- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Functional
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
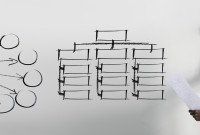
- Matrix Organizational Structures
Matrix Organizational Structures
In recent times the two types of organization structures which have evolved are the matrix organization and the network organization. Rigid departmentalization is being complemented by the use of teams that cross over traditional departmental lines.
In recent times the two types of organization structures which have evolved are the matrix organization and the network organization. Rigid departmentalization is being complemented by the use of teams that cross over traditional departmental lines.
Matrix structure is the combination of two or more structures explained above. This is the structure that is adopted by most of the multinational companies. In a matrix context, the business support functions also ensure coordination across the business functions within each sub-function (such as procurement, production, marketing, distributing, etc.). They are also responsible for specialization related coordination, training, development and learning, problem solving, development of norms, standards and guidelines for functioning as appropriate to the area of specialization.
For example, we can have a functional structure and then assign a manager for each product. Some employees will have two managers: functional manager and product manager.
Main Features of Matrix Structure
Shared Services is the centralization of service offering at one part of an organization or group sharing funding and resourcing. The providing department effectively becomes an internal service provider. The key is the idea of 'sharing' within an organization or group. To accelerate business benefits such as lower cost of operations and improved business processes, the vast majorities of organizations centralize some functions into shared services and outsource various others to third-party service providers because some support functions tend to be similar across industries.
The matrix structure is a combination of the product and functional organization and is usually created for executing a project which requires the skilled services of a functional man as well as the specialized knowledge of a product man. Large turnkey projects in specialized fields require a matrix structure.
The distinguishing characteristic of a matrix structure is that it operates under a dual authority. A person is accountable to two bosses at the same time, one his usual boss and the other his boss for the duration of the project. Obviously the problems emanating from this type of structure relate to conflicting roles and authority arising out of an ambiguous demarcation of authority and responsibility. In a Matrix Structure, people typically have two or more lines of report. This type of organization may combine both functional and divisional lines of responsibility, allowing it to focus on divisional performance while also sharing specialized skills and resources.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Introduction to Legal Entities Concept
Modern business organizations operate globally and leverage a large number of registered legal entities, and operate through complex matrix relationships. To stay competitive in the current global business environment, they must often develop highly diverse and complex organizational structures that cross international borders. Learn more about Legal Entities and their importance for businesses.
-
The purpose of the general ledger is to sort transaction information into meaningful categories and charts of accounts. The general ledger sorts information from the general journal and converts them into account balances and this process converts data into information, necessary to prepare financial statements. This article explains what a general ledger is and some of its major functionalities.
-
Funds contributed by owners in any business are different from all other types of funds. Equity is the residual value of the business enterprise that belongs to the owners or shareholders. The funds contributed by outsiders other than owners that are payable to them in the future. Liabilities are generally classified as Short Term (Current) and Long Term Liabilities. Current liabilities are debts payable within one year.
-
GL - Accrued / Unbilled Revenue
Accrued revenues (also called accrued assets) are revenues already earned but not yet paid by the customer or posted to the general ledger. Understand what we mean by the terms accrued revenue, accrued assets, and unbilled revenue. Explore the business conditions that require recognition of accrued revenue in the books of accounts and some industries where this practice is prevalent.
-
Team-Based Organizational Structure
Team-based structure is a relatively new structure that opposes the traditional hierarchical structure and it slowly gaining acceptance in the corporate world. In such a structure, employees come together as team in order to fulfill their tasks that serve a common goal.
-
Functional Organizational Structures
A functional organizational structure is a structure that consists of activities such as coordination, supervision and task allocation. The organizational structure determines how the organization performs or operates. The term organizational structure refers to how the people in an organization are grouped and to whom they report.
-
GL - Unearned / Deferred Revenue
Unearned revenue is a liability to the entity until the revenue is earned. Learn the concept of unearned revenue, also known as deferred revenue. Gain an understanding of business scenarios in which organizations need to park their receipts as unearned. Look at some real-life examples and understand the accounting treatment for unearned revenue. Finally, look at how the concept is treated in the ERPs or automated systems.
-
Concept of Representative Office
A representative office is the easiest option for a company planning to start its operations in a foreign country. The company need not incorporate a separate legal entity nor trigger corporate income tax, as long as the activities are limited in nature.
-
Network Organizational Structures
The newest, and most divergent, team structure is commonly known as a Network Structure (also called "lean" structure) has central, core functions that operate the strategic business. It outsources or subcontracts non-core functions. When an organization needs to control other organizations or agencies whose participation is essential to the success, a network structure is organized.
-
An account inquiry is a review of any type of financial account, whether it be a depository account or a credit account. In this tutorial, you learn what we mean by drill through functionality in the context of the general ledger system. We will explain the concept of drill-down and how it enables users to perform account and transaction inquiry at a granular level and the benefits of using this functionality.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved