- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Functional
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- Contra & Control Accounts
Contra & Control Accounts
There are five types of core accounts to capture any accounting transaction. Apart from these fundamental accounts, some other special-purpose accounts are used to ensure the integrity of financial transactions. Some examples of such accounts are clearing accounts, suspense accounts, contra accounts, and intercompany accounts. Understand the importance and usage of these accounts.
General Ledger System Accounts:
Automated Accounting Systems are organized set of manual and computerized accounting methods, procedures, and controls to gather, record, classify, analyze, summarize, interpret, and present accurate and timely financial data from computerized systems. For any accounting system to work it needs to understand the distinction between balance sheet and profit and loss items. Automated systems also provide posting of certain special transactions to specified accounts. For these functions to work, seeded account types and accounts are defined in the automated systems. These mandatory pre-defined accounts and account types are referred to as “General Ledger System Accounts”.
Whenever IT professional starts working on any financial project, they encounter certain accounts and account types that are always seeded in the system, they are able to perform setups for those accounts after going through the manual of the software package, but usually explanation about the need and role of these accounts is not available in the product manual/guide. In this tutorial, we will understand what are the minimum account types that need to be seeded in any financial system and "why" certain accounts have to be mandatory in nature before the automated accounting process can start.
In the latter half, we will discuss some special purpose accounts like Suspense Account, Clearing Account, etc. and will focus our discussion on understanding what these accounts are and what roles these accounts play in an automated ERP system. The intended audience for this tutorial is anybody who has a need to work on any financial IT system. This will be helpful to everyone who wants to understand how to design and implement effective automated accounting systems like ERPs. This tutorial focuses on these concepts from the perspective of an IT professional that is expected to work on any project involving design, build or interface to an automated GL system, rather than a student of accounting.
For Information Technology professionals this overview lesson relates important GL accounts to automated accounting systems and will help them understand the role these commonly used accounts play. This chapter will provide a foundation knowledge that will be helpful to IT implementers to explain the future design and ERP functionalities to the end users more effectively. In the setup stages, this will ensure that implementers understand the key differences between different types of accounts and they are able to classify the client's financial data correctly.
During the requirements stage understanding of the system, accounts will help professionals ask relevant questions to understand the company's business processes creating needs for these system accounts. We recommend sharing the video and concepts of this tutorial with the super-users before the requirements gathering session to enable an effective discussion on requirements around system accounts. The concepts presented in this chapter are conceptual in nature and they are applicable to all accounting systems irrespective of the underlying technology. Understanding these concepts is a prerequisite to define and work on an automated General Ledger. This topic is beneficial to both IT professionals as well as end-users. Persons seeking specialized accounting knowledge will also benefit from these discussions.
Mandatory accounts in GL can be classified into two broad categories – Fundamental Accounts and Special Purpose Accounts. In this part of this series, we will focus on defining these account types and will explore the conceptual knowledge behind these accounts. During this tutorial, we will be doing a deep dive into both account types, discussing individual accounts in detail.

TechnoFunc Definitions:
1. Fundamental Accounts:
Business operations may result in financial benefits or losses that arise as a difference in revenue gained from business activity and expenses, costs, and taxes needed to sustain the business activity. Any resultant profit or loss goes to the business owner. Funds can be invested by owners or outsiders known as equity & liabilities and can be used to acquire assets to perform business activities. All general ledger accounts can be classified as belonging to either one of these categories – Equity, Liabilities, Assets, Revenue, and Expenses. These are the fundamental account types from the perspective of automated accounting systems. Based on this classification, closing balances are never carried forward in automated GL systems for Revenue and Expense Accounts.
2. Special Purpose Accounts:
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems integrate internal and external financial and non-financial information across an entire organization. Transaction flow happens between many interdependent processes and business units embracing finance/accounting, manufacturing, sales and service, customer relationship management, etc. When one end to end transaction needs to be routed through multiple processes and modules, special-purpose accounts helps in tracking financial flow and facilitates accounting reconciliation among different input and output transactional processes.
A new category of accounts also classified as “Special Purpose Accounts” like Contra accounts, Intercompany accounts, Clearing accounts, and suspense accounts, etc. are defined to track the entire financial flow and identify and reconcile intermediary handoffs. In any business that is going for large automated accounting systems, you can expect and a large number of business transactions and parallel and sequential processes catering to different business requirements.
Let’s try to understand some flows that are happening at all times:
Business Flows:
The business has its own legal and physical structure. It deals in products or services and interacts with lots of third parties like suppliers and customers who interact with accounting systems while performing normal business transactions with the entity. If business transactions result in financial transactions, these business flows interact with the organization’s Accounting Flows.
Internal Process Flows: Company has its own set of rules, procedures, and processes to perform business activities. Creating repeatable business processes is an important part of building and running an effective organization. Well-designed and documented business processes are critical for the success of business activities. These internal process flows also encompasses material flows. For example, before releasing the material to the end customer it needs to be moved from a wholesale warehouse to a retail warehouse. These process flows are for normal business activities and when these activities are financial in nature they interact with Accounting Flows.
Accounting Flows:
For each of the processes, whether they are internal or external, effective systems should automatically assist the generation of accounting entries and track inventory, assets, liabilities, and profitability of the organization. In these internal processes, there is a need to break the accounting transaction into sub-transactions to identify and track these interdependent steps in these flows. For example when the material is received from the supplier, debit the inventory account and credit the AP Clearing Account (Because at that particular step, Payables Department has not received the invoice for the material received). Once the invoice is recorded in the subsequent Payables Process, the clearing account can be netted off with the actual liability account.
This helps us understand how one single transaction needs to be routed through multiple processes and modules. These special-purpose accounts help in tracking financial flow and facilitates accounting reconciliation among different transactional processes as explained in our example for Inventory and Payables. These clearing accounts are classified as “Special Purpose Accounts” and are used to track the entire financial flow and identify and reconcile intermediary handoffs.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Although technically a general ledger appears to be fairly simple compared to other processes, in large organizations, the general ledger has to provide many functionalities and it becomes considerably large and complex. Modern business organizations are complex, run multiple products and service lines, leveraging a large number of registered legal entities, and have varied reporting needs.
-
In this article we will focus on and understand the accounting process which enables the accounting system to provide the necessary information to business stakeholders. We will deep dive into each of the steps of accounting and will understand how to identify accounting transactions and the process for recording accounting information and transactions.
-
Legal Structures for Multinational Companies
A multinational company generally has offices and/or factories in different countries and a centralized head office where they coordinate global management. A multinational company (MNC)is a corporate organization that owns or controls the production of goods or services in at least one country other than its home country.
-
Defining Organizational Hierarchies
A hierarchy is an ordered series of related objects. You can relate hierarchy with “pyramid” - where each step of the pyramid is subordinate to the one above it. One can use drill up or down to perform multi-dimensional analysis with a hierarchy. Multi-dimensional analysis uses dimension objects organized in a meaningful order and allows users to observe data from various viewpoints.
-
GL - Accrued / Unbilled Revenue
Accrued revenues (also called accrued assets) are revenues already earned but not yet paid by the customer or posted to the general ledger. Understand what we mean by the terms accrued revenue, accrued assets, and unbilled revenue. Explore the business conditions that require recognition of accrued revenue in the books of accounts and some industries where this practice is prevalent.
-
Funds contributed by owners in any business are different from all other types of funds. Equity is the residual value of the business enterprise that belongs to the owners or shareholders. The funds contributed by outsiders other than owners that are payable to them in the future. Liabilities are generally classified as Short Term (Current) and Long Term Liabilities. Current liabilities are debts payable within one year.
-
In this article, we explain some commonly used subsidiary ledgers like accounts receivable subsidiary ledger, accounts payable subsidiary ledger or creditors' subsidiary ledger, inventory subsidiary ledger, fixed assets subsidiary ledger, projects subsidiary ledger, work in progress subsidiary ledger, and cash receipts or payments subsidiary ledger.
-
Network Organizational Structures
The newest, and most divergent, team structure is commonly known as a Network Structure (also called "lean" structure) has central, core functions that operate the strategic business. It outsources or subcontracts non-core functions. When an organization needs to control other organizations or agencies whose participation is essential to the success, a network structure is organized.
-
Multitude of these legal and operational structures clubbed with accounting and reporting needs give rise to many reporting dimensions at which the organization may want to track or report its operational metrics and financial results. This is where business dimensions play a vital role.
-
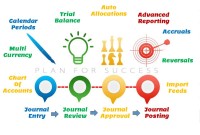
General Ledger - Advanced Features
Modern automated general ledger systems provide detailed and powerful support for financial reporting and budgeting and can report against multiple legal entities from the single system. These systems offer many advanced functionalities right from journal capture to advanced reporting. This article will provide an overview of some advanced features available in today's General Ledgers.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved