- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Functional
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- GL - Journal Entry & Import
GL - Journal Entry & Import
This article explains the process of entering and importing general ledger journals in automated accounting systems. Learn about the basic validations that must happen before the accounting data can be imported from any internal or external sub-system to the general ledger. Finally, understand what we mean by importing in detail or in summary.
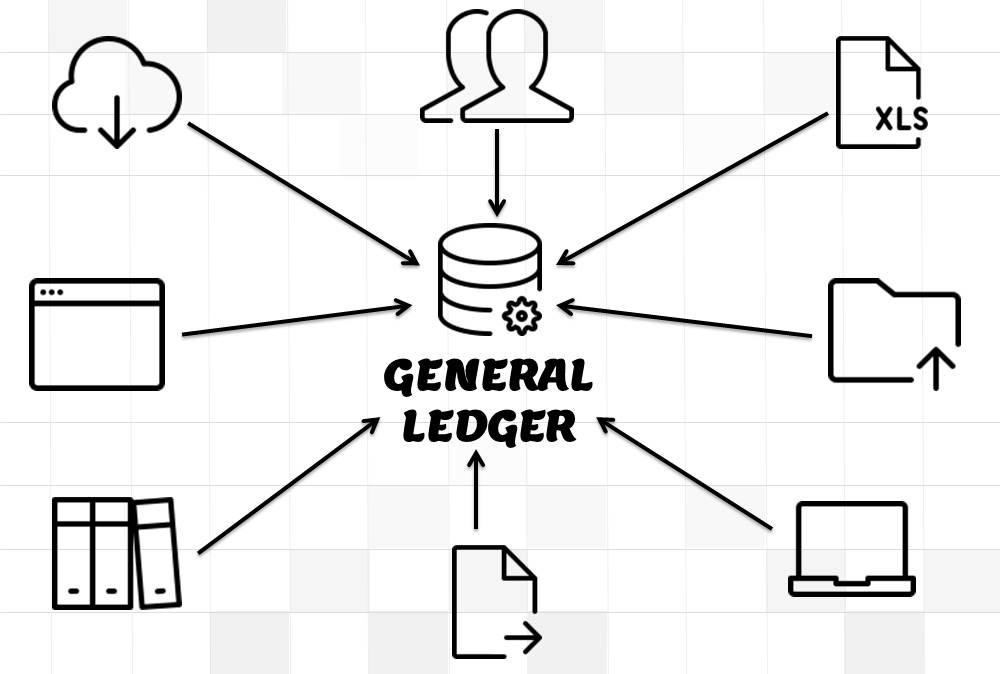
Recording Journals in General Ledger:
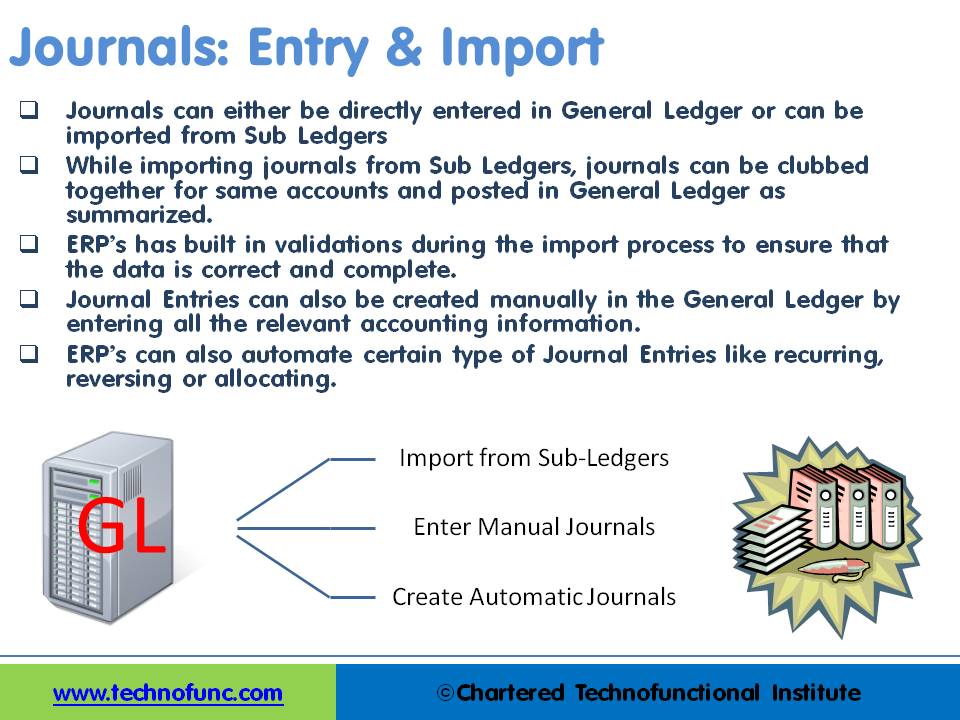
Journals can either be directly entered in General Ledger or can be imported from Sub Ledgers. Most of the journals are created along-with business transactions like sales, purchases, receipts, and payments and get recorded in respective sub-ledgers. As sub-ledgers generally capture data at a more granular level, the relevant accounting information must flow to the general ledger for posting and subsequent reporting. From sub-ledgers, they need to be imported to the general ledger for financial recording and reporting.
Journal Entries can also be created manually in General Ledger by entering all the relevant accounting information. ERPs can also automate certain types of Journal Entries like recurring, reversing, or allocating journals. In case of manual entry follow the steps and guidelines outlined in the Recording Journals tutorial.
Importing – Detail V/s Summarized:
While importing journals from Sub Ledgers, journals can be clubbed together for the same accounts and posted in General Ledger as summarized.
Various general ledger systems provide the functionality to create Summary Journals which summarize all transactions for the same account, period, and currency into one debit or credit journal line. This results in fewer transactions in the general ledger systems and makes financial reports more manageable in size. In the case of summary journal users, lose the one-to-one mapping of detail transactions in the sub-ledger to the summary journal lines created by the import process. However most of the organizations use this feature as this prevents too many transactions in GL Accounts and transactions get clubbed based on category, type, or transaction source.
Using the drill-down functionalities available in most of the modern general ledger systems, users can still perform various review and analysis functions, as even if the system creates summary journals, it can still maintain a mapping of how Journal Import summarizes sub-ledger detail transactions from feeder systems into general ledger journal lines.
Journal Import Validations:
ERP’s and automated accounting systems must have built in validations during the import process to ensure that the data is correct and complete. An effective Journal Import program should validate key accounting information before it creates journal entries in the General Ledger application to prevent errors and reconciliation efforts.
Given below are some of the common data validations that can happen during the GL Import process:
1. Suspense Posting:
Suspense posting puts the remaining amount in the suspense account in case the debits and credits of the journal are not matching. In case it is not required, Journal Import should reject all invalid lines that do not balance.
2. Duplicate Batch Name:
If the batch name is a unique field then Journal Import should ensure that a batch with the same name does not already exist for the same period in the General Ledger application. Similarly, it must also check to ensure that more than one journal entry with the same name does not exist for a batch.
3. Other Attributes:
Attributes that can be validated to ensure that journals contain the appropriate accounting data could be accounting books, period, source, currency, category, accounting date, reversal period, account validation, account code combinations, effective date, roll date, and any other required validations.
Import Using Excel:
In today’s accounting world, financial and operational data typically is stored in a variety of programs and formats. Excel is one of such tools, most widely used by the accountants! When accountants need to prepare a report based on data from various systems, the first step is to export the data into Excel. Many times accounting information is stored in chronological order in excels by the accountants, and examples include adjusting entries and recurring entries.
Benefits of using the excel upload feature are that it makes life much easier for data operator and accounts executives. The great flexibility of excel based application increases productivity and results in reduced training costs as most users are already familiar with the excel functionalities and also improves user acceptance for automated systems. The biggest benefit comes from the fact that excel upload can also work in disconnected environments.
Typically, most of the automated systems provide the functionality to import accounting data from Excel to the general ledger and create journals. Most ERPs provide the ability to upload journals using the MS Excel worksheet. You can create journals in Excel Template and upload directly to General Ledger.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
In this article, we will describe how to determine if an account needs adjustment entries due to the application of the matching concept. Learners will get a thorough understanding of the adjustment process and the nature of the adjustment entries. We will discuss the four types of adjustments resulting from unearned revenue, prepaid expenses, accrued expenses, and accrued revenue.
-
What Is a General Ledger? General Ledger (also known in accounting as the GL or the Nominal Ledger) is at the heart of any accounting system. A general ledger is the master set of accounts that summarize all transactions occurring within an entity. Ledger is the skillful grouping and presentation of the Journal entries. Learn the accounting fundamentals, general ledger process, and general ledger flow.
-
Driving Business Efficiency through Divisions and Departments
In case of a multi-divisional organizational structure, there is one parent company, or head-office. And that parent owns smaller departments, under the same brand name. Dividing the firm, into several self-contained, autonomous units, provides the optimal level of centralization, in a company.
-
Shared Services is the centralization of service offering at one part of an organization or group sharing funding and resourcing. The providing department effectively becomes an internal service provider. The key is the idea of 'sharing' within an organization or group.
-
A subsidiary is a company that is completely or partly owned by another corporation that owns more than half of the subsidiary's stock, and which normally acts as a holding corporation which at least partly or wholly controls the activities and policies of the daughter corporation.
-
The sole trader organization (also called proprietorship) is the oldest form of organization and the most common form of organization for small businesses even today. In a proprietorship the enterprise is owned and controlled only by one person. This form is one of the most popular forms because of the advantages it offers. It is the simplest and easiest to form.
-
Although technically a general ledger appears to be fairly simple compared to other processes, in large organizations, the general ledger has to provide many functionalities and it becomes considerably large and complex. Modern business organizations are complex, run multiple products and service lines, leveraging a large number of registered legal entities, and have varied reporting needs.
-
Matrix Organizational Structures
In recent times the two types of organization structures which have evolved are the matrix organization and the network organization. Rigid departmentalization is being complemented by the use of teams that cross over traditional departmental lines.
-
Reversing Journals are special journals that are automatically reversed after a specified date. A reversing entry is a journal entry to “undo” an adjusting entry. When you create a reversing journal entry it nullifies the accounting impact of the original entry. Reversing entries make it easier to record subsequent transactions by eliminating the need for certain compound entries. See an example of reversing journal entry!
-
Explore the concept of journal reversals and understand the business scenarios in which users may need to reverse the accounting entries that have been already entered into the system. Understand the common sources of errors resulting in the reversal of entries and learn how to correct them. Discuss the reversal of adjustment entries and the reversal functionalities in ERPs.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved