- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Functional
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- Horizontal or Flat Organizational Structures
Horizontal or Flat Organizational Structures
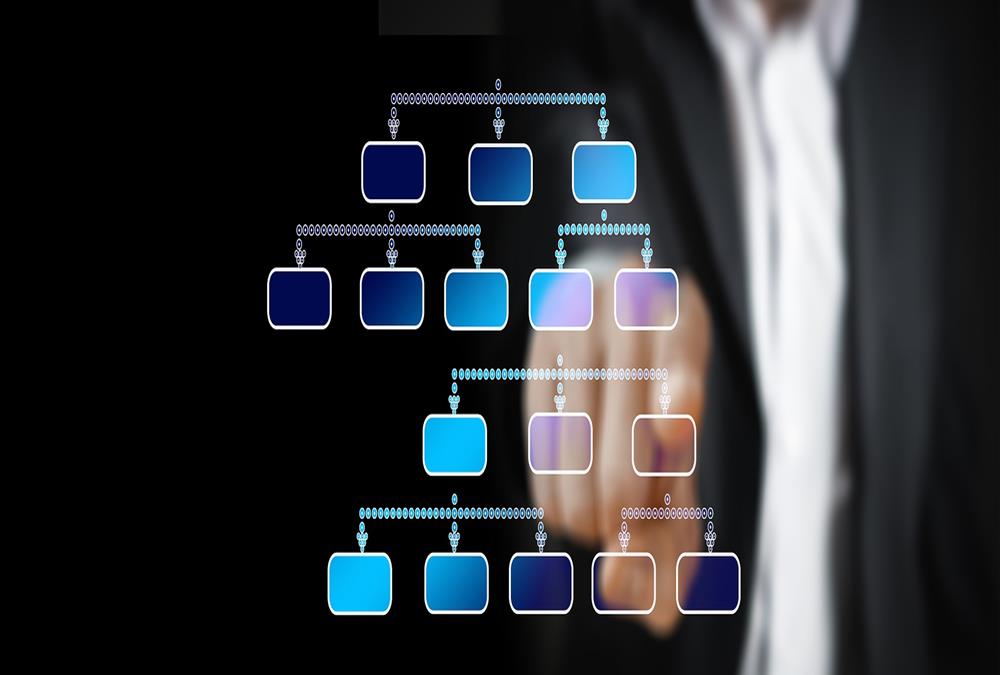
Flat organizational structure is an organizational model with relatively few or no levels of middle management between the executives and the frontline employees. Its goal is to have as little hierarchy as possible between management and staff level employees. In a flat organizational structure, employees have increased involvement in the decision-making process.
Flat organizational structure is an organizational model with relatively few or no levels of middle management between the executives and the frontline employees. Its goal is to have as little hierarchy as possible between management and staff level employees. In a flat organizational structure, employees have increased involvement in the decision-making process.
For a small business with a handful of employees, having a flat or horizontal structure is often the logical approach. The staff-level employees usually report directly to the business owner without a formal management structure. The span of control is wide with each management level controlling a broad area or group. Managers are given significant authority to make business decisions with little to no involvement from the top. In flat organizations, the number of people directly supervised by each manager is large, and the number of people in the chain of command above each person is small.
Main Features
- Better communication and relationships between different roles
- Simple, faster decision making as the chain of command is shorter
- Better ability for the business to change and adapt
- Lower operational costs
- This structure does not support scaling up with growth
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
In this article we will discuss various types of "Management Entities". Various types of operational units, are created by management, to effectively run, manage and control their business. Different types of functional units, and divisional units, are widely used across industry.
-
The purpose of the general ledger is to sort transaction information into meaningful categories and charts of accounts. The general ledger sorts information from the general journal and converts them into account balances and this process converts data into information, necessary to prepare financial statements. This article explains what a general ledger is and some of its major functionalities.
-
For any company that has a large number of transactions, putting all the details in the general ledger is not feasible. Hence it needs to be supported by one or more subsidiary ledgers that provide details for accounts in the general ledger. Understand the concept of the subsidiary ledgers and control accounts.
-
Legal Structures for Multinational Companies
A multinational company generally has offices and/or factories in different countries and a centralized head office where they coordinate global management. A multinational company (MNC)is a corporate organization that owns or controls the production of goods or services in at least one country other than its home country.
-
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles define the accounting procedures, and understanding them is essential to producing accurate and meaningful records. In this article we emphasize on accounting principles and concepts so that the learner can understand the “why” of accounting which will help you gain an understanding of the full significance of accounting.
-
In some of the ERP tools, there are more than 12 accounting periods in a financial year. This article discusses the concept of accounting calendar and accounting periods. Learn why different companies have different accounting periods. Understand some of the commonly used periods across different organizations and the definition & use of an adjustment period.
-
Functional Organizational Structures
A functional organizational structure is a structure that consists of activities such as coordination, supervision and task allocation. The organizational structure determines how the organization performs or operates. The term organizational structure refers to how the people in an organization are grouped and to whom they report.
-
Legal Structures in Businesses
Businesses not only vary in size and industry but also in their ownership. Most businesses evolve from being owned by just one person to a small group of people and eventually being managed by a large numbers of shareholders. Different ownership structures overlap with different legal forms that a business can take. A business’s legal and ownership structure determines many of its legal responsibilities.
-
What is Accounting & Book Keeping
Accounting is a process designed to capture the economic impact of everyday transactions. Each day, many events and activities occur in an entity, these events and activities are in the normal course of business; however, each of these events may or may not have an economic impact. Events or activities that have an effect on the accounting equation are accounting events.
-
McKinsey 7S Framework is most often used as an organizational analysis tool to assess and monitor changes in the internal situation of an organization. The model is based on the theory that, for an organization to perform well, seven elements need to be aligned and mutually reinforcing.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved