- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Functional
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- Introduction to Organizational Structures
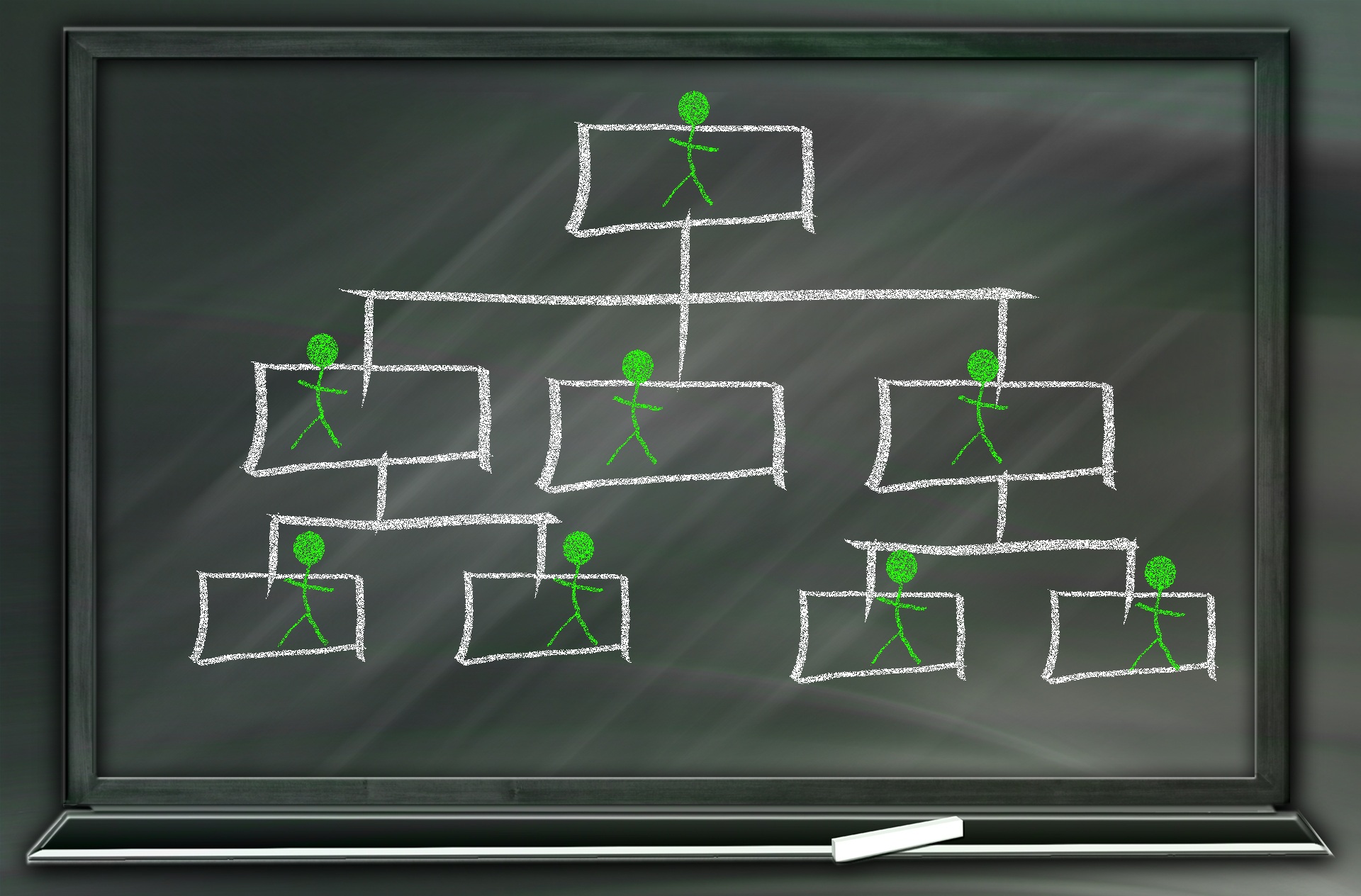
Introduction to Organizational Structures
Organizations are systems of some interacting components. Levitt (1965) sets out a basic framework for understanding organizations. This framework emphasizes four major internal components such as: task, people, technology, and structure. The task of the organization is its mission, purpose or goal for existence. The people are the human resources of the organization.
Organizations are systems of some interacting components. Levitt (1965) sets out a basic framework for understanding organizations. This framework emphasizes four major internal components such as: task, people, technology, and structure. The task of the organization is its mission, purpose or goal for existence. The people are the human resources of the organization.
What is an Organization?
The term organization is derived from the Greek word organon i.e., tool or instrument. It is often been understood as the embodiment of persistent efforts to coordinate, influence and control human behavior in order to reach some desired result. Organizations as Systems Organizations are systems of some interacting components. Levitt (1965) sets out a basic framework for understanding organizations. This framework emphasizes four major internal components such as: task, people, technology, and structure. The task of the organization is its mission, purpose or goal for existence. The people are the human resources of the organization. The technology is the wide range of tools, knowledge and/or techniques used to transform the inputs into outputs. The structure is how work is designed at the micro level, as well as how departments, divisions and the overall organization are designed at the macro level.
In addition to these major internal components of the organization as a system, there is organizations' task environment, such as suppliers, customers, and regulators. In simpler terms it is that part of external environment which is relevant at present or expected in foreseeable future to the organizations' goal attainment (Thompson, 1967).
Features of Organization
Max Weber has defined the following features and dimensions as basic for all organizations:
1. The organization has transparent and definite boundaries and has a collective identity of its own.
2. The organization has a central coordination system to manage the concentrated efforts of the organization
3. The organization is differentiated internally and decisions are implemented by a disciplined, specialized, continuously and rationally operating staff.
4. The organization is legitimate and organizational order, including the distribution of authority, power and responsibilities, is legitimate.
5. The organization's characteristics establish what is achieved and there is a high degree of steadiness between organizational goals, structures, processes, behavior and outcomes.
6. The organization is flexible and are deliberately structured and restructured in order to improve their problem solving capacity and their ability to realize predetermined goals.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Concept of Representative Office
A representative office is the easiest option for a company planning to start its operations in a foreign country. The company need not incorporate a separate legal entity nor trigger corporate income tax, as long as the activities are limited in nature.
-
Trial Balance in General Ledger
One of the greatest benefits of using a double-entry accounting system is the capability to generate a trial balance. What do we mean by trial balance? As the name suggests a trial balance is a report that must have its debits equals to credits. Understand the importance of trial balance and why it is balanced. Learn how it is prepared and in which format.
-
A joint venture (JV) is a business agreement in which the parties agree to develop, for a finite time, a new entity and new assets by contributing equity. They exercise control over the enterprise and consequently share revenues, expenses and assets. A joint venture takes place when two or more parties come together to take on one project.
-
Funds contributed by owners in any business are different from all other types of funds. Equity is the residual value of the business enterprise that belongs to the owners or shareholders. The funds contributed by outsiders other than owners that are payable to them in the future. Liabilities are generally classified as Short Term (Current) and Long Term Liabilities. Current liabilities are debts payable within one year.
-
This article explains the process of entering and importing general ledger journals in automated accounting systems. Learn about the basic validations that must happen before the accounting data can be imported from any internal or external sub-system to the general ledger. Finally, understand what we mean by importing in detail or in summary.
-
A legal entity is an artificial person having separate legal standing in the eyes of law. A Legal entity represents a legal company for which you prepare fiscal or tax reports. A legal entity is any company or organization that has legal rights and responsibilities, including tax filings.
-
Team-Based Organizational Structure
Team-based structure is a relatively new structure that opposes the traditional hierarchical structure and it slowly gaining acceptance in the corporate world. In such a structure, employees come together as team in order to fulfill their tasks that serve a common goal.
-
Learn the typical accounting cycle that takes place in an automated accounting system. We will understand the perquisites for commencing the accounting cycle and the series of steps required to record transactions and convert them into financial reports. This accounting cycle is the standard repetitive process that is undertaken to record and report accounting.
-
GL - Understanding Chart of Accounts
A chart of accounts (COA) is a list of the accounts used by a business entity to record and categorize financial transactions. COA has transitioned from the legacy accounts, capturing just the natural account, to modern-day multidimensional COA structures capturing all accounting dimensions pertaining to underlying data enabling a granular level of reporting. Learn more about the role of COA in modern accounting systems.
-
General Ledger - Advanced Features
Modern automated general ledger systems provide detailed and powerful support for financial reporting and budgeting and can report against multiple legal entities from the single system. These systems offer many advanced functionalities right from journal capture to advanced reporting. This article will provide an overview of some advanced features available in today's General Ledgers.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved