- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Business Processes
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- GL - Accrued Expenses
GL - Accrued Expenses
Accrued expenses, sometimes referred to as accrued liabilities, are expenses that have been incurred but have not been recorded in the accounts. Discuss the need to record accrued liabilities and why they require an adjustment entry. Understand the treatment for these entries once the accounting period is closed and learn to differentiate when the commitments become liabilities.
What are Accrued Expenses?
Accrued expenses, sometimes referred to as accrued liabilities, are expenses that have been incurred but have not been recorded in the accounts. Accrued expenses are expenses that have already been incurred, that the resulting benefit has been received by the business and we have a legal or moral obligation to pay the other party, but not yet paid or recorded. Examples of these types of adjusting entries could be for payroll that has been earned by employees on the last day of the period but not paid until the next payroll date. Other examples include accrued interest on notes payable and accrued taxes.
What is Accrued Liability?
The accrued liability is a liability that was incurred, but for which payment is not yet made, during a given accounting period. Some examples include wages owed and taxes payable. Accrued payroll is an example of accrued expense/liabilities – usually represented in a separate account, which represents the amount earned by employees but not yet paid to them. Since employees are typically paid for time already worked, not in advance, every company has some amount of compensation earned by its employees but not yet paid to them. The only exception would be those companies that pay employees on the last day of their workweek, in which case at the end of a payday they would not owe any money to their employees, until the following day.
Why record accrued expenses and liabilities?
When a company keeps its accounting records on an accrual basis, such liabilities are recorded when they become owed, even though they don't actually have to be paid until later on. The amount of such an accrued but unpaid item at the end of the accounting period is both an expense and a liability. These may be expenses the company has incurred, but for which it has not yet received an invoice to record. In order to make sure the expense gets recorded into the right accounting period, the company's accountants will accrue the liability rather than wait for an invoice to arrive or a check to be issued. Examples might include large purchases for which the supplier has not yet invoiced the company or interest expense on a loan that doesn't get invoiced, but for which the bank will automatically charge the company. This adjusting entry is necessary so that expenses are properly matched to the period in which they were incurred.
Example of Accrued Expenses:
A company gets into an agreement to borrow $2 million from an investment company for six months payable along with interest @2% per month, after six months. The loan was advanced on November, 1 and the company follows the regular accounting calendar from Jan to Dec every year. The amount was repaid on 1st May along with an interest of $240000.
As the company closes its books for the accounting year on December 31, on that date the company will not have an invoice or payment for the interest that the company is incurring. (The reason is that all of the interest will be due on 1st May next year). Without an adjusting entry to accrue the interest expense that the company has incurred for the two months November and December, the company’s financial statements as of December 31 will not be reporting the $80,000 of interest (Interest @2% for 2 months) that the company has incurred in December. In order for the financial statements to be correct on the accrual basis of accounting, the accountant needs to record an adjusting entry dated as of December 31. The adjusting entry will consist of a debit of $80,000 to Interest Expense Account (Expense Accrual) and a credit of $80,000 to Interest Payable (Liability Accrual).
What happens to these entries when amounts are paid?
These types of accrual entries generally reverse next month. To simplify the subsequent recording of the following period’s transactions, some accountants use what is known as reversing entries for certain types of adjustments. Reversing entries can be automated in ERPs and discussed and illustrated in a separate article in this section.
Why accrued expenses result in adjusting entry?
Accrued revenues and expenses are created by unrecorded revenue that has been earned or an unrecorded expense that has been incurred. As the cash outlay has not happened in both these cases, we need to pass an adjustment entry at the end of the accounting period to record these expenses into books of accounts. Prior to recording the adjusting entries, neither accrued revenues nor accrued expenses would have been recorded.
When to convert commitments to Accrued Liability?
Expenses do not get recorded when they are committed when the order is called in when a purchase order is issued, or even when the supplier agrees to supply the goods or services ordered. All those things are simply requests or promises, all of which can be rescinded without penalty. So they're not the irrevocable transactions that we can record. When the supplier acts on that promise to deliver, then we have an accounting event that should be recorded and the money is really spent.
Today, many companies have integrated enterprise accounting systems that can keep track of purchase orders issued but not yet fulfilled, and it's much easier to track and report commitments made for future goods and services. Even so, such commitments cannot be booked as actual expenses until the goods have been delivered and the purchase order satisfied. With that overview in mind, under accrual systems accountants need to book expenses that have already been incurred.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Matrix Organizational Structures
In recent times the two types of organization structures which have evolved are the matrix organization and the network organization. Rigid departmentalization is being complemented by the use of teams that cross over traditional departmental lines.
-
In this article, we explain some commonly used subsidiary ledgers like accounts receivable subsidiary ledger, accounts payable subsidiary ledger or creditors' subsidiary ledger, inventory subsidiary ledger, fixed assets subsidiary ledger, projects subsidiary ledger, work in progress subsidiary ledger, and cash receipts or payments subsidiary ledger.
-
GL - Recurring Journal Entries
A “Recurring Journal” is a journal that needs to be repeated and processed periodically. Recurring Entries are business transactions that are repeated regularly, such as fixed rent or insurance to be paid every month. Learn the various methods that can be used to generate recurring journals. See some examples and explore the generic process to create recurring journals in any automated system.
-
Driving Business Efficiency through Divisions and Departments
In case of a multi-divisional organizational structure, there is one parent company, or head-office. And that parent owns smaller departments, under the same brand name. Dividing the firm, into several self-contained, autonomous units, provides the optimal level of centralization, in a company.
-
There are two commonly used methods of accounting - Cash Basis and the Accruals Basis. Understand the difference between accruals and reversals. Recap the earlier discussion we had on accruals and reversals and see the comparison between these two different but related accounting concepts. Understand how the action of accruing results in reversals subsequently in the accounting cycle.
-
What is a Business Eco System?
The goal of a business is to generate capital appreciation and profits for its owners or stakeholders by engaging in provision of goods and services to customers within the eco system/framework governed by respective laws(local/international). The eco system involves various entities that the business works with for delivery of a product or service.
-
What is Accounting & Book Keeping
Accounting is a process designed to capture the economic impact of everyday transactions. Each day, many events and activities occur in an entity, these events and activities are in the normal course of business; however, each of these events may or may not have an economic impact. Events or activities that have an effect on the accounting equation are accounting events.
-
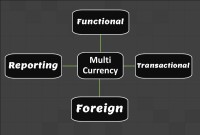
Multi Currency - Functional & Foriegn
Currency is the generally accepted form of money that is issued by a government and circulated within an economy. Accountants use different terms in the context of currency such as functional currency, accounting currency, foreign currency, and transactional currency. Are they the same or different and why we have so many terms? Read this article to learn currency concepts.
-
In this article we will help you understand the double-entry accounting system and state the accounting equation and define each element of the equation. Then we will describe and illustrate how business transactions can be recorded in terms of the resulting change in the elements of the accounting equation.
-
For any company that has a large number of transactions, putting all the details in the general ledger is not feasible. Hence it needs to be supported by one or more subsidiary ledgers that provide details for accounts in the general ledger. Understand the concept of the subsidiary ledgers and control accounts.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved