- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Functional
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- Divisional Organizational Structures
Divisional Organizational Structures
The divisional structure or product structure consists of self-contained divisions. A division is a collection of functions which produce a product. It also utilizes a plan to compete and operate as a separate business or profit center. Divisional structure is based on external or internal parameters like product /customer segment/ geographical location etc.
The divisional structure or product structure consists of self-contained divisions. A division is a collection of functions which produce a product. It also utilizes a plan to compete and operate as a separate business or profit center. Divisional structure is based on external or internal parameters like product /customer segment/ geographical location etc. For example, each division is responsible for certain product and has its own resources such as finance, marketing, warehouse, maintenance etc.
Business Division:
A division of a business or business division is one of the parts into which a business, organization or company is divided. The divisions are distinct parts of that business. In case of a multi-divisional organizational structure, there is one parent company or head-office, and that parent company/head-office owns smaller companies/departments that use its brand and name. The whole organization is ultimately controlled by central management, but most decisions are left to autonomous divisions/departments.
Dividing the firm based on output into several autonomous units, provides the optimal level of centralization in a company. Central management could still dictate the overall direction of the firm, while each division operates autonomously to cater to its own needs, is held accountable for its own profits, and can remain productive even if the other divisions fail.
In a simplistic scenario, these divisions are all part of the same company and that company is legally responsible for all of the obligations and debts of the divisions. However, this may change in case of large organizations, where various parts of the business may be run by different subsidiaries, and a business division may include one or many subsidiaries. Each subsidiary in such a case is a separate legal entity owned by the primary business or by another subsidiary in the hierarchy. Often a division operates under a separate name and companies often setup business units to operate in divisions prior to the legal formation of subsidiaries.
Given below are common methods of differentiation:
- By Product
- By Geographical Location
- By Type of Customer
- By Process
Differentiation by Product
As a company moves from a single product or service to manufacturing a wide range of products it may find that the functional structure is no longer effective. This is especially true if the products are very different from each other in terms of the technology, raw material and manufacturing process used and the final product. In such a situation, the company may then have to adopt a structure which revolves around individual products or product lines. Grouping activities according to a specific product or service, thus placing all activities related to the product or the service under one manager. Each major product area in the corporation is under the authority of a senior manager who is specialist in, and is responsible for, everything related to the product line.
Johnson & Johnson manufactures and markets a wide range of specialized surgical sutures and accessories as well as a range of products for children. Product based departmentalization ensures that the two major product lines operate as independent profit divisions since there is almost no commonality in terms of the manufacturing process, marketing skills and market segments served.
LA Gear is another example of company that uses product departmentalization. Its structure is based on its varied product lines which include women’s footwear etc.
Hindustan Lever manufacturing and marketing detergents, toiletries, chemicals, and agro-based products
Procter and Gamble (P&G), USA, operates under three entities in India - two listed entities 'Procter & Gamble Hygiene and Health Care Limited' and 'Gillette India Limited', as well as one 100 per cent subsidiary of the parent company in the US called 'Procter & Gamble Home Products'. P&G with its range of Vicks products, Clearasil cream and soap have structures revolving around different products.
The extent of differentiation would vary from one company to another. One company may club all its toilet soaps, detergents, and washing powders in one product line, while another may differentiate between toilet soaps and detergents or even between individual toilet soaps if they cater to distinct market segments or have a very different raw material base.
The main advantages of using a product based organization structure are that it facilitates optional utilization of specialized machinery and technological processes, permits greater co-ordination, where specialized customer service is required, and enables product managers to be responsible for the profit generation of their department.
The biggest disadvantage of this type of structure is that it leads to duplication of managerial manpower thus leading to higher costs. It also requires a strong leader to control the various product groups so that they do not become alienated from the overall organizational objectives.
Differentiation by Location
When an organization is departmentalized on the basis of location of different tasks and activities, then the organization is geographically organized. The biggest advantage of differentiating the functions geographically is that it allows for maximum utilization of local resources and talents, as well as speedy decision-making in response to changes in local conditions. In fact, where the participation of local people is essential to the success of the organization as in voluntary and social organizations, a geographic differentiation is ideal. The problems associated with this type of structure relate to problems of top management control and require a large number of executives with general management skills to head the various area operations.
The organization structure of Coca-Cola has reflected the company’s operation in two broad geographic areas – the North American sector and the international sector, which includes the Pacific Rim, the European Community, Northeast Europe, Africa and Latin America groups.
Differentiation by Type of Customers
Another kind of possible grouping is by the type of customer served. Grouping activities on the basis of common customers or types of customers. Jobs may be grouped according to the type of customer served by the organization. The assumption is that customers in each department have a common set of problems and needs that can best be met by specialists. The sales activities in an office supply firm can be broken down into three departments that serve retail, wholesale and government accounts.
A Delhi based company manufacturing electronic typewriters and desk top photocopiers had organized its sales force on the basis of its two product lines. Its major customer segments were Government organizations (public sector companies, ministries, departmental undertakings, public libraries etc.) and private sector companies. The company was not very successful in its marketing efforts. Investigation revealed that the same customer (organization) was being visited by two different salesmen (one each for typewriter and copier) resulting in unnecessary duplication of effort and time. Moreover, the Government and private sector organizations each had a very different set of criteria governing their decision to purchase. The sales approach which succeeded in a private sector company could not be similarly applied to a government set-up. The company then re-organized its sales force into two teams, one catering to the government sector and the other to the private sector, with each team having responsibility for both the product lines. With the reorganized structure the company was able to make a dent in the highly competitive market.
An example of this would be to look at Hewlett Packard (HP), the computer and printer company. HP operates in several countries and they may be separate geographies under each product lines like Printer division, Printing & Multifunction division, Handheld Devices division and the Servers division etc. However in different countries they operate as distinct legal entities with subsidiaries like Hewlett Packard (India) Software Operation Private Limited (India), Hewlett Packard (Thailand) Ltd. (Thailand), Hewlett Packard Customer Delivery Services SL (Spain) etc., all using the HP brand name.
Another more obvious example is that Google Video is a division of Google, and is part of the same corporate entity. But the YouTube video service is a subsidiary of Google because it remains operated as YouTube, LLC, a separate business entity even though it is owned by Google.
Differentiation by Process
Grouping activities on the basis of product or service or customer flow. Because each process requires different skills, process departmentalization allows homogeneous activities to be grouped together. Departmentalization by process, benefit from the advantages that are found in high specialization, and tends to be very efficient in some instances. A high degree of specialization leads to the development of proficiency and professional competence, as well as it enables, and implies, the development of centralized control functions.
Example: Applicants might need to go through several departments, namely validation, licensing and treasury, before receiving a driver’s license.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
GL - Review & Approve Journals
Review and Approval mechanisms ensure that the accounting transaction is reasonable, necessary, and comply with applicable policies. Understand why we need review and approval processes, what are they, and how they are performed in automated general ledger systems. Learn the benefits of having journal approval mechanisms in place.
-
GL - Recurring Journal Entries
A “Recurring Journal” is a journal that needs to be repeated and processed periodically. Recurring Entries are business transactions that are repeated regularly, such as fixed rent or insurance to be paid every month. Learn the various methods that can be used to generate recurring journals. See some examples and explore the generic process to create recurring journals in any automated system.
-
Introduction to Legal Entities Concept
Modern business organizations operate globally and leverage a large number of registered legal entities, and operate through complex matrix relationships. To stay competitive in the current global business environment, they must often develop highly diverse and complex organizational structures that cross international borders. Learn more about Legal Entities and their importance for businesses.
-
This article explains the process of entering and importing general ledger journals in automated accounting systems. Learn about the basic validations that must happen before the accounting data can be imported from any internal or external sub-system to the general ledger. Finally, understand what we mean by importing in detail or in summary.
-
In this article we will focus on and understand the accounting process which enables the accounting system to provide the necessary information to business stakeholders. We will deep dive into each of the steps of accounting and will understand how to identify accounting transactions and the process for recording accounting information and transactions.
-
A subsidiary is a company that is completely or partly owned by another corporation that owns more than half of the subsidiary's stock, and which normally acts as a holding corporation which at least partly or wholly controls the activities and policies of the daughter corporation.
-
Matrix Organizational Structures
In recent times the two types of organization structures which have evolved are the matrix organization and the network organization. Rigid departmentalization is being complemented by the use of teams that cross over traditional departmental lines.
-
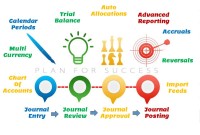
General Ledger - Advanced Features
Modern automated general ledger systems provide detailed and powerful support for financial reporting and budgeting and can report against multiple legal entities from the single system. These systems offer many advanced functionalities right from journal capture to advanced reporting. This article will provide an overview of some advanced features available in today's General Ledgers.
-
As the business grows, the company may want to transition to a branch structure as branches are allowed to conduct a much broader range of activity than representative offices. Branches can buy and sell goods, sign contracts, build things, render services, and generally everything that a regular business can do. A company expands its business by opening up its branch offices in various parts of the country as well as in other countries.
-
Five Core General Ledger Accounts
Typically, the accounts of the general ledger are sorted into five categories within a chart of accounts. Double-entry accounting uses five and only five account types to record all the transactions that can possibly be recorded in any accounting system. These five accounts are the basis for any accounting system, whether it is a manual or an automated accounting system. These five categories are assets, liabilities, owner's equity, revenue, and expenses.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved