- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Functional
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- GL - Inquiry & Drilldown
GL - Inquiry & Drilldown
An account inquiry is a review of any type of financial account, whether it be a depository account or a credit account. In this tutorial, you learn what we mean by drill through functionality in the context of the general ledger system. We will explain the concept of drill-down and how it enables users to perform account and transaction inquiry at a granular level and the benefits of using this functionality.
What is Account Drilldown?
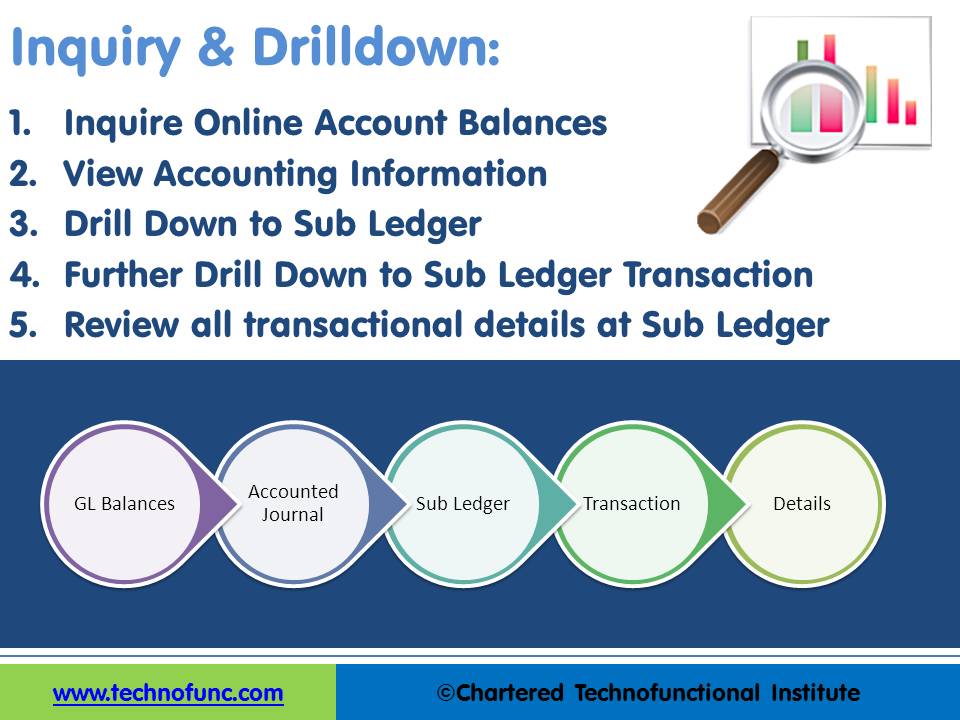
In information technology, to drill down means to move from summary information to detailed data by zooming in on something. In an ERP environment, "drilling-down" may involve clicking on some account balance or summary representation in order to reveal transactional data.
To drill down is to navigate through a series of steps, for example, the user starts with the summary balances that are made up of a group of accounts with individual balances, and drill down takes the user through the hierarchy to the individual account balances. The individual account balances are made up of transactions that have been posted in those accounts for a specified period and further drill down at this second level takes the user to the set of transactions. These steps of moving from summary balance to account balance belong to the general ledger system, however, the transactions might have originated from a subsidiary ledger. Further drill down at this level will take the user to a level of greater detail where the user can see the original transaction in the sub-ledger itself. Here in the drill-down process, the user is navigating from a higher level of consolidated information to a deeper level into data, without leaving the source system or changing user access.
When one drills down, one performs de facto data analysis on a parent attribute and inquiry of the detailed attributes that constitute the parent attribute. Drilling down provides a method of exploring multidimensional data by moving from one level of detail to the next. Drill-down levels depend on the data granularity and drill-down is a sub-function of inquiry and analysis. Drilldown functionality allows business users to gain better business insight to make critical decisions in order to beat out their competition.
Upstream & Downstream Systems:
Upstream Systems: In geography, upstream literally means towards the source of a stream or river, or against the normal direction of water flow. In the context of general ledger, upstream systems refer to the systems that send data to the general ledger system. In other words, upstream systems are subsidiary ledgers and other source systems that are capturing the transactional data and sending the accounting data to the general ledger for further processing.
Downstream Systems: Similarly, in geography, downstream literally means away from the source of a stream or river, or in the normal direction of water flow. In the context of the general ledger system, downstream systems refer to the systems that take data from the general ledger as their input. Some examples are consolidation systems, enterprise performance management systems (EPM), reconciliation systems, or business intelligence systems. The financial data from the general ledger are carried over as input for these downstream systems for further processing.
Drilldown from General Ledger to Upstream Systems:
In the advances general ledger systems, users can drill down to sub-ledgers details from General Ledger and can get all of the transaction details that comprise an account balance, regardless of which sub-ledger originated the transaction. This functionality helps in analyzing any account balance by understanding the source of the transaction and viewing additional information that has been captured in the source system and not imported into the general ledger system.
Drilldown from Downstream Systems to General Ledger:
Many advanced EPM or Consolidation downstream systems provides the users with the capability to drill down from their system to underlying Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) transaction data. Some examples with the ability to drill down from Enterprise Performance Management (EPM) applications are Oracle Hyperion Financial Management System and Oracle Hyperion Planning. An example of a consolidation system is Oracle Financial Consolidation Hub. These systems allow the user to drill down from consolidated information to the related general ledger system. This provides users with greater visibility into business processes and a greater understanding of the consolidated data.
For most organizations, the basis for global financial consolidation, reporting and analysis, planning, budgeting, and forecasting are derived from a company's existing operational information which is generally stored in many different general ledgers like Oracle, SAP, PeopleSoft, or JD Edwards systems and drill down allows the user to see the actual data in the various general ledgers that constitute the data in these systems.
Drilldown within General Ledger System:
There are various drill-downs that are available in the general ledger system. We will briefly explain each one of them:
1. Interactive Report:
A Drill-Down Report is also called an Interactive Report and has more detail and capability to analyze and inquire data at a granular level. For example, the user is looking at the Balance Sheet Report with drill-down functionalities. The top-level information contains consolidated balances for a group of accounts such as current assets, fixed assets, etc. The drill-down functionality helps the user to select a line item (e.g., fixed assets) and drill-down further to a detailed list (secondary list) which displays various components of the fixed assets such as land, buildings, machinery, etc.
2. Summary Balances:
Some general ledgers provide the functionality to maintain summary accounts that contain consolidated balance for the group of accounts clubbed under that summary account. Users may drill-down to individual group accounts by using the drill-down functionality.
3. Account Balances:
Drilling down on balances in the general ledger may take the user to line level transactions constituting those balances.
4. Account Transactions:
Drilling down on balances will take the user to the journal where the transaction has been captured in the source system.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Different Types of Organizational Structures
Modern business organizations run multiple product and service lines, operate globally, leverage large number of registered legal entities, and operate through complex matrix relationships. To stay competitive in the current global business environment, they must often develop highly diverse and complex organizational structures that cross international borders.
-
Horizontal or Flat Organizational Structures
Flat organizational structure is an organizational model with relatively few or no levels of middle management between the executives and the frontline employees. Its goal is to have as little hierarchy as possible between management and staff level employees. In a flat organizational structure, employees have increased involvement in the decision-making process.
-
In most of the automated financial systems, you can define more than 12 accounting periods in a financial year. This article will explain the concept of the adjustment period and the benefits of having adjustment periods. Adjustment periods have their inherent challenges for the users of financial statements and there is a workaround for those who don’t want to use adjustment periods.
-
Although technically a general ledger appears to be fairly simple compared to other processes, in large organizations, the general ledger has to provide many functionalities and it becomes considerably large and complex. Modern business organizations are complex, run multiple products and service lines, leveraging a large number of registered legal entities, and have varied reporting needs.
-
An organizational design is the process by which a company defines and manages elements of structure so that an organization can control the activities necessary to achieve its goals. Good organizational structure and design helps improve communication, increase productivity, and inspire innovation. Organizational structure is the formal system of task and activity relationships to clearly define how people coordinate their actions and use resources to achieve organizational goals.
-
Divisional Organizational Structures
The divisional structure or product structure consists of self-contained divisions. A division is a collection of functions which produce a product. It also utilizes a plan to compete and operate as a separate business or profit center. Divisional structure is based on external or internal parameters like product /customer segment/ geographical location etc.
-
Learn the typical accounting cycle that takes place in an automated accounting system. We will understand the perquisites for commencing the accounting cycle and the series of steps required to record transactions and convert them into financial reports. This accounting cycle is the standard repetitive process that is undertaken to record and report accounting.
-
Explore the concept of journal reversals and understand the business scenarios in which users may need to reverse the accounting entries that have been already entered into the system. Understand the common sources of errors resulting in the reversal of entries and learn how to correct them. Discuss the reversal of adjustment entries and the reversal functionalities in ERPs.
-
The purpose of the general ledger is to sort transaction information into meaningful categories and charts of accounts. The general ledger sorts information from the general journal and converts them into account balances and this process converts data into information, necessary to prepare financial statements. This article explains what a general ledger is and some of its major functionalities.
-
Concept of Representative Office
A representative office is the easiest option for a company planning to start its operations in a foreign country. The company need not incorporate a separate legal entity nor trigger corporate income tax, as long as the activities are limited in nature.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved