- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Functional
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- Different Types of Organizational Structures
Different Types of Organizational Structures
Modern business organizations run multiple product and service lines, operate globally, leverage large number of registered legal entities, and operate through complex matrix relationships. To stay competitive in the current global business environment, they must often develop highly diverse and complex organizational structures that cross international borders.
Modern business organizations run multiple product and service lines, operate globally, leverage large number of registered legal entities, and operate through complex matrix relationships. To stay competitive in the current global business environment, they must often develop highly diverse and complex organizational structures that cross international borders.
The various, multifaceted tasks and activities of an organization have to be divided into smaller, manageable components to facilitate efficient achievement of business objectives. Regulatory and management needs are the main driving forces behind organizational structures. These complexities create need for advanced operational and supporting business processes to drive organization wide effectiveness, efficiency and achieve business objectives.
This forces companies to create a diverse array of subsidiaries, legal entities, organizations, and accounting processes to ensure a smooth and profitable business flow. Tax considerations also impact how businesses construct these complex legal structures. In this section we will explore the different legal and operational structures that are commonly adopted by these global conglomerates.
Legal Structure - Driven by regulatory needs
Every organization must have a registered or legislated legal structure. In rapidly changing national and global business environment, it has become necessary that regulation of corporate entities is in tune with the emerging economic trends, encourage good corporate governance and enable protection of the interests of the investors and other stakeholders. Further, due to continuous increase in the complexities of business operation, the forms of corporate organizations are constantly changing.
Legal structures are driven by compliance and is used for external purposes. They are generally mandatory for all businesses. Banks, investors, customers, suppliers, lenders and regulators use these business structures to make contacts, approve loans, lines of credits and to make sure you are following regulatory requirements.
When you are just starting out you may not worry too much about the formal decision making process in your business. But, as your business grows issues about who has the authority to make what decisions could undercut your ability to make deals or grow as quickly as you want to. It is even more important to make sure the lines of authority are clear when multiple people own the business. Different business structures allow for different types of decision-making processes and lines of authority. If you want to avoid a legal battle in the future over who is in charge of your business, you have to choose the right business entity. You will also want to make sure those details are spelled out in any legal formation documents drafted by your business lawyer.
When choosing a business entity you are also committing to doing what is needed to maintain the legal status of your business. Different types of companies have different types of compliance burdens. The simplest structure is the sole proprietorship, which usually involves just one individual who owns and operates the enterprise. If your business will be owned and operated by several individuals, you'll want to take a look at structuring your business as a partnership. The corporate structure is more complex and expensive than most other business structures. A corporation is an independent legal entity, separate from its owners, and as such, it requires complying with more regulations and tax requirements.
Types of Legal Structures:
- Sole Proprietorship
- Partnership
- Limited Liability
- Legal Entity
- Subsidiary
- Representative Office
- Branches - Domestic and Foreign
- Joint Venture
- Corporation or Conglomerate
Operational Structure - Driven by management needs
The company defines its operational structures to assign roles and responsibilities and fix accountability at various levels where actual business activities take place. These levels are used to divide the control of economic resources and operational processes in a business. People at these operating levels have a duty to maximize the use of scarce resources, improve processes, and account for their performance. These levels are known as operating units and used to record and report financial/other information that is not legally required, but that is used for internal control.
Types of internal organizational structures:
- Hierarchical organizational structures
- Functional organizational structures
- Horizontal or flat organizational structures
- Divisional organizational structures (market-based, product-based, geographic)
- Matrix organizational structures
- Team-based organizational structures
- Network organizational structures
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Multitude of these legal and operational structures clubbed with accounting and reporting needs give rise to many reporting dimensions at which the organization may want to track or report its operational metrics and financial results. This is where business dimensions play a vital role.
-
Concept of Representative Office
A representative office is the easiest option for a company planning to start its operations in a foreign country. The company need not incorporate a separate legal entity nor trigger corporate income tax, as long as the activities are limited in nature.
-
Introduction to Legal Entities Concept
Modern business organizations operate globally and leverage a large number of registered legal entities, and operate through complex matrix relationships. To stay competitive in the current global business environment, they must often develop highly diverse and complex organizational structures that cross international borders. Learn more about Legal Entities and their importance for businesses.
-
A legal entity is an artificial person having separate legal standing in the eyes of law. A Legal entity represents a legal company for which you prepare fiscal or tax reports. A legal entity is any company or organization that has legal rights and responsibilities, including tax filings.
-
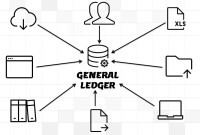
This article explains the process of entering and importing general ledger journals in automated accounting systems. Learn about the basic validations that must happen before the accounting data can be imported from any internal or external sub-system to the general ledger. Finally, understand what we mean by importing in detail or in summary.
-
When the quantum of business is expected to be moderate and the entrepreneur desires that the risk involved in the operation be shared, he or she may prefer a partnership. A partnership comes into existence when two or more persons agree to share the profits of a business, which they run together.
-
Five Core General Ledger Accounts
Typically, the accounts of the general ledger are sorted into five categories within a chart of accounts. Double-entry accounting uses five and only five account types to record all the transactions that can possibly be recorded in any accounting system. These five accounts are the basis for any accounting system, whether it is a manual or an automated accounting system. These five categories are assets, liabilities, owner's equity, revenue, and expenses.
-
There are five types of core accounts to capture any accounting transaction. Apart from these fundamental accounts, some other special-purpose accounts are used to ensure the integrity of financial transactions. Some examples of such accounts are clearing accounts, suspense accounts, contra accounts, and intercompany accounts. Understand the importance and usage of these accounts.
-
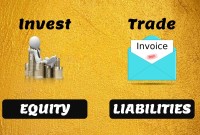
Funds contributed by owners in any business are different from all other types of funds. Equity is the residual value of the business enterprise that belongs to the owners or shareholders. The funds contributed by outsiders other than owners that are payable to them in the future. Liabilities are generally classified as Short Term (Current) and Long Term Liabilities. Current liabilities are debts payable within one year.
-
As the business grows, the company may want to transition to a branch structure as branches are allowed to conduct a much broader range of activity than representative offices. Branches can buy and sell goods, sign contracts, build things, render services, and generally everything that a regular business can do. A company expands its business by opening up its branch offices in various parts of the country as well as in other countries.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved