organizations run multiple product and service lines, operate globally, leverage large number of registered legal entities, and operate through complex matrix relationships. To stay competitive in the current global business environment, they must often develop highly diverse and complex organizational structures that cross international borders.
-
A subsidiary is a company that is completely or partly owned by another corporation that owns more than half of the subsidiary's stock, and which normally acts as a holding corporation which at least partly or wholly controls the activities and policies of the daughter corporation.
-
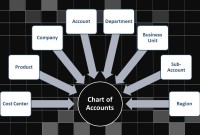
GL - Understanding Chart of Accounts
A chart of accounts (COA) is a list of the accounts used by a business entity to record and categorize financial transactions. COA has transitioned from the legacy accounts, capturing just the natural account, to modern-day multidimensional COA structures capturing all accounting dimensions pertaining to underlying data enabling a granular level of reporting. Learn more about the role of COA in modern accounting systems.
-
The purpose of the general ledger is to sort transaction information into meaningful categories and charts of accounts. The general ledger sorts information from the general journal and converts them into account balances and this process converts data into information, necessary to prepare financial statements. This article explains what a general ledger is and some of its major functionalities.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved